Junchi Yu
A Fragile Guardrail: Diffusion LLM's Safety Blessing and Its Failure Mode
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Diffusion large language models (D-LLMs) offer an alternative to autoregressive LLMs (AR-LLMs) and have demonstrated advantages in generation efficiency. Beyond the utility benefits, we argue that D-LLMs exhibit a previously underexplored safety blessing: their diffusion-style generation confers intrinsic robustness against jailbreak attacks originally designed for AR-LLMs. In this work, we provide an initial analysis of the underlying mechanism, showing that the diffusion trajectory induces a stepwise reduction effect that progressively suppresses unsafe generations. This robustness, however, is not absolute. We identify a simple yet effective failure mode, termed context nesting, where harmful requests are embedded within structured benign contexts, effectively bypassing the stepwise reduction mechanism. Empirically, we show that this simple strategy is sufficient to bypass D-LLMs' safety blessing, achieving state-of-the-art attack success rates across models and benchmarks. Most notably, it enables the first successful jailbreak of Gemini Diffusion, to our knowledge, exposing a critical vulnerability in commercial D-LLMs. Together, our results characterize both the origins and the limits of D-LLMs' safety blessing, constituting an early-stage red-teaming of D-LLMs.
The Alignment Curse: Cross-Modality Jailbreak Transfer in Omni-Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in end-to-end trained omni-models have significantly improved multimodal understanding. At the same time, safety red-teaming has expanded beyond text to encompass audio-based jailbreak attacks. However, an important bridge between textual and audio jailbreaks remains underexplored. In this work, we study the cross-modality transfer of jailbreak attacks from text to audio, motivated by the semantic similarity between the two modalities and the maturity of textual jailbreak methods. We first analyze the connection between modality alignment and cross-modality jailbreak transfer, showing that strong alignment can inadvertently propagate textual vulnerabilities to the audio modality, which we term the alignment curse. Guided by this analysis, we conduct an empirical evaluation of textual jailbreaks, text-transferred audio jailbreaks, and existing audio-based jailbreaks on recent omni-models. Our results show that text-transferred audio jailbreaks perform comparably to, and often better than, audio-based jailbreaks, establishing them as simple yet powerful baselines for future audio red-teaming. We further demonstrate strong cross-model transferability and show that text-transferred audio attacks remain effective even under a stricter audio-only access threat model.
Reasoning via Video: The First Evaluation of Video Models' Reasoning Abilities through Maze-Solving Tasks
Nov 19, 2025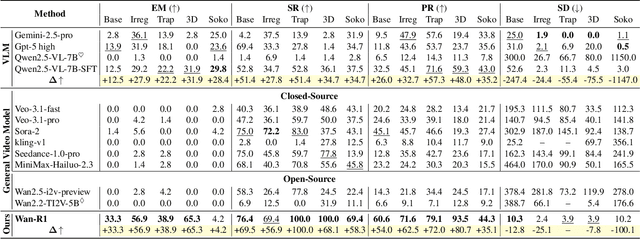

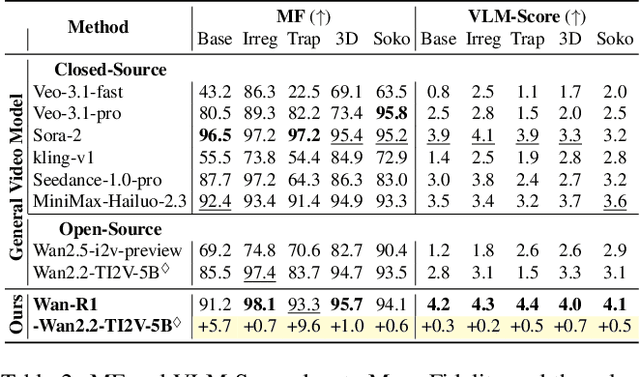
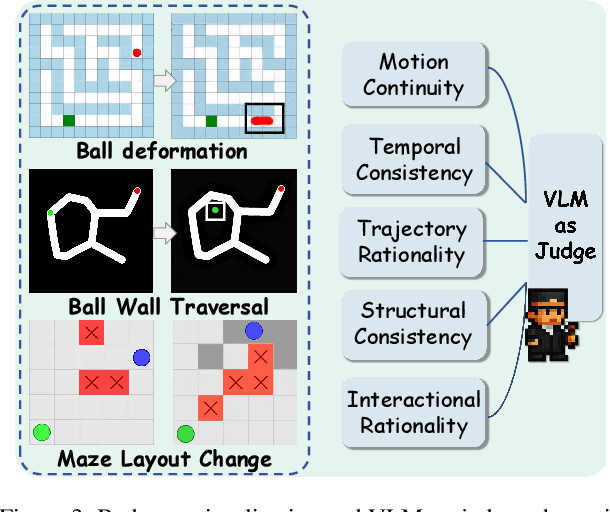
Abstract:Video Models have achieved remarkable success in high-fidelity video generation with coherent motion dynamics. Analogous to the development from text generation to text-based reasoning in language modeling, the development of video models motivates us to ask: Can video models reason via video generation? Compared with the discrete text corpus, video grounds reasoning in explicit spatial layouts and temporal continuity, which serves as an ideal substrate for spatial reasoning. In this work, we explore the reasoning via video paradigm and introduce VR-Bench -- a comprehensive benchmark designed to systematically evaluate video models' reasoning capabilities. Grounded in maze-solving tasks that inherently require spatial planning and multi-step reasoning, VR-Bench contains 7,920 procedurally generated videos across five maze types and diverse visual styles. Our empirical analysis demonstrates that SFT can efficiently elicit the reasoning ability of video model. Video models exhibit stronger spatial perception during reasoning, outperforming leading VLMs and generalizing well across diverse scenarios, tasks, and levels of complexity. We further discover a test-time scaling effect, where diverse sampling during inference improves reasoning reliability by 10--20%. These findings highlight the unique potential and scalability of reasoning via video for spatial reasoning tasks.
ARCHE: A Novel Task to Evaluate LLMs on Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction
Nov 16, 2025



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in scientific domains. While they can produce reasoning-like content via methods such as chain-of-thought prompting, these outputs are typically unstructured and informal, obscuring whether models truly understand the fundamental reasoning paradigms that underpin scientific inference. To address this, we introduce a novel task named Latent Reasoning Chain Extraction (ARCHE), in which models must decompose complex reasoning arguments into combinations of standard reasoning paradigms in the form of a Reasoning Logic Tree (RLT). In RLT, all reasoning steps are explicitly categorized as one of three variants of Peirce's fundamental inference modes: deduction, induction, or abduction. To facilitate this task, we release ARCHE Bench, a new benchmark derived from 70 Nature Communications articles, including more than 1,900 references and 38,000 viewpoints. We propose two logic-aware evaluation metrics: Entity Coverage (EC) for content completeness and Reasoning Edge Accuracy (REA) for step-by-step logical validity. Evaluations on 10 leading LLMs on ARCHE Bench reveal that models exhibit a trade-off between REA and EC, and none are yet able to extract a complete and standard reasoning chain. These findings highlight a substantial gap between the abilities of current reasoning models and the rigor required for scientific argumentation.
Generative Explanations for Graph Neural Network: Methods and Evaluations
Nov 09, 2023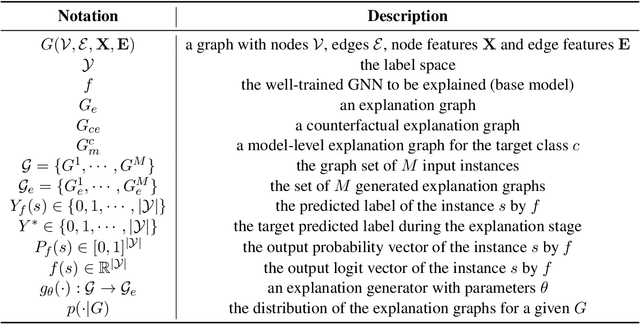
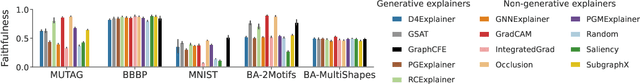
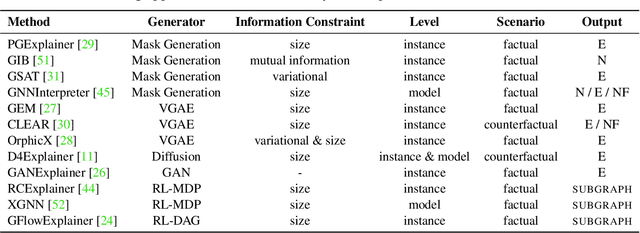
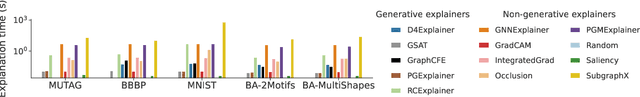
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) achieve state-of-the-art performance in various graph-related tasks. However, the black-box nature often limits their interpretability and trustworthiness. Numerous explainability methods have been proposed to uncover the decision-making logic of GNNs, by generating underlying explanatory substructures. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive review of the existing explanation methods for GNNs from the perspective of graph generation. Specifically, we propose a unified optimization objective for generative explanation methods, comprising two sub-objectives: Attribution and Information constraints. We further demonstrate their specific manifestations in various generative model architectures and different explanation scenarios. With the unified objective of the explanation problem, we reveal the shared characteristics and distinctions among current methods, laying the foundation for future methodological advancements. Empirical results demonstrate the advantages and limitations of different explainability approaches in terms of explanation performance, efficiency, and generalizability.
Thought Propagation: An Analogical Approach to Complex Reasoning with Large Language Models
Oct 09, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success in reasoning tasks with the development of prompting methods. However, existing prompting approaches cannot reuse insights of solving similar problems and suffer from accumulated errors in multi-step reasoning, since they prompt LLMs to reason \textit{from scratch}. To address these issues, we propose \textbf{\textit{Thought Propagation} (TP)}, which explores the analogous problems and leverages their solutions to enhance the complex reasoning ability of LLMs. These analogous problems are related to the input one, with reusable solutions and problem-solving strategies. Thus, it is promising to propagate insights of solving previous analogous problems to inspire new problem-solving. To achieve this, TP first prompts LLMs to propose and solve a set of analogous problems that are related to the input one. Then, TP reuses the results of analogous problems to directly yield a new solution or derive a knowledge-intensive plan for execution to amend the initial solution obtained from scratch. TP is compatible with existing prompting approaches, allowing plug-and-play generalization and enhancement in a wide range of tasks without much labor in task-specific prompt engineering. Experiments across three challenging tasks demonstrate TP enjoys a substantial improvement over the baselines by an average of 12\% absolute increase in finding the optimal solutions in Shortest-path Reasoning, 13\% improvement of human preference in Creative Writing, and 15\% enhancement in the task completion rate of LLM-Agent Planning.
Rumor Detection with Diverse Counterfactual Evidence
Jul 18, 2023



Abstract:The growth in social media has exacerbated the threat of fake news to individuals and communities. This draws increasing attention to developing efficient and timely rumor detection methods. The prevailing approaches resort to graph neural networks (GNNs) to exploit the post-propagation patterns of the rumor-spreading process. However, these methods lack inherent interpretation of rumor detection due to the black-box nature of GNNs. Moreover, these methods suffer from less robust results as they employ all the propagation patterns for rumor detection. In this paper, we address the above issues with the proposed Diverse Counterfactual Evidence framework for Rumor Detection (DCE-RD). Our intuition is to exploit the diverse counterfactual evidence of an event graph to serve as multi-view interpretations, which are further aggregated for robust rumor detection results. Specifically, our method first designs a subgraph generation strategy to efficiently generate different subgraphs of the event graph. We constrain the removal of these subgraphs to cause the change in rumor detection results. Thus, these subgraphs naturally serve as counterfactual evidence for rumor detection. To achieve multi-view interpretation, we design a diversity loss inspired by Determinantal Point Processes (DPP) to encourage diversity among the counterfactual evidence. A GNN-based rumor detection model further aggregates the diverse counterfactual evidence discovered by the proposed DCE-RD to achieve interpretable and robust rumor detection results. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets show the superior performance of our method. Our code is available at https://github.com/Vicinity111/DCE-RD.
Mind the Label Shift of Augmentation-based Graph OOD Generalization
Mar 27, 2023



Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization is an important issue for Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). Recent works employ different graph editions to generate augmented environments and learn an invariant GNN for generalization. However, the label shift usually occurs in augmentation since graph structural edition inevitably alters the graph label. This brings inconsistent predictive relationships among augmented environments, which is harmful to generalization. To address this issue, we propose \textbf{LiSA}, which generates label-invariant augmentations to facilitate graph OOD generalization. Instead of resorting to graph editions, LiSA exploits \textbf{L}abel-\textbf{i}nvariant \textbf{S}ubgraphs of the training graphs to construct \textbf{A}ugmented environments. Specifically, LiSA first designs the variational subgraph generators to extract locally predictive patterns and construct multiple label-invariant subgraphs efficiently. Then, the subgraphs produced by different generators are collected to build different augmented environments. To promote diversity among augmented environments, LiSA further introduces a tractable energy-based regularization to enlarge pair-wise distances between the distributions of environments. In this manner, LiSA generates diverse augmented environments with a consistent predictive relationship and facilitates learning an invariant GNN. Extensive experiments on node-level and graph-level OOD benchmarks show that LiSA achieves impressive generalization performance with different GNN backbones. Code is available on \url{https://github.com/Samyu0304/LiSA}.
ScoreMix: A Scalable Augmentation Strategy for Training GANs with Limited Data
Nov 04, 2022



Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) typically suffer from overfitting when limited training data is available. To facilitate GAN training, current methods propose to use data-specific augmentation techniques. Despite the effectiveness, it is difficult for these methods to scale to practical applications. In this work, we present ScoreMix, a novel and scalable data augmentation approach for various image synthesis tasks. We first produce augmented samples using the convex combinations of the real samples. Then, we optimize the augmented samples by minimizing the norms of the data scores, i.e., the gradients of the log-density functions. This procedure enforces the augmented samples close to the data manifold. To estimate the scores, we train a deep estimation network with multi-scale score matching. For different image synthesis tasks, we train the score estimation network using different data. We do not require the tuning of the hyperparameters or modifications to the network architecture. The ScoreMix method effectively increases the diversity of data and reduces the overfitting problem. Moreover, it can be easily incorporated into existing GAN models with minor modifications. Experimental results on numerous tasks demonstrate that GAN models equipped with the ScoreMix method achieve significant improvements.
Finding Diverse and Predictable Subgraphs for Graph Domain Generalization
Jun 19, 2022



Abstract:This paper focuses on out-of-distribution generalization on graphs where performance drops due to the unseen distribution shift. Previous graph domain generalization works always resort to learning an invariant predictor among different source domains. However, they assume sufficient source domains are available during training, posing huge challenges for realistic applications. By contrast, we propose a new graph domain generalization framework, dubbed as DPS, by constructing multiple populations from the source domains. Specifically, DPS aims to discover multiple \textbf{D}iverse and \textbf{P}redictable \textbf{S}ubgraphs with a set of generators, namely, subgraphs are different from each other but all the them share the same semantics with the input graph. These generated source domains are exploited to learn an \textit{equi-predictive} graph neural network (GNN) across domains, which is expected to generalize well to unseen target domains. Generally, DPS is model-agnostic that can be incorporated with various GNN backbones. Extensive experiments on both node-level and graph-level benchmarks shows that the proposed DPS achieves impressive performance for various graph domain generalization tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge