Fernando Alonso-Fernandez
Leveraging Large-Scale Face Datasets for Deep Periocular Recognition via Ocular Cropping
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We focus on ocular biometrics, specifically the periocular region (the area around the eye), which offers high discrimination and minimal acquisition constraints. We evaluate three Convolutional Neural Network architectures of varying depth and complexity to assess their effectiveness for periocular recognition. The networks are trained on 1,907,572 ocular crops extracted from the large-scale VGGFace2 database. This significantly contrasts with existing works, which typically rely on small-scale periocular datasets for training having only a few thousand images. Experiments are conducted with ocular images from VGGFace2-Pose, a subset of VGGFace2 containing in-the-wild face images, and the UFPR-Periocular database, which consists of selfies captured via mobile devices with user guidance on the screen. Due to the uncontrolled conditions of VGGFace2, the Equal Error Rates (EERs) obtained with ocular crops range from 9-15%, noticeably higher than the 3-6% EERs achieved using full-face images. In contrast, UFPR-Periocular yields significantly better performance (EERs of 1-2%), thanks to higher image quality and more consistent acquisition protocols. To the best of our knowledge, these are the lowest reported EERs on the UFPR dataset to date.
Exploring the correlation between the type of music and the emotions evoked: A study using subjective questionnaires and EEG
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:The subject of this work is to check how different types of music affect human emotions. While listening to music, a subjective survey and brain activity measurements were carried out using an EEG helmet. The aim is to demonstrate the impact of different music genres on emotions. The research involved a diverse group of participants of different gender and musical preferences. This had the effect of capturing a wide range of emotional responses to music. After the experiment, a relationship analysis of the respondents' questionnaires with EEG signals was performed. The analysis revealed connections between emotions and observed brain activity.
Exploring Complementarity and Explainability in CNNs for Periocular Verification Across Acquisition Distances
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We study the complementarity of different CNNs for periocular verification at different distances on the UBIPr database. We train three architectures of increasing complexity (SqueezeNet, MobileNetv2, and ResNet50) on a large set of eye crops from VGGFace2. We analyse performance with cosine and chi2 metrics, compare different network initialisations, and apply score-level fusion via logistic regression. In addition, we use LIME heatmaps and Jensen-Shannon divergence to compare attention patterns of the CNNs. While ResNet50 consistently performs best individually, the fusion provides substantial gains, especially when combining all three networks. Heatmaps show that networks usually focus on distinct regions of a given image, which explains their complementarity. Our method significantly outperforms previous works on UBIPr, achieving a new state-of-the-art.
Blimp-based Crime Scene Analysis
Apr 22, 2025



Abstract:To tackle the crucial problem of crime, evidence at indoor crime scenes must be analyzed before it becomes contaminated or degraded. Here, as an application of artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision, and robotics, we explore how a blimp could be designed as a kind of "floating camera" to drift over and record evidence with minimal disturbance. In particular, rapid prototyping is used to develop a proof-of-concept to gain insight into what such blimps could do, manually piloted or semi-autonomously. As a result, we show the feasibility of attaching various components to an indoor blimp, and confirm our basic premise, that blimps can sense evidence without producing much wind. Some additional suggestions--regarding mapping, sensing, and path-finding--aim to stimulate the flow of ideas for further exploration.
Nano Drone-based Indoor Crime Scene Analysis
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:Technologies such as robotics, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and Computer Vision (CV) can be applied to crime scene analysis (CSA) to help protect lives, facilitate justice, and deter crime, but an overview of the tasks that can be automated has been lacking. Here we follow a speculate prototyping approach: First, the STAIR tool is used to rapidly review the literature and identify tasks that seem to have not received much attention, like accessing crime sites through a window, mapping/gathering evidence, and analyzing blood smears. Secondly, we present a prototype of a small drone that implements these three tasks with 75%, 85%, and 80% performance, to perform a minimal analysis of an indoor crime scene. Lessons learned are reported, toward guiding next work in the area.
Combined CNN and ViT features off-the-shelf: Another astounding baseline for recognition
Jul 28, 2024



Abstract:We apply pre-trained architectures, originally developed for the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge, for periocular recognition. These architectures have demonstrated significant success in various computer vision tasks beyond the ones for which they were designed. This work builds on our previous study using off-the-shelf Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and extends it to include the more recently proposed Vision Transformers (ViT). Despite being trained for generic object classification, middle-layer features from CNNs and ViTs are a suitable way to recognize individuals based on periocular images. We also demonstrate that CNNs and ViTs are highly complementary since their combination results in boosted accuracy. In addition, we show that a small portion of these pre-trained models can achieve good accuracy, resulting in thinner models with fewer parameters, suitable for resource-limited environments such as mobiles. This efficiency improves if traditional handcrafted features are added as well.
Deep Network Pruning: A Comparative Study on CNNs in Face Recognition
May 28, 2024Abstract:The widespread use of mobile devices for all kind of transactions makes necessary reliable and real-time identity authentication, leading to the adoption of face recognition (FR) via the cameras embedded in such devices. Progress of deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) has provided substantial advances in FR. Nonetheless, the size of state-of-the-art architectures is unsuitable for mobile deployment, since they often encompass hundreds of megabytes and millions of parameters. We address this by studying methods for deep network compression applied to FR. In particular, we apply network pruning based on Taylor scores, where less important filters are removed iteratively. The method is tested on three networks based on the small SqueezeNet (1.24M parameters) and the popular MobileNetv2 (3.5M) and ResNet50 (23.5M) architectures. These have been selected to showcase the method on CNNs with different complexities and sizes. We observe that a substantial percentage of filters can be removed with minimal performance loss. Also, filters with the highest amount of output channels tend to be removed first, suggesting that high-dimensional spaces within popular CNNs are over-dimensionated.
Understanding and Improving CNNs with Complex Structure Tensor: A Biometrics Study
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:Our study provides evidence that CNNs struggle to effectively extract orientation features. We show that the use of Complex Structure Tensor, which contains compact orientation features with certainties, as input to CNNs consistently improves identification accuracy compared to using grayscale inputs alone. Experiments also demonstrated that our inputs, which were provided by mini complex conv-nets, combined with reduced CNN sizes, outperformed full-fledged, prevailing CNN architectures. This suggests that the upfront use of orientation features in CNNs, a strategy seen in mammalian vision, not only mitigates their limitations but also enhances their explainability and relevance to thin-clients. Experiments were done on publicly available data sets comprising periocular images for biometric identification and verification (Close and Open World) using 6 State of the Art CNN architectures. We reduced SOA Equal Error Rate (EER) on the PolyU dataset by 5-26% depending on data and scenario.
Predicting Overtakes in Trucks Using CAN Data
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:Safe overtakes in trucks are crucial to prevent accidents, reduce congestion, and ensure efficient traffic flow, making early prediction essential for timely and informed driving decisions. Accordingly, we investigate the detection of truck overtakes from CAN data. Three classifiers, Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), Random Forest, and Support Vector Machines (SVM), are employed for the task. Our analysis covers up to 10 seconds before the overtaking event, using an overlapping sliding window of 1 second to extract CAN features. We observe that the prediction scores of the overtake class tend to increase as we approach the overtake trigger, while the no-overtake class remain stable or oscillates depending on the classifier. Thus, the best accuracy is achieved when approaching the trigger, making early overtaking prediction challenging. The classifiers show good accuracy in classifying overtakes (Recall/TPR > 93%), but accuracy is suboptimal in classifying no-overtakes (TNR typically 80-90% and below 60% for one SVM variant). We further combine two classifiers (Random Forest and linear SVM) by averaging their output scores. The fusion is observed to improve no-overtake classification (TNR > 92%) at the expense of reducing overtake accuracy (TPR). However, the latter is kept above 91% near the overtake trigger. Therefore, the fusion balances TPR and TNR, providing more consistent performance than individual classifiers.
Designing Robots to Help Women
Apr 05, 2024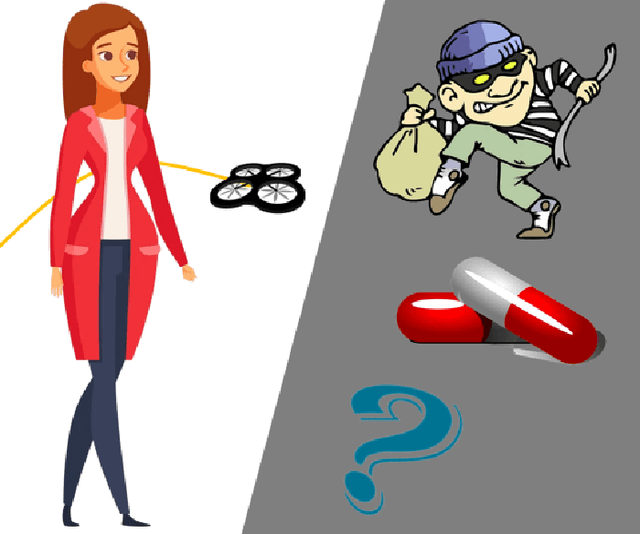
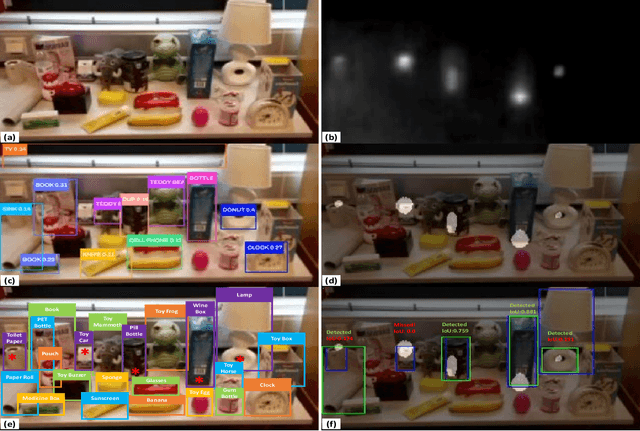
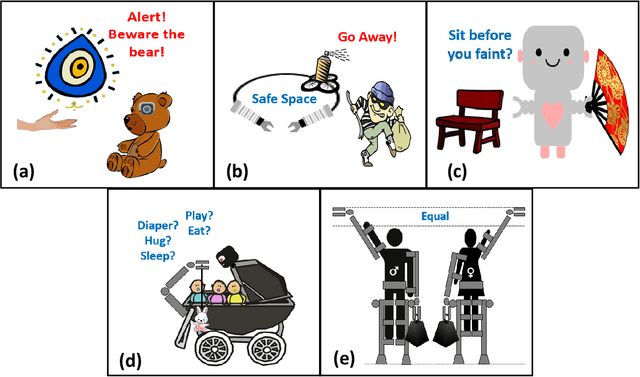


Abstract:Robots are being designed to help people in an increasing variety of settings--but seemingly little attention has been given so far to the specific needs of women, who represent roughly half of the world's population but are highly underrepresented in robotics. Here we used a speculative prototyping approach to explore this expansive design space: First, we identified some potential challenges of interest, including crimes and illnesses that disproportionately affect women, as well as potential opportunities for designers, which were visualized in five sketches. Then, one of the sketched scenarios was further explored by developing a prototype, of a robotic helper drone equipped with computer vision to detect hidden cameras that could be used to spy on women. While object detection introduced some errors, hidden cameras were identified with a reasonable accuracy of 80\% (Intersection over Union (IoU) score: 0.40). Our aim is that the identified challenges and opportunities could help spark discussion and inspire designers, toward realizing a safer, more inclusive future through responsible use of technology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge