Judith Dineley
Multilingual Lexical Feature Analysis of Spoken Language for Predicting Major Depression Symptom Severity
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Background: Captured between clinical appointments using mobile devices, spoken language has potential for objective, more regular assessment of symptom severity and earlier detection of relapse in major depressive disorder. However, research to date has largely been in non-clinical cross-sectional samples of written language using complex machine learning (ML) approaches with limited interpretability. Methods: We describe an initial exploratory analysis of longitudinal speech data and PHQ-8 assessments from 5,836 recordings of 586 participants in the UK, Netherlands, and Spain, collected in the RADAR-MDD study. We sought to identify interpretable lexical features associated with MDD symptom severity with linear mixed-effects modelling. Interpretable features and high-dimensional vector embeddings were also used to test the prediction performance of four regressor ML models. Results: In English data, MDD symptom severity was associated with 7 features including lexical diversity measures and absolutist language. In Dutch, associations were observed with words per sentence and positive word frequency; no associations were observed in recordings collected in Spain. The predictive power of lexical features and vector embeddings was near chance level across all languages. Limitations: Smaller samples in non-English speech and methodological choices, such as the elicitation prompt, may have also limited the effect sizes observable. A lack of NLP tools in languages other than English restricted our feature choice. Conclusion: To understand the value of lexical markers in clinical research and practice, further research is needed in larger samples across several languages using improved protocols, and ML models that account for within- and between-individual variations in language.
A pilot protocol and cohort for the investigation of non-pathological variability in speech
Jun 11, 2024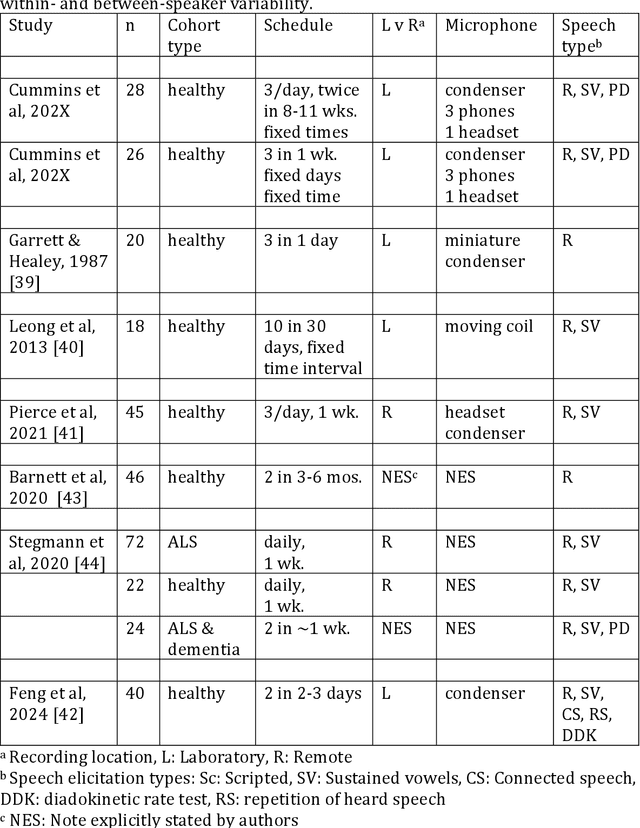
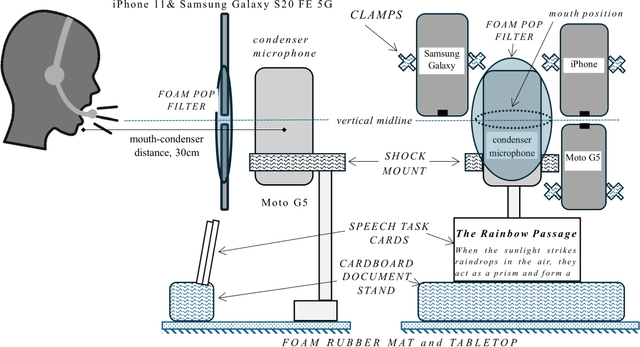
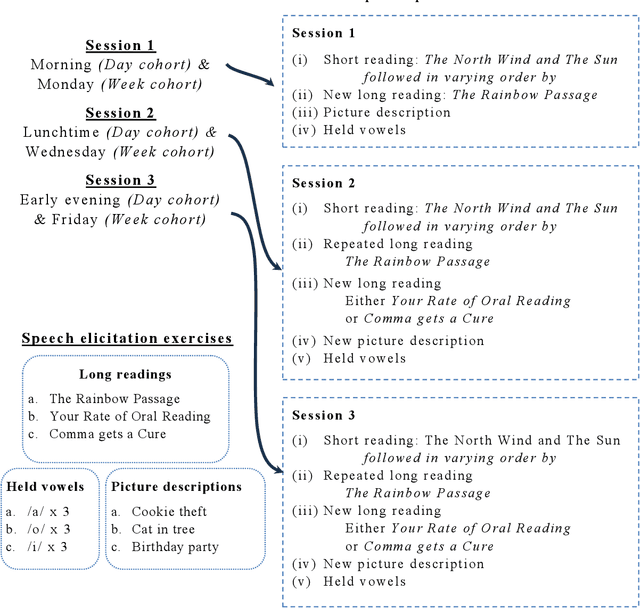

Abstract:Background Speech-based biomarkers have potential as a means for regular, objective assessment of symptom severity, remotely and in-clinic in combination with advanced analytical models. However, the complex nature of speech and the often subtle changes associated with health mean that findings are highly dependent on methodological and cohort choices. These are often not reported adequately in studies investigating speech-based health assessment Objective To develop and apply an exemplar protocol to generate a pilot dataset of healthy speech with detailed metadata for the assessment of factors in the speech recording-analysis pipeline, including device choice, speech elicitation task and non-pathological variability. Methods We developed our collection protocol and choice of exemplar speech features based on a thematic literature review. Our protocol includes the elicitation of three different speech types. With a focus towards remote applications, we also choose to collect speech with three different microphone types. We developed a pipeline to extract a set of 14 exemplar speech features. Results We collected speech from 28 individuals three times in one day, repeated at the same times 8-11 weeks later, and from 25 healthy individuals three times in one week. Participant characteristics collected included sex, age, native language status and voice use habits of the participant. A preliminary set of 14 speech features covering timing, prosody, voice quality, articulation and spectral moment characteristics were extracted that provide a resource of normative values. Conclusions There are multiple methodological factors involved in the collection, processing and analysis of speech recordings. Consistent reporting and greater harmonisation of study protocols are urgently required to aid the translation of speech processing into clinical research and practice.
Identifying depression-related topics in smartphone-collected free-response speech recordings using an automatic speech recognition system and a deep learning topic model
Sep 05, 2023



Abstract:Language use has been shown to correlate with depression, but large-scale validation is needed. Traditional methods like clinic studies are expensive. So, natural language processing has been employed on social media to predict depression, but limitations remain-lack of validated labels, biased user samples, and no context. Our study identified 29 topics in 3919 smartphone-collected speech recordings from 265 participants using the Whisper tool and BERTopic model. Six topics with a median PHQ-8 greater than or equal to 10 were regarded as risk topics for depression: No Expectations, Sleep, Mental Therapy, Haircut, Studying, and Coursework. To elucidate the topic emergence and associations with depression, we compared behavioral (from wearables) and linguistic characteristics across identified topics. The correlation between topic shifts and changes in depression severity over time was also investigated, indicating the importance of longitudinally monitoring language use. We also tested the BERTopic model on a similar smaller dataset (356 speech recordings from 57 participants), obtaining some consistent results. In summary, our findings demonstrate specific speech topics may indicate depression severity. The presented data-driven workflow provides a practical approach to collecting and analyzing large-scale speech data from real-world settings for digital health research.
Towards robust paralinguistic assessment for real-world mobile health (mHealth) monitoring: an initial study of reverberation effects on speech
May 21, 2023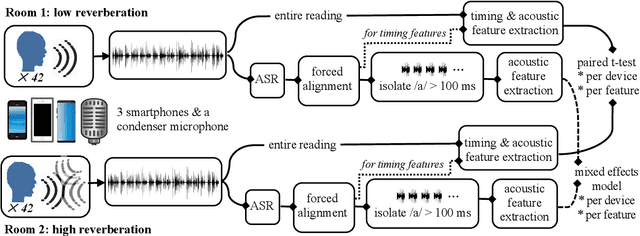
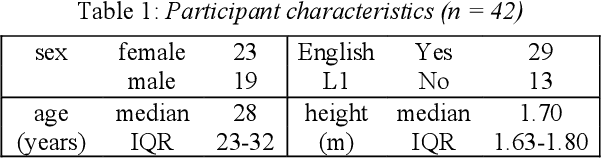
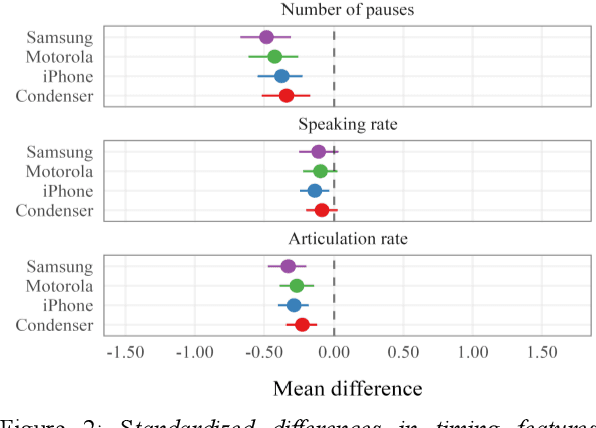
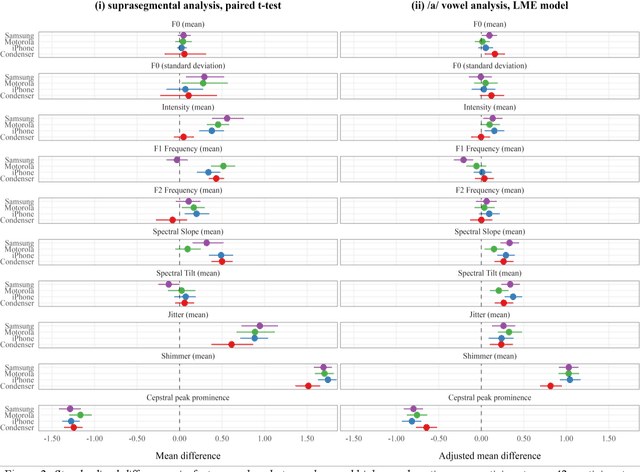
Abstract:Speech is promising as an objective, convenient tool to monitor health remotely over time using mobile devices. Numerous paralinguistic features have been demonstrated to contain salient information related to an individual's health. However, mobile device specification and acoustic environments vary widely, risking the reliability of the extracted features. In an initial step towards quantifying these effects, we report the variability of 13 exemplar paralinguistic features commonly reported in the speech-health literature and extracted from the speech of 42 healthy volunteers recorded consecutively in rooms with low and high reverberation with one budget and two higher-end smartphones and a condenser microphone. Our results show reverberation has a clear effect on several features, in particular voice quality markers. They point to new research directions investigating how best to record and process in-the-wild speech for reliable longitudinal health state assessment.
HEAR4Health: A blueprint for making computer audition a staple of modern healthcare
Jan 25, 2023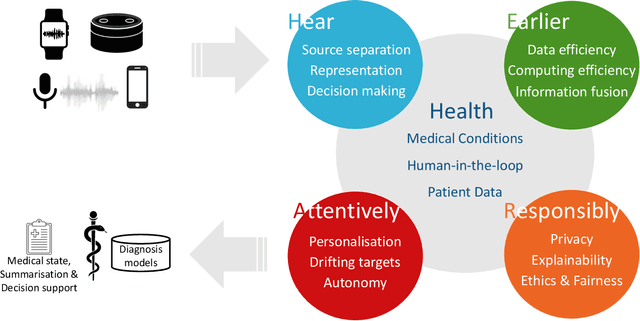

Abstract:Recent years have seen a rapid increase in digital medicine research in an attempt to transform traditional healthcare systems to their modern, intelligent, and versatile equivalents that are adequately equipped to tackle contemporary challenges. This has led to a wave of applications that utilise AI technologies; first and foremost in the fields of medical imaging, but also in the use of wearables and other intelligent sensors. In comparison, computer audition can be seen to be lagging behind, at least in terms of commercial interest. Yet, audition has long been a staple assistant for medical practitioners, with the stethoscope being the quintessential sign of doctors around the world. Transforming this traditional technology with the use of AI entails a set of unique challenges. We categorise the advances needed in four key pillars: Hear, corresponding to the cornerstone technologies needed to analyse auditory signals in real-life conditions; Earlier, for the advances needed in computational and data efficiency; Attentively, for accounting to individual differences and handling the longitudinal nature of medical data; and, finally, Responsibly, for ensuring compliance to the ethical standards accorded to the field of medicine.
Detecting the Severity of Major Depressive Disorder from Speech: A Novel HARD-Training Methodology
Jun 02, 2022
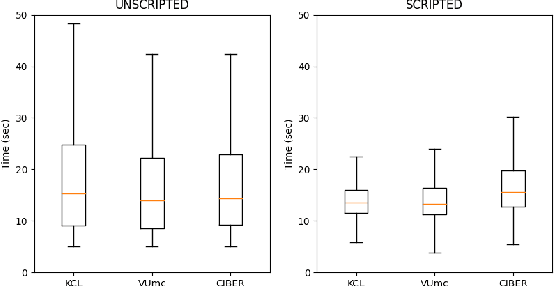
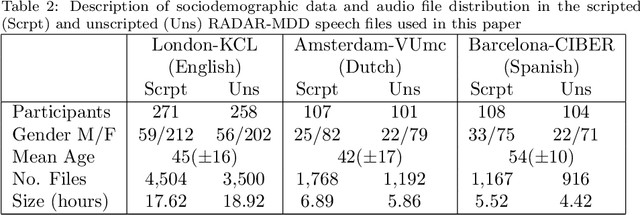
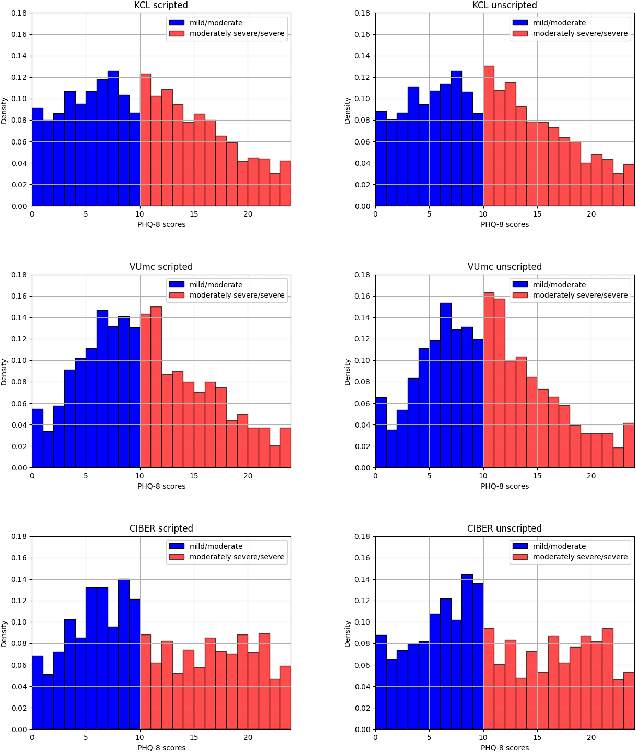
Abstract:Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a common worldwide mental health issue with high associated socioeconomic costs. The prediction and automatic detection of MDD can, therefore, make a huge impact on society. Speech, as a non-invasive, easy to collect signal, is a promising marker to aid the diagnosis and assessment of MDD. In this regard, speech samples were collected as part of the Remote Assessment of Disease and Relapse in Major Depressive Disorder (RADAR-MDD) research programme. RADAR-MDD was an observational cohort study in which speech and other digital biomarkers were collected from a cohort of individuals with a history of MDD in Spain, United Kingdom and the Netherlands. In this paper, the RADAR-MDD speech corpus was taken as an experimental framework to test the efficacy of a Sequence-to-Sequence model with a local attention mechanism in a two-class depression severity classification paradigm. Additionally, a novel training method, HARD-Training, is proposed. It is a methodology based on the selection of more ambiguous samples for the model training, and inspired by the curriculum learning paradigm. HARD-Training was found to consistently improve - with an average increment of 8.6% - the performance of our classifiers for both of two speech elicitation tasks used and each collection site of the RADAR-MDD speech corpus. With this novel methodology, our Sequence-to-Sequence model was able to effectively detect MDD severity regardless of language. Finally, recognising the need for greater awareness of potential algorithmic bias, we conduct an additional analysis of our results separately for each gender.
Fitbeat: COVID-19 Estimation based on Wristband Heart Rate
Apr 19, 2021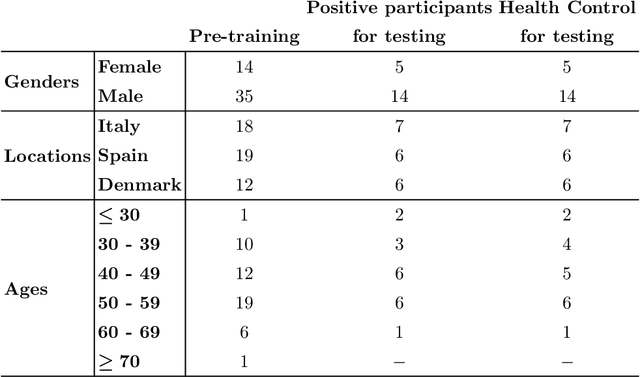

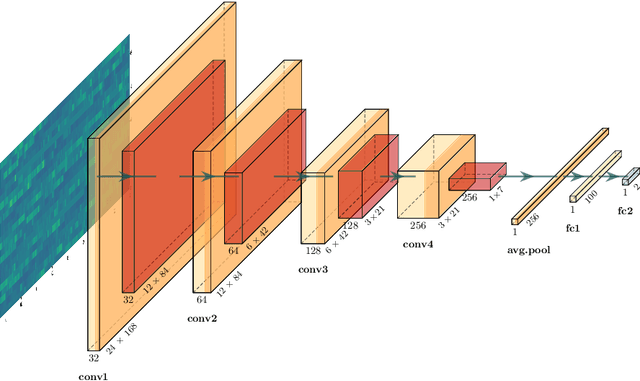
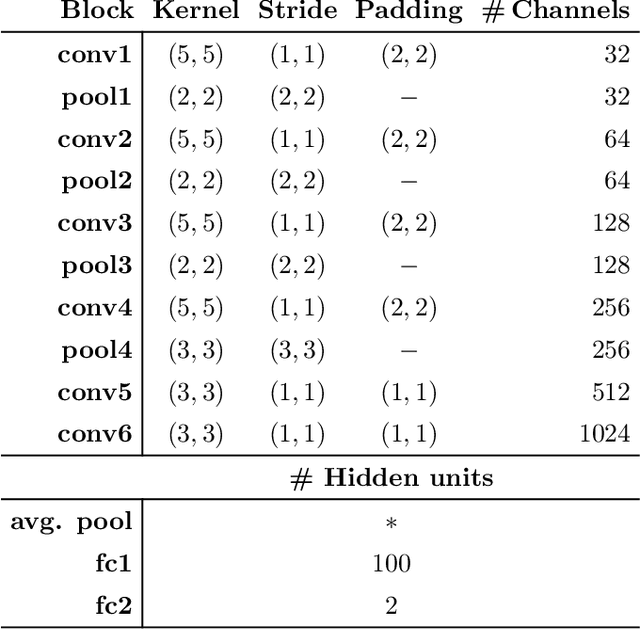
Abstract:This study investigates the potential of deep learning methods to identify individuals with suspected COVID-19 infection using remotely collected heart-rate data. The study utilises data from the ongoing EU IMI RADAR-CNS research project that is investigating the feasibility of wearable devices and smart phones to monitor individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS), depression or epilepsy. Aspart of the project protocol, heart-rate data was collected from participants using a Fitbit wristband. The presence of COVID-19 in the cohort in this work was either confirmed through a positive swab test, or inferred through the self-reporting of a combination of symptoms including fever, respiratory symptoms, loss of smell or taste, tiredness and gastrointestinal symptoms. Experimental results indicate that our proposed contrastive convolutional auto-encoder (contrastive CAE), i. e., a combined architecture of an auto-encoder and contrastive loss, outperforms a conventional convolutional neural network (CNN), as well as a convolutional auto-encoder (CAE) without using contrastive loss. Our final contrastive CAE achieves 95.3% unweighted average recall, 86.4% precision, anF1 measure of 88.2%, a sensitivity of 100% and a specificity of 90.6% on a testset of 19 participants with MS who reported symptoms of COVID-19. Each of these participants was paired with a participant with MS with no COVID-19 symptoms.
Voice command generation using Progressive Wavegans
Mar 13, 2019


Abstract:Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have become exceedingly popular in a wide range of data-driven research fields, due in part to their success in image generation. Their ability to generate new samples, often from only a small amount of input data, makes them an exciting research tool in areas with limited data resources. One less-explored application of GANs is the synthesis of speech and audio samples. Herein, we propose a set of extensions to the WaveGAN paradigm, a recently proposed approach for sound generation using GANs. The aim of these extensions - preprocessing, Audio-to-Audio generation, skip connections and progressive structures - is to improve the human likeness of synthetic speech samples. Scores from listening tests with 30 volunteers demonstrated a moderate improvement (Cohen's d coefficient of 0.65) in human likeness using the proposed extensions compared to the original WaveGAN approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge