Kamlesh Pawar
Motion-Informed Deep Learning for Brain MR Image Reconstruction Framework
May 28, 2024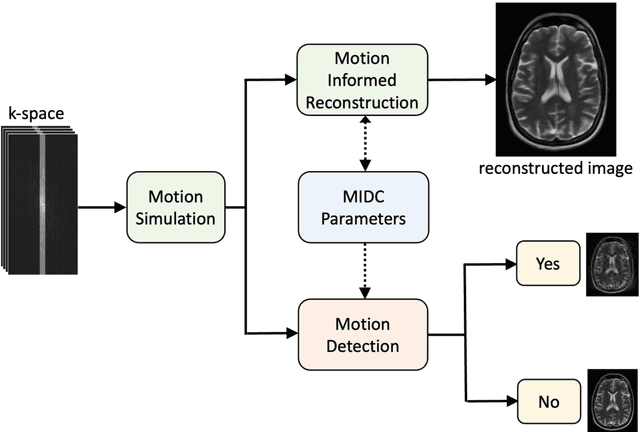
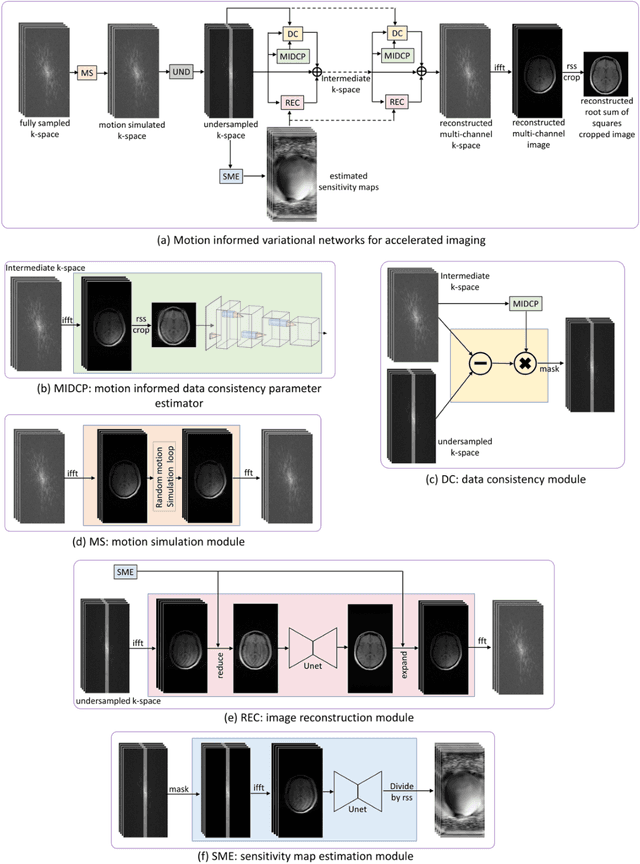
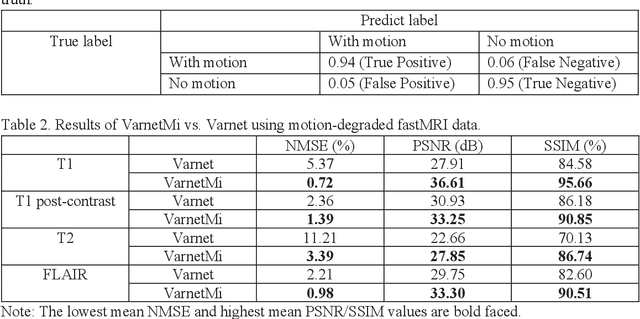
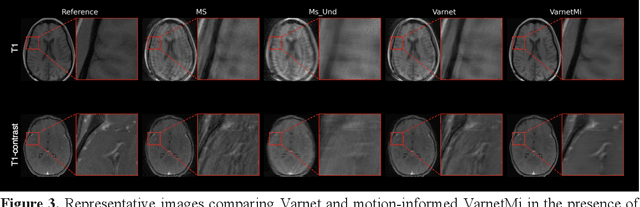
Abstract:Motion artifacts in Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are one of the frequently occurring artifacts due to patient movements during scanning. Motion is estimated to be present in approximately 30% of clinical MRI scans; however, motion has not been explicitly modeled within deep learning image reconstruction models. Deep learning (DL) algorithms have been demonstrated to be effective for both the image reconstruction task and the motion correction task, but the two tasks are considered separately. The image reconstruction task involves removing undersampling artifacts such as noise and aliasing artifacts, whereas motion correction involves removing artifacts including blurring, ghosting, and ringing. In this work, we propose a novel method to simultaneously accelerate imaging and correct motion. This is achieved by integrating a motion module into the deep learning-based MRI reconstruction process, enabling real-time detection and correction of motion. We model motion as a tightly integrated auxiliary layer in the deep learning model during training, making the deep learning model 'motion-informed'. During inference, image reconstruction is performed from undersampled raw k-space data using a trained motion-informed DL model. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed motion-informed deep learning image reconstruction network outperformed the conventional image reconstruction network for motion-degraded MRI datasets.
PixCUE: Joint Uncertainty Estimation and Image Reconstruction in MRI using Deep Pixel Classification
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:Deep learning (DL) models are capable of successfully exploiting latent representations in MR data and have become state-of-the-art for accelerated MRI reconstruction. However, undersampling the measurements in k-space as well as the over- or under-parameterized and non-transparent nature of DL make these models exposed to uncertainty. Consequently, uncertainty estimation has become a major issue in DL MRI reconstruction. To estimate uncertainty, Monte Carlo (MC) inference techniques have become a common practice where multiple reconstructions are utilized to compute the variance in reconstruction as a measurement of uncertainty. However, these methods demand high computational costs as they require multiple inferences through the DL model. To this end, we introduce a method to estimate uncertainty during MRI reconstruction using a pixel classification framework. The proposed method, PixCUE (stands for Pixel Classification Uncertainty Estimation) produces the reconstructed image along with an uncertainty map during a single forward pass through the DL model. We demonstrate that this approach generates uncertainty maps that highly correlate with the reconstruction errors with respect to various MR imaging sequences and under numerous adversarial conditions. We also show that the estimated uncertainties are correlated to that of the conventional MC method. We further provide an empirical relationship between the uncertainty estimations using PixCUE and well-established reconstruction metrics such as NMSE, PSNR, and SSIM. We conclude that PixCUE is capable of reliably estimating the uncertainty in MRI reconstruction with a minimum additional computational cost.
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Multi-head Cascaded Swin Transformers with Attention to k-space Sampling Pattern for Accelerated MRI Reconstruction
Jul 18, 2022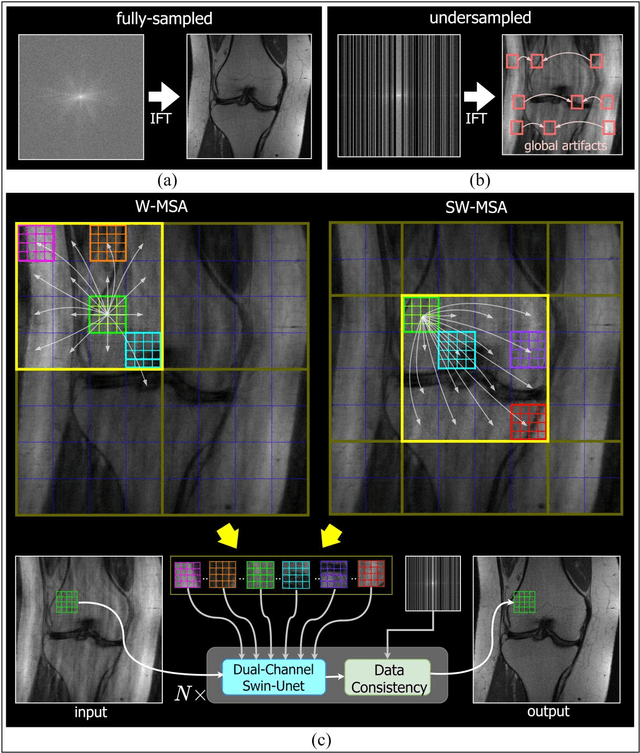
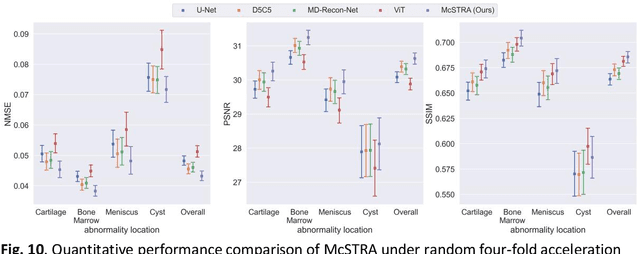
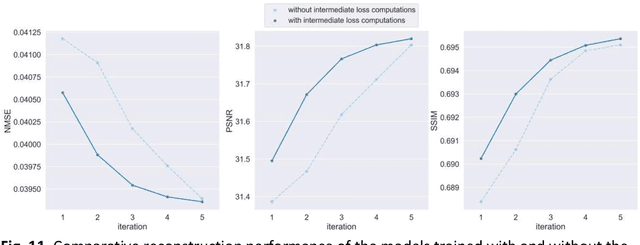

Abstract:Global correlations are widely seen in human anatomical structures due to similarity across tissues and bones. These correlations are reflected in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans as a result of close-range proton density and T1/T2 parameter. Furthermore, to achieve accelerated MRI, k-space data are undersampled which causes global aliasing artifacts. Convolutional neural network (CNN) models are widely utilized for accelerated MRI reconstruction, but those models are limited in capturing global correlations due to the intrinsic locality of the convolution operation. The self-attention-based transformer models are capable of capturing global correlations among image features, however, the current contributions of transformer models for MRI reconstruction are minute. The existing contributions mostly provide CNN-transformer hybrid solutions and rarely leverage the physics of MRI. In this paper, we propose a physics-based stand-alone (convolution free) transformer model titled, the Multi-head Cascaded Swin Transformers (McSTRA) for accelerated MRI reconstruction. McSTRA combines several interconnected MRI physics-related concepts with the transformer networks: it exploits global MR features via the shifted window self-attention mechanism; it extracts MR features belonging to different spectral components separately using a multi-head setup; it iterates between intermediate de-aliasing and k-space correction via a cascaded network with data consistency in k-space and intermediate loss computations; furthermore, we propose a novel positional embedding generation mechanism to guide self-attention utilizing the point spread function corresponding to the undersampling mask. Our model significantly outperforms state-of-the-art MRI reconstruction methods both visually and quantitatively while depicting improved resolution and removal of aliasing artifacts.
MoCoNet: Motion Correction in 3D MPRAGE images using a Convolutional Neural Network approach
Jul 29, 2018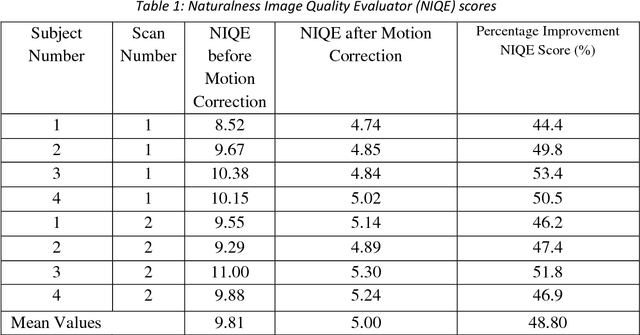
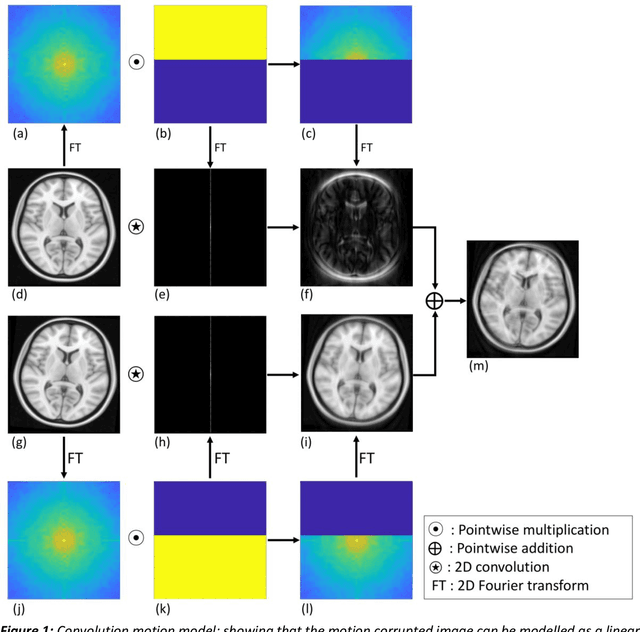
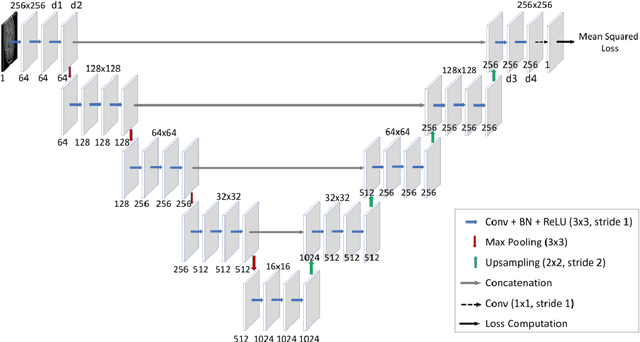
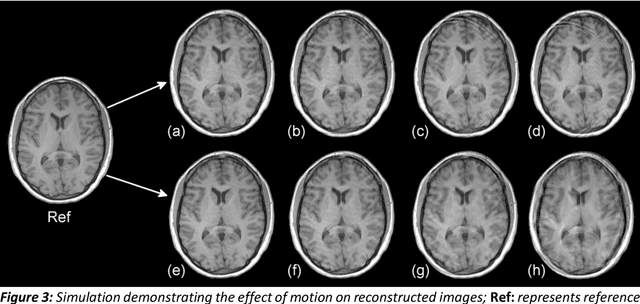
Abstract:Purpose: The suppression of motion artefacts from MR images is a challenging task. The purpose of this paper is to develop a standalone novel technique to suppress motion artefacts from MR images using a data-driven deep learning approach. Methods: A deep learning convolutional neural network (CNN) was developed to remove motion artefacts in brain MR images. A CNN was trained on simulated motion corrupted images to identify and suppress artefacts due to the motion. The network was an encoder-decoder CNN architecture where the encoder decomposed the motion corrupted images into a set of feature maps. The feature maps were then combined by the decoder network to generate a motion-corrected image. The network was tested on an unseen simulated dataset and an experimental, motion corrupted in vivo brain dataset. Results: The trained network was able to suppress the motion artefacts in the simulated motion corrupted images, and the mean percentage error in the motion corrected images was 2.69 % with a standard deviation of 0.95 %. The network was able to effectively suppress the motion artefacts from the experimental dataset, demonstrating the generalisation capability of the trained network. Conclusion: A novel and generic motion correction technique has been developed that can suppress motion artefacts from motion corrupted MR images. The proposed technique is a standalone post-processing method that does not interfere with data acquisition or reconstruction parameters, thus making it suitable for a multitude of MR sequences.
Multichannel Compressive Sensing MRI Using Noiselet Encoding
Jul 22, 2014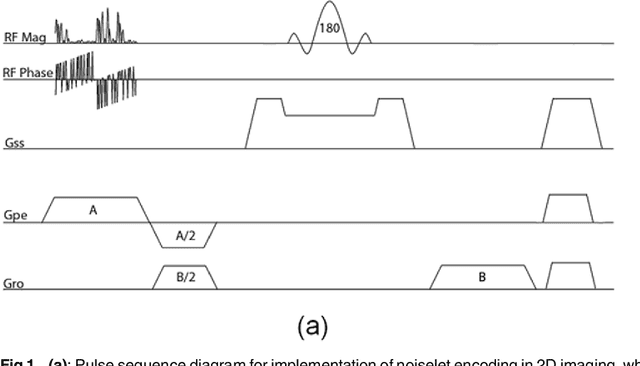
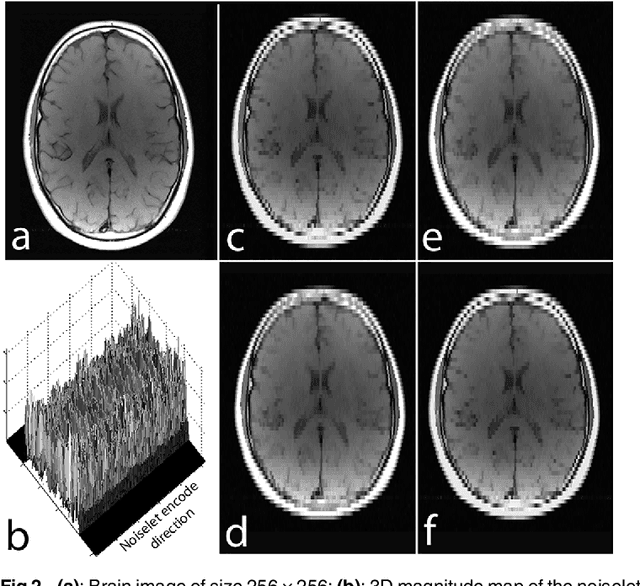
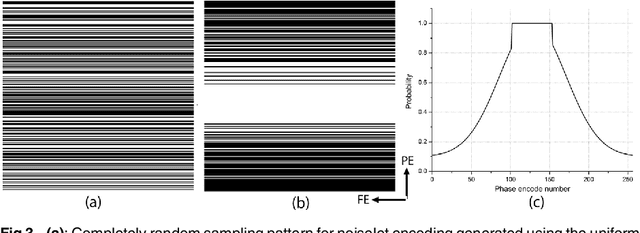
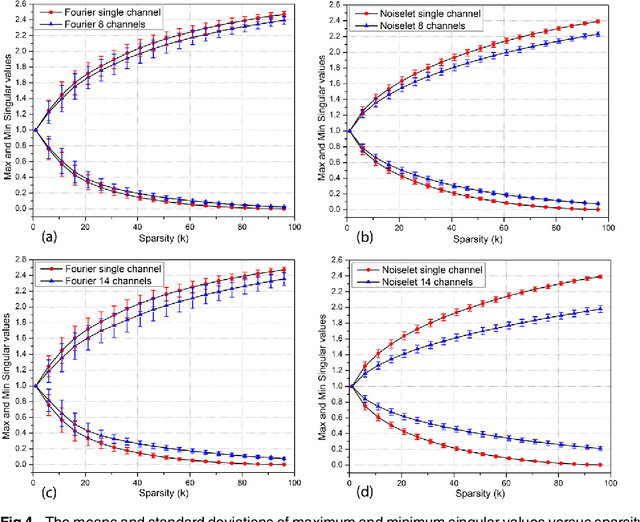
Abstract:The incoherence between measurement and sparsifying transform matrices and the restricted isometry property (RIP) of measurement matrix are two of the key factors in determining the performance of compressive sensing (CS). In CS-MRI, the randomly under-sampled Fourier matrix is used as the measurement matrix and the wavelet transform is usually used as sparsifying transform matrix. However, the incoherence between the randomly under-sampled Fourier matrix and the wavelet matrix is not optimal, which can deteriorate the performance of CS-MRI. Using the mathematical result that noiselets are maximally incoherent with wavelets, this paper introduces the noiselet unitary bases as the measurement matrix to improve the incoherence and RIP in CS-MRI, and presents a method to design the pulse sequence for the noiselet encoding. This novel encoding scheme is combined with the multichannel compressive sensing (MCS) framework to take the advantage of multichannel data acquisition used in MRI scanners. An empirical RIP analysis is presented to compare the multichannel noiselet and multichannel Fourier measurement matrices in MCS. Simulations are presented in the MCS framework to compare the performance of noiselet encoding reconstructions and Fourier encoding reconstructions at different acceleration factors. The comparisons indicate that multichannel noiselet measurement matrix has better RIP than that of its Fourier counterpart, and that noiselet encoded MCS-MRI outperforms Fourier encoded MCS-MRI in preserving image resolution and can achieve higher acceleration factors. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed noiselet encoding scheme, two pulse sequences with tailored spatially selective RF excitation pulses was designed and implemented on a 3T scanner to acquire the data in the noiselet domain from a phantom and a human brain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge