Carmen Garcia-Mateo
Detecting the Severity of Major Depressive Disorder from Speech: A Novel HARD-Training Methodology
Jun 02, 2022
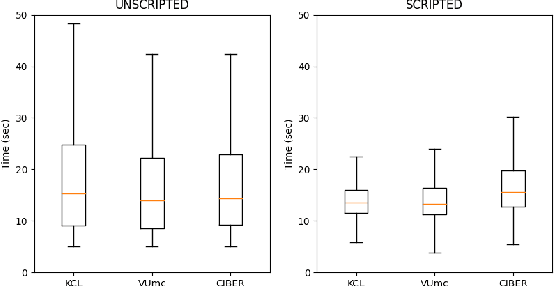
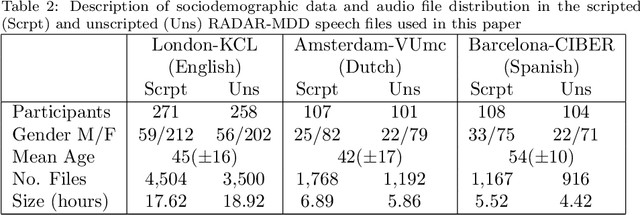
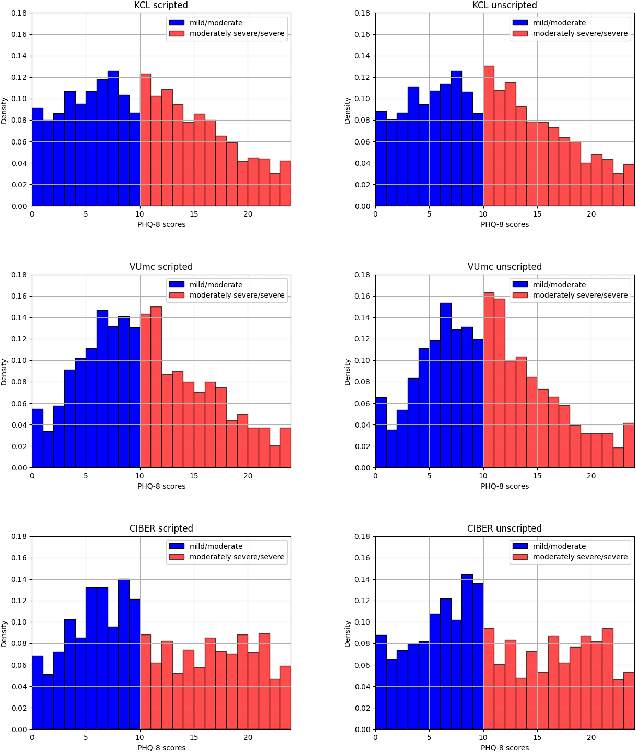
Abstract:Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is a common worldwide mental health issue with high associated socioeconomic costs. The prediction and automatic detection of MDD can, therefore, make a huge impact on society. Speech, as a non-invasive, easy to collect signal, is a promising marker to aid the diagnosis and assessment of MDD. In this regard, speech samples were collected as part of the Remote Assessment of Disease and Relapse in Major Depressive Disorder (RADAR-MDD) research programme. RADAR-MDD was an observational cohort study in which speech and other digital biomarkers were collected from a cohort of individuals with a history of MDD in Spain, United Kingdom and the Netherlands. In this paper, the RADAR-MDD speech corpus was taken as an experimental framework to test the efficacy of a Sequence-to-Sequence model with a local attention mechanism in a two-class depression severity classification paradigm. Additionally, a novel training method, HARD-Training, is proposed. It is a methodology based on the selection of more ambiguous samples for the model training, and inspired by the curriculum learning paradigm. HARD-Training was found to consistently improve - with an average increment of 8.6% - the performance of our classifiers for both of two speech elicitation tasks used and each collection site of the RADAR-MDD speech corpus. With this novel methodology, our Sequence-to-Sequence model was able to effectively detect MDD severity regardless of language. Finally, recognising the need for greater awareness of potential algorithmic bias, we conduct an additional analysis of our results separately for each gender.
The Multiscenario Multienvironment BioSecure Multimodal Database (BMDB)
Nov 17, 2021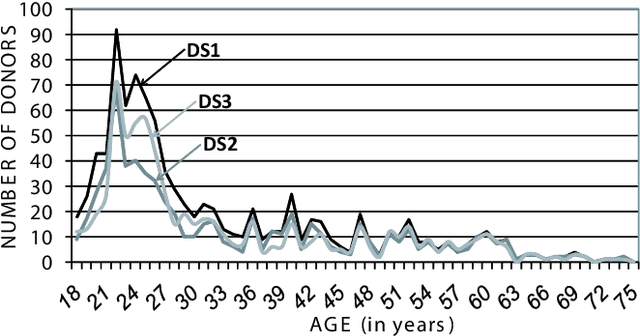

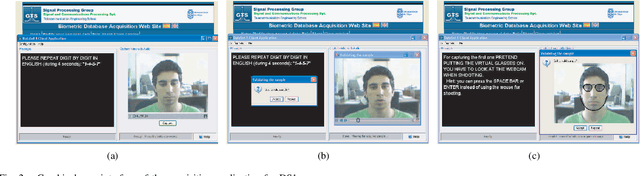

Abstract:A new multimodal biometric database designed and acquired within the framework of the European BioSecure Network of Excellence is presented. It is comprised of more than 600 individuals acquired simultaneously in three scenarios: 1) over the Internet, 2) in an office environment with desktop PC, and 3) in indoor/outdoor environments with mobile portable hardware. The three scenarios include a common part of audio/video data. Also, signature and fingerprint data have been acquired both with desktop PC and mobile portable hardware. Additionally, hand and iris data were acquired in the second scenario using desktop PC. Acquisition has been conducted by 11 European institutions. Additional features of the BioSecure Multimodal Database (BMDB) are: two acquisition sessions, several sensors in certain modalities, balanced gender and age distributions, multimodal realistic scenarios with simple and quick tasks per modality, cross-European diversity, availability of demographic data, and compatibility with other multimodal databases. The novel acquisition conditions of the BMDB allow us to perform new challenging research and evaluation of either monomodal or multimodal biometric systems, as in the recent BioSecure Multimodal Evaluation campaign. A description of this campaign including baseline results of individual modalities from the new database is also given. The database is expected to be available for research purposes through the BioSecure Association during 2008
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge