Guanyu Hu
Time-Varying Home Field Advantage in Football: Learning from a Non-Stationary Causal Process
Jun 13, 2025



Abstract:In sports analytics, home field advantage is a robust phenomenon where the home team wins more games than the away team. However, discovering the causal factors behind home field advantage presents unique challenges due to the non-stationary, time-varying environment of sports matches. In response, we propose a novel causal discovery method, DYnamic Non-stAtionary local M-estimatOrs (DYNAMO), to learn the time-varying causal structures of home field advantage. DYNAMO offers flexibility by integrating various loss functions, making it practical for learning linear and non-linear causal structures from a general class of non-stationary causal processes. By leveraging local information, we provide theoretical guarantees for the identifiability and estimation consistency of non-stationary causal structures without imposing additional assumptions. Simulation studies validate the efficacy of DYNAMO in recovering time-varying causal structures. We apply our method to high-resolution event data from the 2020-2021 and 2021-2022 English Premier League seasons, during which the former season had no audience presence. Our results reveal intriguing, time-varying, team-specific field advantages influenced by referee bias, which differ significantly with and without crowd support. Furthermore, the time-varying causal structures learned by our method improve goal prediction accuracy compared to existing methods.
Rethinking Affect Analysis: A Protocol for Ensuring Fairness and Consistency
Aug 07, 2024



Abstract:Evaluating affect analysis methods presents challenges due to inconsistencies in database partitioning and evaluation protocols, leading to unfair and biased results. Previous studies claim continuous performance improvements, but our findings challenge such assertions. Using these insights, we propose a unified protocol for database partitioning that ensures fairness and comparability. We provide detailed demographic annotations (in terms of race, gender and age), evaluation metrics, and a common framework for expression recognition, action unit detection and valence-arousal estimation. We also rerun the methods with the new protocol and introduce a new leaderboards to encourage future research in affect recognition with a fairer comparison. Our annotations, code, and pre-trained models are available on \hyperlink{https://github.com/dkollias/Fair-Consistent-Affect-Analysis}{Github}.
Robust Facial Reactions Generation: An Emotion-Aware Framework with Modality Compensation
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:The objective of the Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation (MAFRG) task is to produce contextually appropriate and diverse listener facial behavioural responses based on the multimodal behavioural data of the conversational partner (i.e., the speaker). Current methodologies typically assume continuous availability of speech and facial modality data, neglecting real-world scenarios where these data may be intermittently unavailable, which often results in model failures. Furthermore, despite utilising advanced deep learning models to extract information from the speaker's multimodal inputs, these models fail to adequately leverage the speaker's emotional context, which is vital for eliciting appropriate facial reactions from human listeners. To address these limitations, we propose an Emotion-aware Modality Compensatory (EMC) framework. This versatile solution can be seamlessly integrated into existing models, thereby preserving their advantages while significantly enhancing performance and robustness in scenarios with missing modalities. Our framework ensures resilience when faced with missing modality data through the Compensatory Modality Alignment (CMA) module. It also generates more appropriate emotion-aware reactions via the Emotion-aware Attention (EA) module, which incorporates the speaker's emotional information throughout the entire encoding and decoding process. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework improves the appropriateness metric FRCorr by an average of 57.2\% compared to the original model structure. In scenarios where speech modality data is missing, the performance of appropriate generation shows an improvement, and when facial data is missing, it only exhibits minimal degradation.
7th ABAW Competition: Multi-Task Learning and Compound Expression Recognition
Jul 04, 2024



Abstract:This paper describes the 7th Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-wild (ABAW) Competition, which is part of the respective Workshop held in conjunction with ECCV 2024. The 7th ABAW Competition addresses novel challenges in understanding human expressions and behaviors, crucial for the development of human-centered technologies. The Competition comprises of two sub-challenges: i) Multi-Task Learning (the goal is to learn at the same time, in a multi-task learning setting, to estimate two continuous affect dimensions, valence and arousal, to recognise between the mutually exclusive classes of the 7 basic expressions and 'other'), and to detect 12 Action Units); and ii) Compound Expression Recognition (the target is to recognise between the 7 mutually exclusive compound expression classes). s-Aff-Wild2, which is a static version of the A/V Aff-Wild2 database and contains annotations for valence-arousal, expressions and Action Units, is utilized for the purposes of the Multi-Task Learning Challenge; a part of C-EXPR-DB, which is an A/V in-the-wild database with compound expression annotations, is utilized for the purposes of the Compound Expression Recognition Challenge. In this paper, we introduce the two challenges, detailing their datasets and the protocols followed for each. We also outline the evaluation metrics, and highlight the baseline systems and their results. Additional information about the competition can be found at \url{https://affective-behavior-analysis-in-the-wild.github.io/7th}.
Bridging the Gap: Protocol Towards Fair and Consistent Affect Analysis
May 16, 2024Abstract:The increasing integration of machine learning algorithms in daily life underscores the critical need for fairness and equity in their deployment. As these technologies play a pivotal role in decision-making, addressing biases across diverse subpopulation groups, including age, gender, and race, becomes paramount. Automatic affect analysis, at the intersection of physiology, psychology, and machine learning, has seen significant development. However, existing databases and methodologies lack uniformity, leading to biased evaluations. This work addresses these issues by analyzing six affective databases, annotating demographic attributes, and proposing a common protocol for database partitioning. Emphasis is placed on fairness in evaluations. Extensive experiments with baseline and state-of-the-art methods demonstrate the impact of these changes, revealing the inadequacy of prior assessments. The findings underscore the importance of considering demographic attributes in affect analysis research and provide a foundation for more equitable methodologies. Our annotations, code and pre-trained models are available at: https://github.com/dkollias/Fair-Consistent-Affect-Analysis
The 6th Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-wild Competition
Mar 12, 2024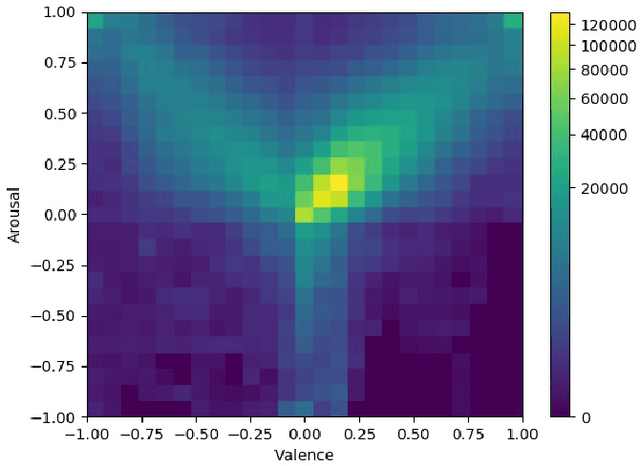
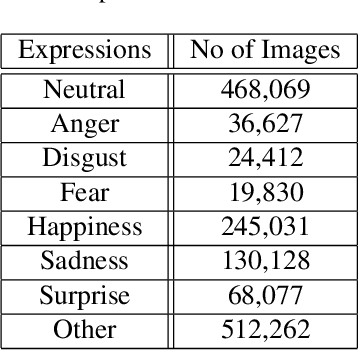
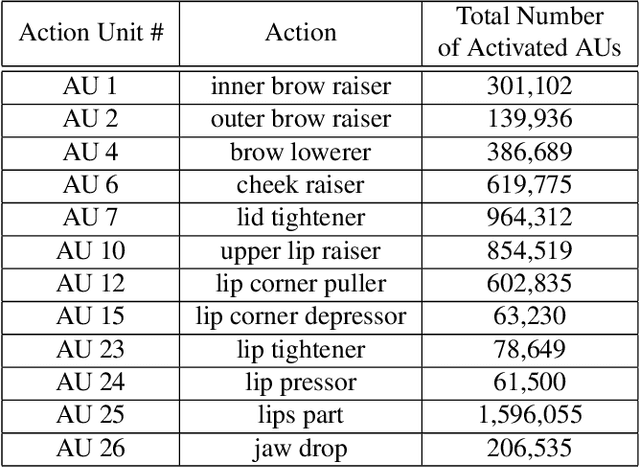
Abstract:This paper describes the 6th Affective Behavior Analysis in-the-wild (ABAW) Competition, which is part of the respective Workshop held in conjunction with IEEE CVPR 2024. The 6th ABAW Competition addresses contemporary challenges in understanding human emotions and behaviors, crucial for the development of human-centered technologies. In more detail, the Competition focuses on affect related benchmarking tasks and comprises of five sub-challenges: i) Valence-Arousal Estimation (the target is to estimate two continuous affect dimensions, valence and arousal), ii) Expression Recognition (the target is to recognise between the mutually exclusive classes of the 7 basic expressions and 'other'), iii) Action Unit Detection (the target is to detect 12 action units), iv) Compound Expression Recognition (the target is to recognise between the 7 mutually exclusive compound expression classes), and v) Emotional Mimicry Intensity Estimation (the target is to estimate six continuous emotion dimensions). In the paper, we present these Challenges, describe their respective datasets and challenge protocols (we outline the evaluation metrics) and present the baseline systems as well as their obtained performance. More information for the Competition can be found in: https://affective-behavior-analysis-in-the-wild.github.io/6th.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge