Jungin Lee
ValSub: Subsampling Validation Data to Mitigate Forgetting during ASR Personalization
Mar 12, 2025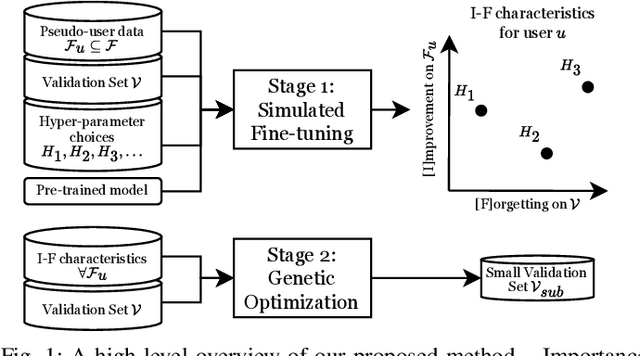
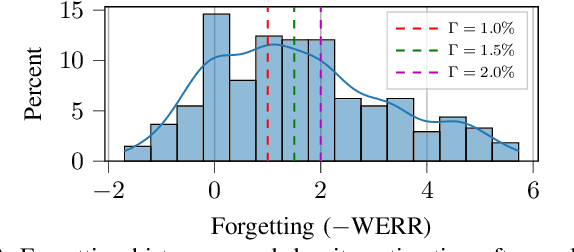
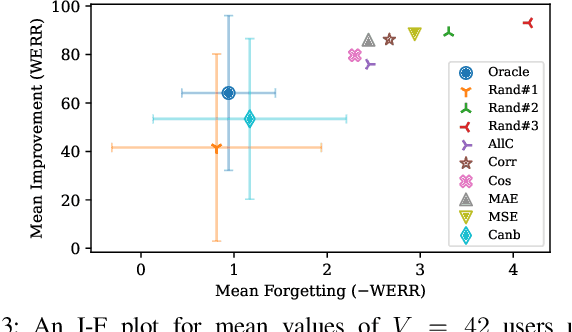
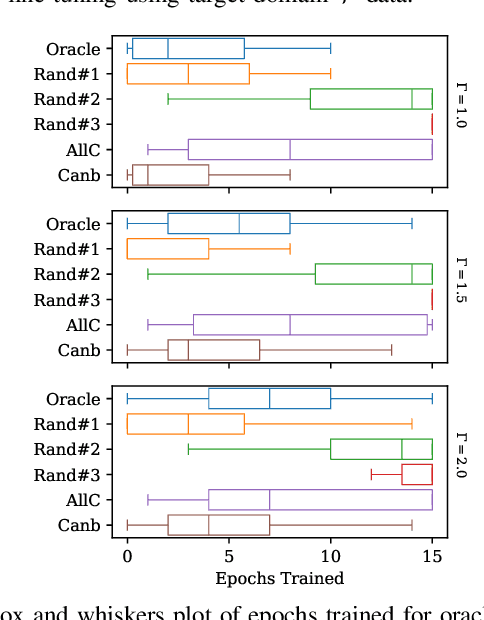
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is widely used within consumer devices such as mobile phones. Recently, personalization or on-device model fine-tuning has shown that adaptation of ASR models towards target user speech improves their performance over rare words or accented speech. Despite these gains, fine-tuning on user data (target domain) risks the personalized model to forget knowledge about its original training distribution (source domain) i.e. catastrophic forgetting, leading to subpar general ASR performance. A simple and efficient approach to combat catastrophic forgetting is to measure forgetting via a validation set that represents the source domain distribution. However, such validation sets are large and impractical for mobile devices. Towards this, we propose a novel method to subsample a substantially large validation set into a smaller one while maintaining the ability to estimate forgetting. We demonstrate the efficacy of such a dataset in mitigating forgetting by utilizing it to dynamically determine the number of ideal fine-tuning epochs. When measuring the deviations in per user fine-tuning epochs against a 50x larger validation set (oracle), our method achieves a lower mean-absolute-error (3.39) compared to randomly selected subsets of the same size (3.78-8.65). Unlike random baselines, our method consistently tracks the oracle's behaviour across three different forgetting thresholds.
persoDA: Personalized Data Augmentation for Personalized ASR
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:Data augmentation (DA) is ubiquitously used in training of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models. DA offers increased data variability, robustness and generalization against different acoustic distortions. Recently, personalization of ASR models on mobile devices has been shown to improve Word Error Rate (WER). This paper evaluates data augmentation in this context and proposes persoDA; a DA method driven by user's data utilized to personalize ASR. persoDA aims to augment training with data specifically tuned towards acoustic characteristics of the end-user, as opposed to standard augmentation based on Multi-Condition Training (MCT) that applies random reverberation and noises. Our evaluation with an ASR conformer-based baseline trained on Librispeech and personalized for VOICES shows that persoDA achieves a 13.9% relative WER reduction over using standard data augmentation (using random noise & reverberation). Furthermore, persoDA shows 16% to 20% faster convergence over MCT.
persoDA: Personalized Data Augmentation forPersonalized ASR
Jan 15, 2025



Abstract:Data augmentation (DA) is ubiquitously used in training of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models. DA offers increased data variability, robustness and generalization against different acoustic distortions. Recently, personalization of ASR models on mobile devices has been shown to improve Word Error Rate (WER). This paper evaluates data augmentation in this context and proposes persoDA; a DA method driven by user's data utilized to personalize ASR. persoDA aims to augment training with data specifically tuned towards acoustic characteristics of the end-user, as opposed to standard augmentation based on Multi-Condition Training (MCT) that applies random reverberation and noises. Our evaluation with an ASR conformer-based baseline trained on Librispeech and personalized for VOICES shows that persoDA achieves a 13.9% relative WER reduction over using standard data augmentation (using random noise & reverberation). Furthermore, persoDA shows 16% to 20% faster convergence over MCT.
Locality enhanced dynamic biasing and sampling strategies for contextual ASR
Jan 23, 2024Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) still face challenges when recognizing time-variant rare-phrases. Contextual biasing (CB) modules bias ASR model towards such contextually-relevant phrases. During training, a list of biasing phrases are selected from a large pool of phrases following a sampling strategy. In this work we firstly analyse different sampling strategies to provide insights into the training of CB for ASR with correlation plots between the bias embeddings among various training stages. Secondly, we introduce a neighbourhood attention (NA) that localizes self attention (SA) to the nearest neighbouring frames to further refine the CB output. The results show that this proposed approach provides on average a 25.84% relative WER improvement on LibriSpeech sets and rare-word evaluation compared to the baseline.
Consistency Based Unsupervised Self-training For ASR Personalisation
Jan 22, 2024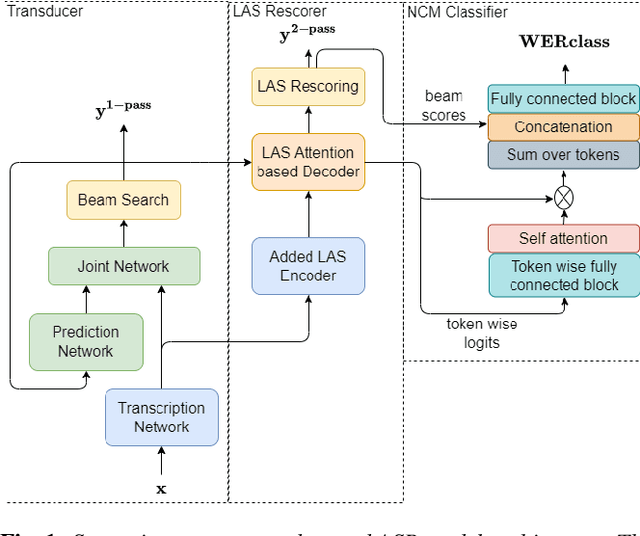

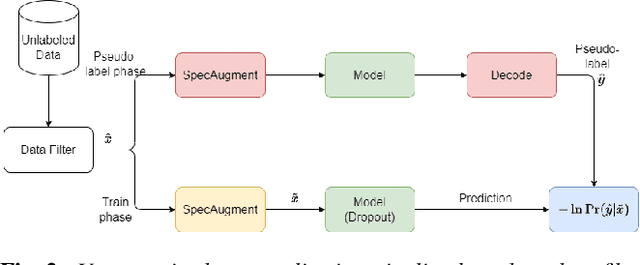
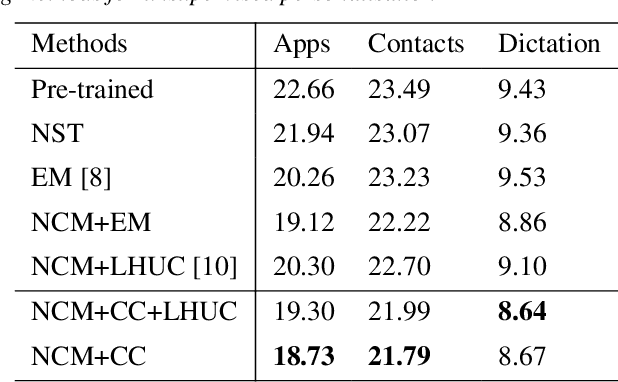
Abstract:On-device Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models trained on speech data of a large population might underperform for individuals unseen during training. This is due to a domain shift between user data and the original training data, differed by user's speaking characteristics and environmental acoustic conditions. ASR personalisation is a solution that aims to exploit user data to improve model robustness. The majority of ASR personalisation methods assume labelled user data for supervision. Personalisation without any labelled data is challenging due to limited data size and poor quality of recorded audio samples. This work addresses unsupervised personalisation by developing a novel consistency based training method via pseudo-labelling. Our method achieves a relative Word Error Rate Reduction (WERR) of 17.3% on unlabelled training data and 8.1% on held-out data compared to a pre-trained model, and outperforms the current state-of-the art methods.
Adaptable Multi-Domain Language Model for Transformer ASR
Aug 14, 2020



Abstract:We propose an adapter based multi-domain Transformer based language model (LM) for Transformer ASR. The model consists of a big size common LM and small size adapters. The model can perform multi-domain adaptation with only the small size adapters and its related layers. The proposed model can reuse the full fine-tuned LM which is fine-tuned using all layers of an original model. The proposed LM can be expanded to new domains by adding about 2% of parameters for a first domain and 13% parameters for after second domain. The proposed model is also effective in reducing the model maintenance cost because it is possible to omit the costly and time-consuming common LM pre-training process. Using proposed adapter based approach, we observed that a general LM with adapter can outperform a dedicated music domain LM in terms of word error rate (WER).
Attention based on-device streaming speech recognition with large speech corpus
Jan 02, 2020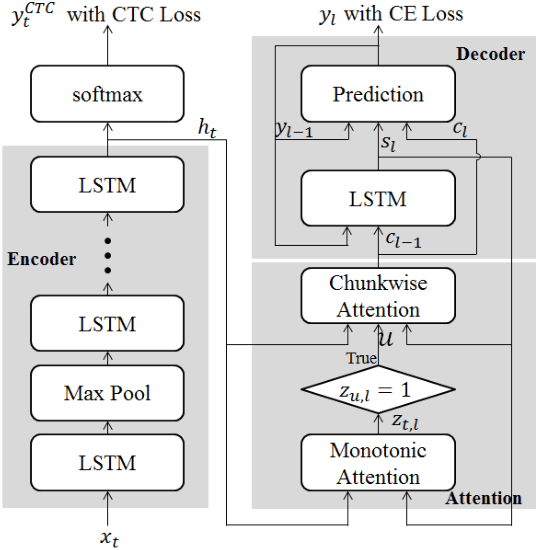
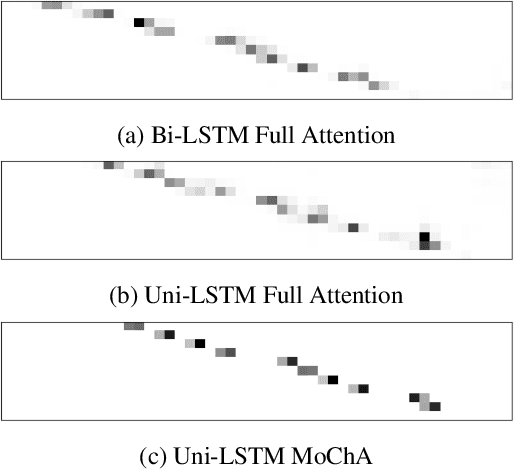
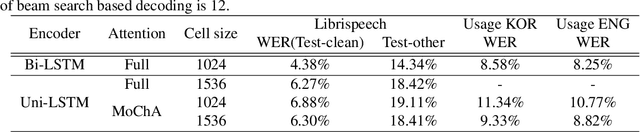

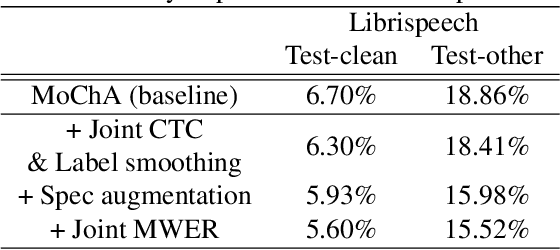
Abstract:In this paper, we present a new on-device automatic speech recognition (ASR) system based on monotonic chunk-wise attention (MoChA) models trained with large (> 10K hours) corpus. We attained around 90% of a word recognition rate for general domain mainly by using joint training of connectionist temporal classifier (CTC) and cross entropy (CE) losses, minimum word error rate (MWER) training, layer-wise pre-training and data augmentation methods. In addition, we compressed our models by more than 3.4 times smaller using an iterative hyper low-rank approximation (LRA) method while minimizing the degradation in recognition accuracy. The memory footprint was further reduced with 8-bit quantization to bring down the final model size to lower than 39 MB. For on-demand adaptation, we fused the MoChA models with statistical n-gram models, and we could achieve a relatively 36% improvement on average in word error rate (WER) for target domains including the general domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge