Jie Wei
Dept. of Computer Science, City College of New York
Exploring Classical Piano Performance Generation with Expressive Music Variational AutoEncoder
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:The creativity of classical music arises not only from composers who craft the musical sheets but also from performers who interpret the static notations with expressive nuances. This paper addresses the challenge of generating classical piano performances from scratch, aiming to emulate the dual roles of composer and pianist in the creative process. We introduce the Expressive Compound Word (ECP) representation, which effectively captures both the metrical structure and expressive nuances of classical performances. Building on this, we propose the Expressive Music Variational AutoEncoder (XMVAE), a model featuring two branches: a Vector Quantized Variational AutoEncoder (VQ-VAE) branch that generates score-related content, representing the Composer, and a vanilla VAE branch that produces expressive details, fulfilling the role of Pianist. These branches are jointly trained with similar Seq2Seq architectures, leveraging a multiscale encoder to capture beat-level contextual information and an orthogonal Transformer decoder for efficient compound tokens decoding. Both objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that XMVAE generates classical performances with superior musical quality compared to state-of-the-art models. Furthermore, pretraining the Composer branch on extra musical score datasets contribute to a significant performance gain.
Investigating Vision-Language Model for Point Cloud-based Vehicle Classification
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Heavy-duty trucks pose significant safety challenges due to their large size and limited maneuverability compared to passenger vehicles. A deeper understanding of truck characteristics is essential for enhancing the safety perspective of cooperative autonomous driving. Traditional LiDAR-based truck classification methods rely on extensive manual annotations, which makes them labor-intensive and costly. The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) trained on massive datasets presents an opportunity to leverage their few-shot learning capabilities for truck classification. However, existing vision-language models (VLMs) are primarily trained on image datasets, which makes it challenging to directly process point cloud data. This study introduces a novel framework that integrates roadside LiDAR point cloud data with VLMs to facilitate efficient and accurate truck classification, which supports cooperative and safe driving environments. This study introduces three key innovations: (1) leveraging real-world LiDAR datasets for model development, (2) designing a preprocessing pipeline to adapt point cloud data for VLM input, including point cloud registration for dense 3D rendering and mathematical morphological techniques to enhance feature representation, and (3) utilizing in-context learning with few-shot prompting to enable vehicle classification with minimally labeled training data. Experimental results demonstrate encouraging performance of this method and present its potential to reduce annotation efforts while improving classification accuracy.
Rethinking Affect Analysis: A Protocol for Ensuring Fairness and Consistency
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:Evaluating affect analysis methods presents challenges due to inconsistencies in database partitioning and evaluation protocols, leading to unfair and biased results. Previous studies claim continuous performance improvements, but our findings challenge such assertions. Using these insights, we propose a unified protocol for database partitioning that ensures fairness and comparability. We provide detailed demographic annotations (in terms of race, gender and age), evaluation metrics, and a common framework for expression recognition, action unit detection and valence-arousal estimation. We also rerun the methods with the new protocol and introduce a new leaderboards to encourage future research in affect recognition with a fairer comparison. Our annotations, code, and pre-trained models are available on \hyperlink{https://github.com/dkollias/Fair-Consistent-Affect-Analysis}{Github}.
Robust Facial Reactions Generation: An Emotion-Aware Framework with Modality Compensation
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:The objective of the Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation (MAFRG) task is to produce contextually appropriate and diverse listener facial behavioural responses based on the multimodal behavioural data of the conversational partner (i.e., the speaker). Current methodologies typically assume continuous availability of speech and facial modality data, neglecting real-world scenarios where these data may be intermittently unavailable, which often results in model failures. Furthermore, despite utilising advanced deep learning models to extract information from the speaker's multimodal inputs, these models fail to adequately leverage the speaker's emotional context, which is vital for eliciting appropriate facial reactions from human listeners. To address these limitations, we propose an Emotion-aware Modality Compensatory (EMC) framework. This versatile solution can be seamlessly integrated into existing models, thereby preserving their advantages while significantly enhancing performance and robustness in scenarios with missing modalities. Our framework ensures resilience when faced with missing modality data through the Compensatory Modality Alignment (CMA) module. It also generates more appropriate emotion-aware reactions via the Emotion-aware Attention (EA) module, which incorporates the speaker's emotional information throughout the entire encoding and decoding process. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework improves the appropriateness metric FRCorr by an average of 57.2\% compared to the original model structure. In scenarios where speech modality data is missing, the performance of appropriate generation shows an improvement, and when facial data is missing, it only exhibits minimal degradation.
Efficient Temporal Action Segmentation via Boundary-aware Query Voting
May 25, 2024Abstract:Although the performance of Temporal Action Segmentation (TAS) has improved in recent years, achieving promising results often comes with a high computational cost due to dense inputs, complex model structures, and resource-intensive post-processing requirements. To improve the efficiency while keeping the performance, we present a novel perspective centered on per-segment classification. By harnessing the capabilities of Transformers, we tokenize each video segment as an instance token, endowed with intrinsic instance segmentation. To realize efficient action segmentation, we introduce BaFormer, a boundary-aware Transformer network. It employs instance queries for instance segmentation and a global query for class-agnostic boundary prediction, yielding continuous segment proposals. During inference, BaFormer employs a simple yet effective voting strategy to classify boundary-wise segments based on instance segmentation. Remarkably, as a single-stage approach, BaFormer significantly reduces the computational costs, utilizing only 6% of the running time compared to state-of-the-art method DiffAct, while producing better or comparable accuracy over several popular benchmarks. The code for this project is publicly available at https://github.com/peiyao-w/BaFormer.
Bridging the Gap: Protocol Towards Fair and Consistent Affect Analysis
May 16, 2024Abstract:The increasing integration of machine learning algorithms in daily life underscores the critical need for fairness and equity in their deployment. As these technologies play a pivotal role in decision-making, addressing biases across diverse subpopulation groups, including age, gender, and race, becomes paramount. Automatic affect analysis, at the intersection of physiology, psychology, and machine learning, has seen significant development. However, existing databases and methodologies lack uniformity, leading to biased evaluations. This work addresses these issues by analyzing six affective databases, annotating demographic attributes, and proposing a common protocol for database partitioning. Emphasis is placed on fairness in evaluations. Extensive experiments with baseline and state-of-the-art methods demonstrate the impact of these changes, revealing the inadequacy of prior assessments. The findings underscore the importance of considering demographic attributes in affect analysis research and provide a foundation for more equitable methodologies. Our annotations, code and pre-trained models are available at: https://github.com/dkollias/Fair-Consistent-Affect-Analysis
Image Prior and Posterior Conditional Probability Representation for Efficient Damage Assessment
Oct 26, 2023


Abstract:It is important to quantify Damage Assessment (DA) for Human Assistance and Disaster Response (HADR) applications. In this paper, to achieve efficient and scalable DA in HADR, an image prior and posterior conditional probability (IP2CP) is developed as an effective computational imaging representation. Equipped with the IP2CP representation, the matching pre- and post-disaster images are effectively encoded into one image that is then processed using deep learning approaches to determine the damage levels. Two scenarios of crucial importance for the practical use of DA in HADR applications are examined: pixel-wise semantic segmentation and patch-based contrastive learning-based global damage classification. Results achieved by IP2CP in both scenarios demonstrate promising performances, showing that our IP2CP-based methods within the deep learning framework can effectively achieve data and computational efficiency, which is of utmost importance for the DA in HADR applications.
Transparent Object Tracking with Enhanced Fusion Module
Sep 13, 2023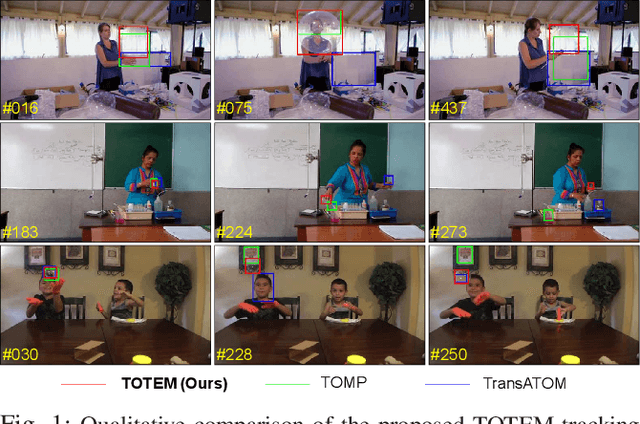



Abstract:Accurate tracking of transparent objects, such as glasses, plays a critical role in many robotic tasks such as robot-assisted living. Due to the adaptive and often reflective texture of such objects, traditional tracking algorithms that rely on general-purpose learned features suffer from reduced performance. Recent research has proposed to instill transparency awareness into existing general object trackers by fusing purpose-built features. However, with the existing fusion techniques, the addition of new features causes a change in the latent space making it impossible to incorporate transparency awareness on trackers with fixed latent spaces. For example, many of the current days transformer-based trackers are fully pre-trained and are sensitive to any latent space perturbations. In this paper, we present a new feature fusion technique that integrates transparency information into a fixed feature space, enabling its use in a broader range of trackers. Our proposed fusion module, composed of a transformer encoder and an MLP module, leverages key query-based transformations to embed the transparency information into the tracking pipeline. We also present a new two-step training strategy for our fusion module to effectively merge transparency features. We propose a new tracker architecture that uses our fusion techniques to achieve superior results for transparent object tracking. Our proposed method achieves competitive results with state-of-the-art trackers on TOTB, which is the largest transparent object tracking benchmark recently released. Our results and the implementation of code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/kalyan0510/TOTEM.
CCTV-Gun: Benchmarking Handgun Detection in CCTV Images
Apr 02, 2023

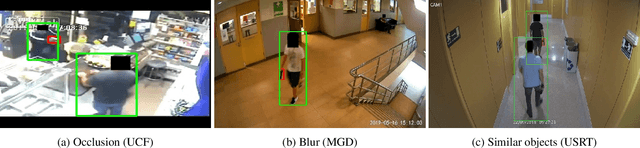

Abstract:Gun violence is a critical security problem, and it is imperative for the computer vision community to develop effective gun detection algorithms for real-world scenarios, particularly in Closed Circuit Television (CCTV) surveillance data. Despite significant progress in visual object detection, detecting guns in real-world CCTV images remains a challenging and under-explored task. Firearms, especially handguns, are typically very small in size, non-salient in appearance, and often severely occluded or indistinguishable from other small objects. Additionally, the lack of principled benchmarks and difficulty collecting relevant datasets further hinder algorithmic development. In this paper, we present a meticulously crafted and annotated benchmark, called \textbf{CCTV-Gun}, which addresses the challenges of detecting handguns in real-world CCTV images. Our contribution is three-fold. Firstly, we carefully select and analyze real-world CCTV images from three datasets, manually annotate handguns and their holders, and assign each image with relevant challenge factors such as blur and occlusion. Secondly, we propose a new cross-dataset evaluation protocol in addition to the standard intra-dataset protocol, which is vital for gun detection in practical settings. Finally, we comprehensively evaluate both classical and state-of-the-art object detection algorithms, providing an in-depth analysis of their generalizing abilities. The benchmark will facilitate further research and development on this topic and ultimately enhance security. Code, annotations, and trained models are available at https://github.com/srikarym/CCTV-Gun.
NIDA-CLIFGAN: Natural Infrastructure Damage Assessment through Efficient Classification Combining Contrastive Learning, Information Fusion and Generative Adversarial Networks
Oct 27, 2021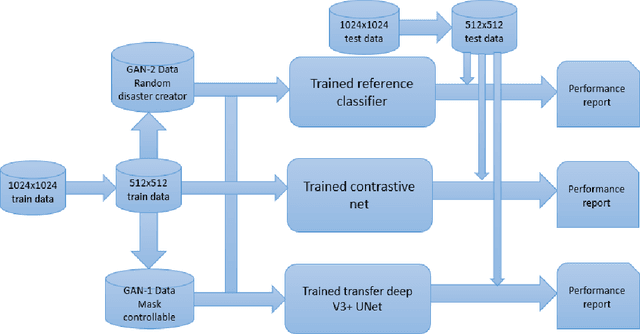
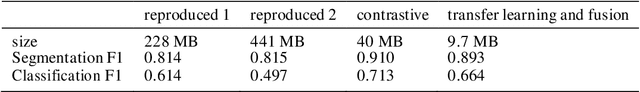
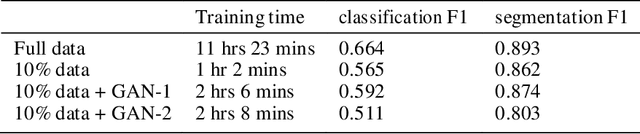
Abstract:During natural disasters, aircraft and satellites are used to survey the impacted regions. Usually human experts are needed to manually label the degrees of the building damage so that proper humanitarian assistance and disaster response (HADR) can be achieved, which is labor-intensive and time-consuming. Expecting human labeling of major disasters over a wide area gravely slows down the HADR efforts. It is thus of crucial interest to take advantage of the cutting-edge Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning techniques to speed up the natural infrastructure damage assessment process to achieve effective HADR. Accordingly, the paper demonstrates a systematic effort to achieve efficient building damage classification. First, two novel generative adversarial nets (GANs) are designed to augment data used to train the deep-learning-based classifier. Second, a contrastive learning based method using novel data structures is developed to achieve great performance. Third, by using information fusion, the classifier is effectively trained with very few training data samples for transfer learning. All the classifiers are small enough to be loaded in a smart phone or simple laptop for first responders. Based on the available overhead imagery dataset, results demonstrate data and computational efficiency with 10% of the collected data combined with a GAN reducing the time of computation from roughly half a day to about 1 hour with roughly similar classification performances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge