Junru Gu
DriveVLM: The Convergence of Autonomous Driving and Large Vision-Language Models
Feb 25, 2024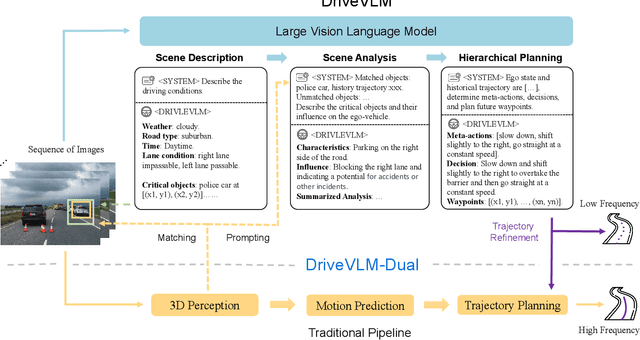
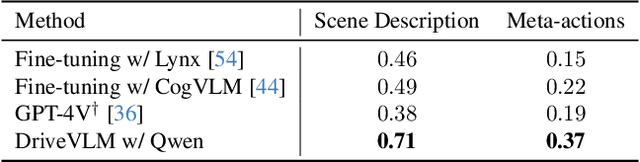
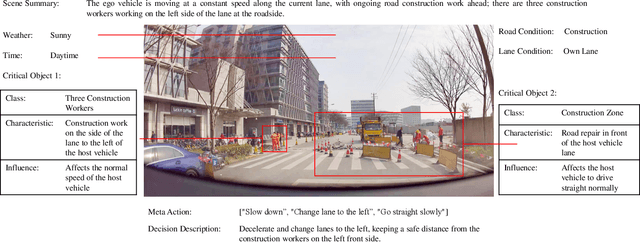
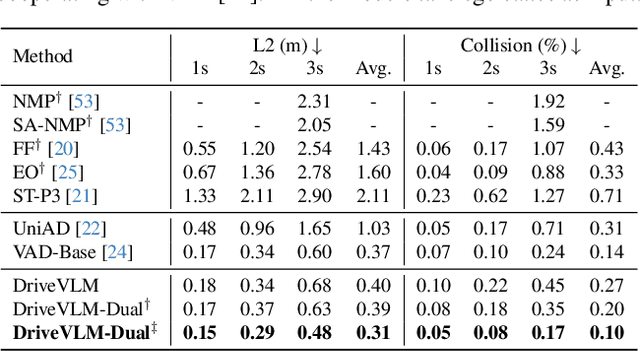
Abstract:A primary hurdle of autonomous driving in urban environments is understanding complex and long-tail scenarios, such as challenging road conditions and delicate human behaviors. We introduce DriveVLM, an autonomous driving system leveraging Vision-Language Models (VLMs) for enhanced scene understanding and planning capabilities. DriveVLM integrates a unique combination of chain-of-thought (CoT) modules for scene description, scene analysis, and hierarchical planning. Furthermore, recognizing the limitations of VLMs in spatial reasoning and heavy computational requirements, we propose DriveVLM-Dual, a hybrid system that synergizes the strengths of DriveVLM with the traditional autonomous driving pipeline. DriveVLM-Dual achieves robust spatial understanding and real-time inference speed. Extensive experiments on both the nuScenes dataset and our SUP-AD dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of DriveVLM and the enhanced performance of DriveVLM-Dual, surpassing existing methods in complex and unpredictable driving conditions.
VectorFlow: Combining Images and Vectors for Traffic Occupancy and Flow Prediction
Aug 09, 2022


Abstract:Predicting future behaviors of road agents is a key task in autonomous driving. While existing models have demonstrated great success in predicting marginal agent future behaviors, it remains a challenge to efficiently predict consistent joint behaviors of multiple agents. Recently, the occupancy flow fields representation was proposed to represent joint future states of road agents through a combination of occupancy grid and flow, which supports efficient and consistent joint predictions. In this work, we propose a novel occupancy flow fields predictor to produce accurate occupancy and flow predictions, by combining the power of an image encoder that learns features from a rasterized traffic image and a vector encoder that captures information of continuous agent trajectories and map states. The two encoded features are fused by multiple attention modules before generating final predictions. Our simple but effective model ranks 3rd place on the Waymo Open Dataset Occupancy and Flow Prediction Challenge, and achieves the best performance in the occluded occupancy and flow prediction task.
ViP3D: End-to-end Visual Trajectory Prediction via 3D Agent Queries
Aug 02, 2022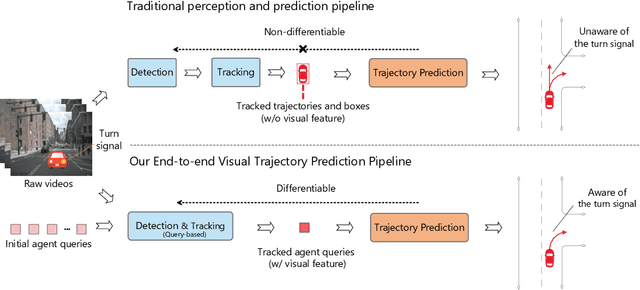
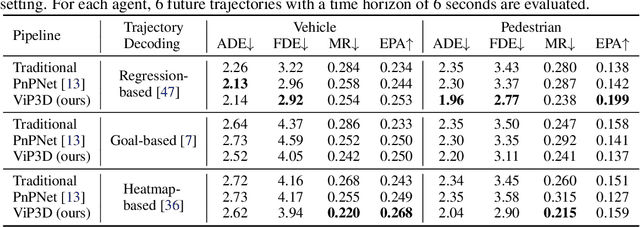
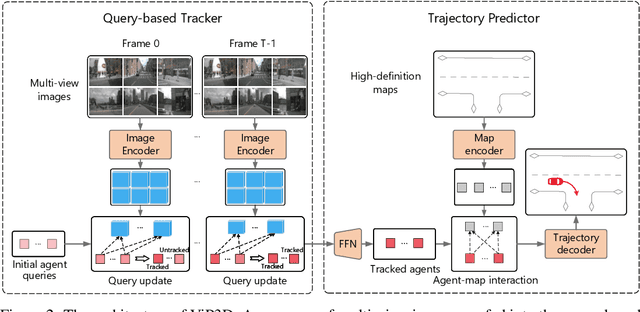
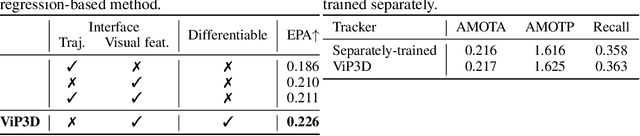
Abstract:Existing autonomous driving pipelines separate the perception module from the prediction module. The two modules communicate via hand-picked features such as agent boxes and trajectories as interfaces. Due to this separation, the prediction module only receives partial information from the perception module. Even worse, errors from the perception modules can propagate and accumulate, adversely affecting the prediction results. In this work, we propose ViP3D, a visual trajectory prediction pipeline that leverages the rich information from raw videos to predict future trajectories of agents in a scene. ViP3D employs sparse agent queries throughout the pipeline, making it fully differentiable and interpretable. Furthermore, we propose an evaluation metric for this novel end-to-end visual trajectory prediction task. Extensive experimental results on the nuScenes dataset show the strong performance of ViP3D over traditional pipelines and previous end-to-end models.
M2I: From Factored Marginal Trajectory Prediction to Interactive Prediction
Mar 28, 2022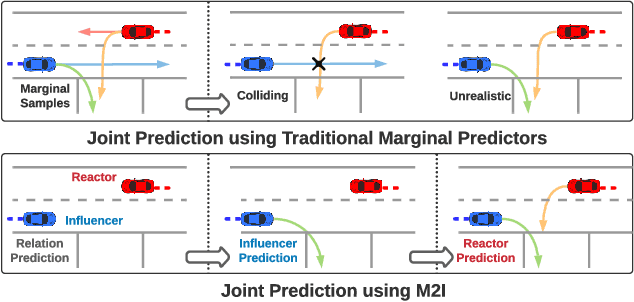
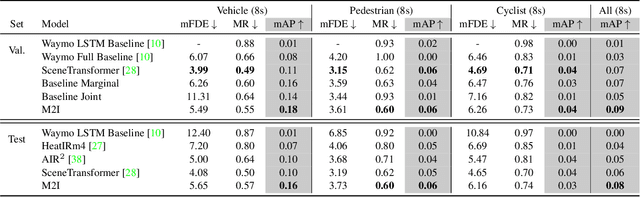
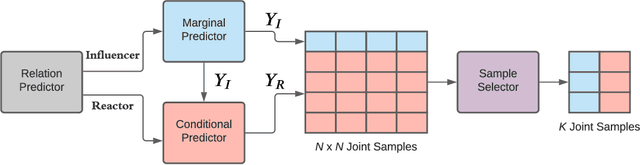
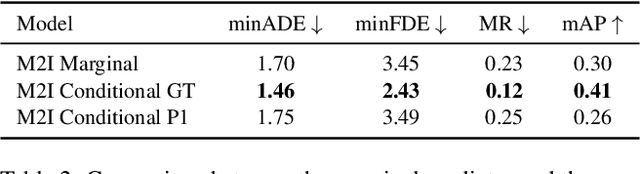
Abstract:Predicting future motions of road participants is an important task for driving autonomously in urban scenes. Existing models excel at predicting marginal trajectories for single agents, yet it remains an open question to jointly predict scene compliant trajectories over multiple agents. The challenge is due to exponentially increasing prediction space as a function of the number of agents. In this work, we exploit the underlying relations between interacting agents and decouple the joint prediction problem into marginal prediction problems. Our proposed approach M2I first classifies interacting agents as pairs of influencers and reactors, and then leverages a marginal prediction model and a conditional prediction model to predict trajectories for the influencers and reactors, respectively. The predictions from interacting agents are combined and selected according to their joint likelihoods. Experiments show that our simple but effective approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Waymo Open Motion Dataset interactive prediction benchmark.
DenseTNT: End-to-end Trajectory Prediction from Dense Goal Sets
Aug 22, 2021



Abstract:Due to the stochasticity of human behaviors, predicting the future trajectories of road agents is challenging for autonomous driving. Recently, goal-based multi-trajectory prediction methods are proved to be effective, where they first score over-sampled goal candidates and then select a final set from them. However, these methods usually involve goal predictions based on sparse pre-defined anchors and heuristic goal selection algorithms. In this work, we propose an anchor-free and end-to-end trajectory prediction model, named DenseTNT, that directly outputs a set of trajectories from dense goal candidates. In addition, we introduce an offline optimization-based technique to provide multi-future pseudo-labels for our final online model. Experiments show that DenseTNT achieves state-of-the-art performance, ranking 1st on the Argoverse motion forecasting benchmark and being the 1st place winner of the 2021 Waymo Open Dataset Motion Prediction Challenge.
DenseTNT: Waymo Open Dataset Motion Prediction Challenge 1st Place Solution
Jun 27, 2021



Abstract:In autonomous driving, goal-based multi-trajectory prediction methods are proved to be effective recently, where they first score goal candidates, then select a final set of goals, and finally complete trajectories based on the selected goals. However, these methods usually involve goal predictions based on sparse predefined anchors. In this work, we propose an anchor-free model, named DenseTNT, which performs dense goal probability estimation for trajectory prediction. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance, and ranks 1st on the Waymo Open Dataset Motion Prediction Challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge