Jie Jia
Learning Occlusion-aware Decision-making from Agent Interaction via Active Perception
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:Occlusion-aware decision-making is essential in autonomous driving due to the high uncertainty of various occlusions. Recent occlusion-aware decision-making methods encounter issues such as high computational complexity, scenario scalability challenges, or reliance on limited expert data. Benefiting from automatically generating data by exploration randomization, we uncover that reinforcement learning (RL) may show promise in occlusion-aware decision-making. However, previous occlusion-aware RL faces challenges in expanding to various dynamic and static occlusion scenarios, low learning efficiency, and lack of predictive ability. To address these issues, we introduce Pad-AI, a self-reinforcing framework to learn occlusion-aware decision-making through active perception. Pad-AI utilizes vectorized representation to represent occluded environments efficiently and learns over the semantic motion primitives to focus on high-level active perception exploration. Furthermore, Pad-AI integrates prediction and RL within a unified framework to provide risk-aware learning and security guarantees. Our framework was tested in challenging scenarios under both dynamic and static occlusions and demonstrated efficient and general perception-aware exploration performance to other strong baselines in closed-loop evaluations.
O2V-Mapping: Online Open-Vocabulary Mapping with Neural Implicit Representation
Apr 10, 2024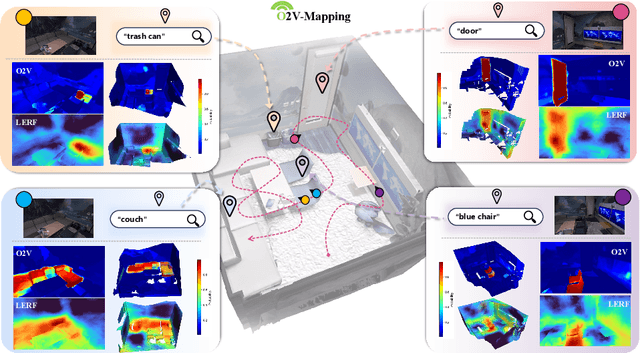
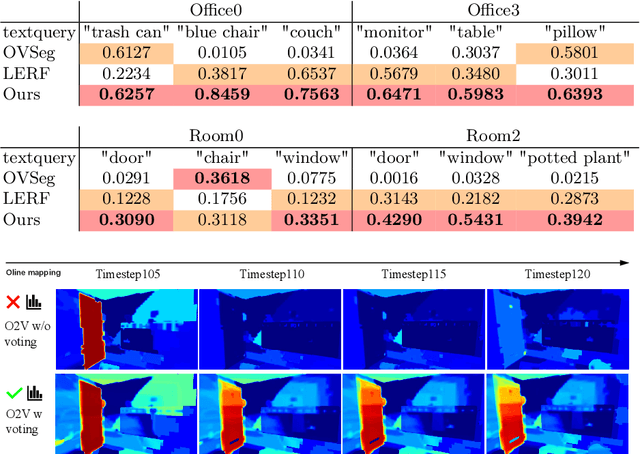
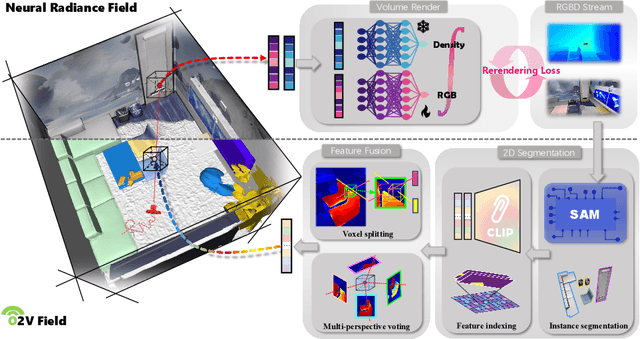
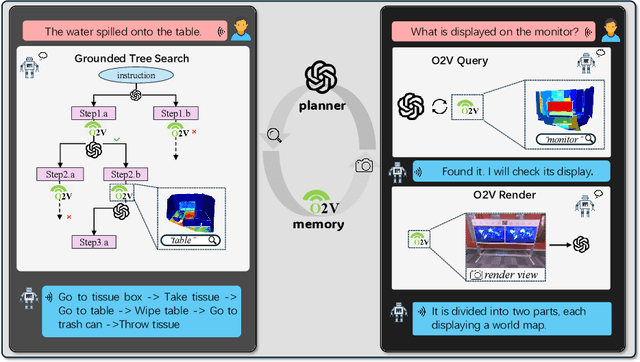
Abstract:Online construction of open-ended language scenes is crucial for robotic applications, where open-vocabulary interactive scene understanding is required. Recently, neural implicit representation has provided a promising direction for online interactive mapping. However, implementing open-vocabulary scene understanding capability into online neural implicit mapping still faces three challenges: lack of local scene updating ability, blurry spatial hierarchical semantic segmentation and difficulty in maintaining multi-view consistency. To this end, we proposed O2V-mapping, which utilizes voxel-based language and geometric features to create an open-vocabulary field, thus allowing for local updates during online training process. Additionally, we leverage a foundational model for image segmentation to extract language features on object-level entities, achieving clear segmentation boundaries and hierarchical semantic features. For the purpose of preserving consistency in 3D object properties across different viewpoints, we propose a spatial adaptive voxel adjustment mechanism and a multi-view weight selection method. Extensive experiments on open-vocabulary object localization and semantic segmentation demonstrate that O2V-mapping achieves online construction of language scenes while enhancing accuracy, outperforming the previous SOTA method.
Improving Visual Speech Enhancement Network by Learning Audio-visual Affinity with Multi-head Attention
Jun 30, 2022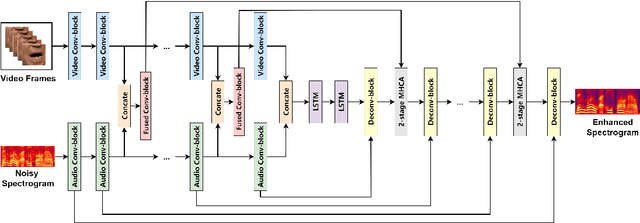
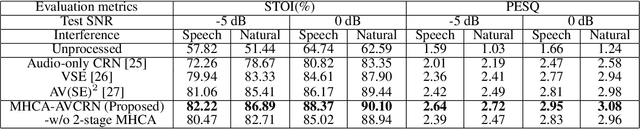
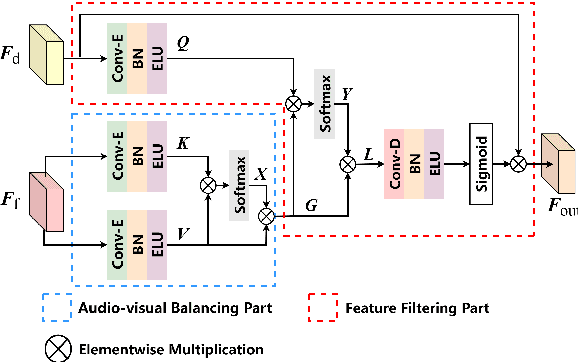
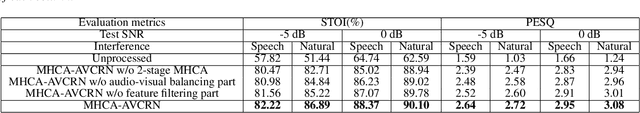
Abstract:Audio-visual speech enhancement system is regarded as one of promising solutions for isolating and enhancing speech of desired speaker. Typical methods focus on predicting clean speech spectrum via a naive convolution neural network based encoder-decoder architecture, and these methods a) are not adequate to use data fully, b) are unable to effectively balance audio-visual features. The proposed model alleviates these drawbacks by a) applying a model that fuses audio and visual features layer by layer in encoding phase, and that feeds fused audio-visual features to each corresponding decoder layer, and more importantly, b) introducing a 2-stage multi-head cross attention (MHCA) mechanism to infer audio-visual speech enhancement for balancing the fused audio-visual features and eliminating irrelevant features. This paper proposes attentional audio-visual multi-layer feature fusion model, in which MHCA units are applied to feature mapping at every layer of decoder. The proposed model demonstrates the superior performance of the network against the state-of-the-art models.
GLD-Net: Improving Monaural Speech Enhancement by Learning Global and Local Dependency Features with GLD Block
Jun 30, 2022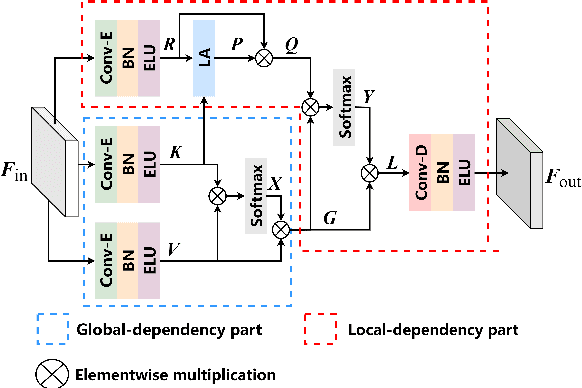
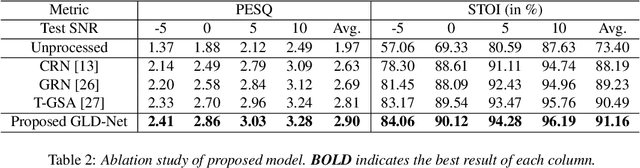
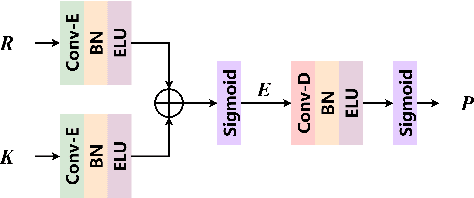
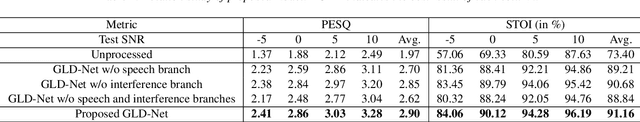
Abstract:For monaural speech enhancement, contextual information is important for accurate speech estimation. However, commonly used convolution neural networks (CNNs) are weak in capturing temporal contexts since they only build blocks that process one local neighborhood at a time. To address this problem, we learn from human auditory perception to introduce a two-stage trainable reasoning mechanism, referred as global-local dependency (GLD) block. GLD blocks capture long-term dependency of time-frequency bins both in global level and local level from the noisy spectrogram to help detecting correlations among speech part, noise part, and whole noisy input. What is more, we conduct a monaural speech enhancement network called GLD-Net, which adopts encoder-decoder architecture and consists of speech object branch, interference branch, and global noisy branch. The extracted speech feature at global-level and local-level are efficiently reasoned and aggregated in each of the branches. We compare the proposed GLD-Net with existing state-of-art methods on WSJ0 and DEMAND dataset. The results show that GLD-Net outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of PESQ and STOI.
Indoor Localization Using Smartphone Magnetic with Multi-Scale TCN and LSTM
Sep 24, 2021



Abstract:A novel multi-scale temporal convolutional network (TCN) and long short-term memory network (LSTM) based magnetic localization approach is proposed. To enhance the discernibility of geomagnetic signals, the time-series preprocessing approach is constructed at first. Next, the TCN is invoked to expand the feature dimensions on the basis of keeping the time-series characteristics of LSTM model. Then, a multi-scale time-series layer is constructed with multiple TCNs of different dilation factors to address the problem of inconsistent time-series speed between localization model and mobile users. A stacking framework of multi-scale TCN and LSTM is eventually proposed for indoor magnetic localization. Experiment results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in indoor localization.
VSEGAN: Visual Speech Enhancement Generative Adversarial Network
Feb 04, 2021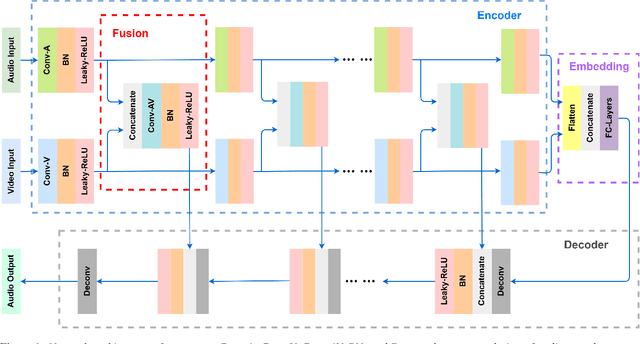
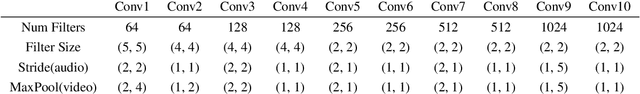
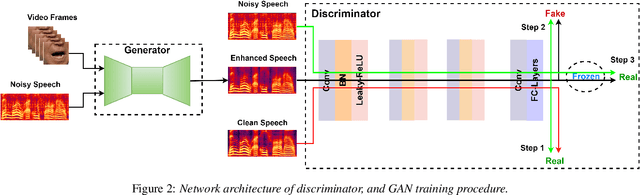
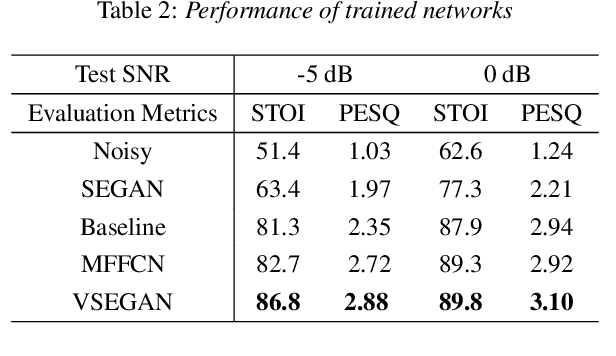
Abstract:Speech enhancement is an essential task of improving speech quality in noise scenario. Several state-of-the-art approaches have introduced visual information for speech enhancement,since the visual aspect of speech is essentially unaffected by acoustic environment. This paper proposes a novel frameworkthat involves visual information for speech enhancement, by in-corporating a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). In par-ticular, the proposed visual speech enhancement GAN consistof two networks trained in adversarial manner, i) a generator that adopts multi-layer feature fusion convolution network to enhance input noisy speech, and ii) a discriminator that attemptsto minimize the discrepancy between the distributions of the clean speech signal and enhanced speech signal. Experiment re-sults demonstrated superior performance of the proposed modelagainst several state-of-the-art
AMFFCN: Attentional Multi-layer Feature Fusion Convolution Network for Audio-visual Speech Enhancement
Feb 04, 2021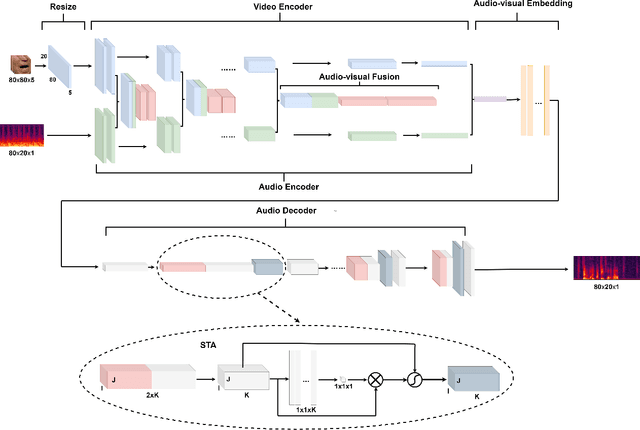
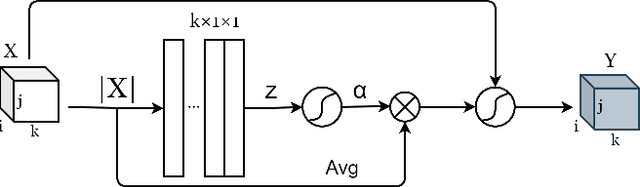
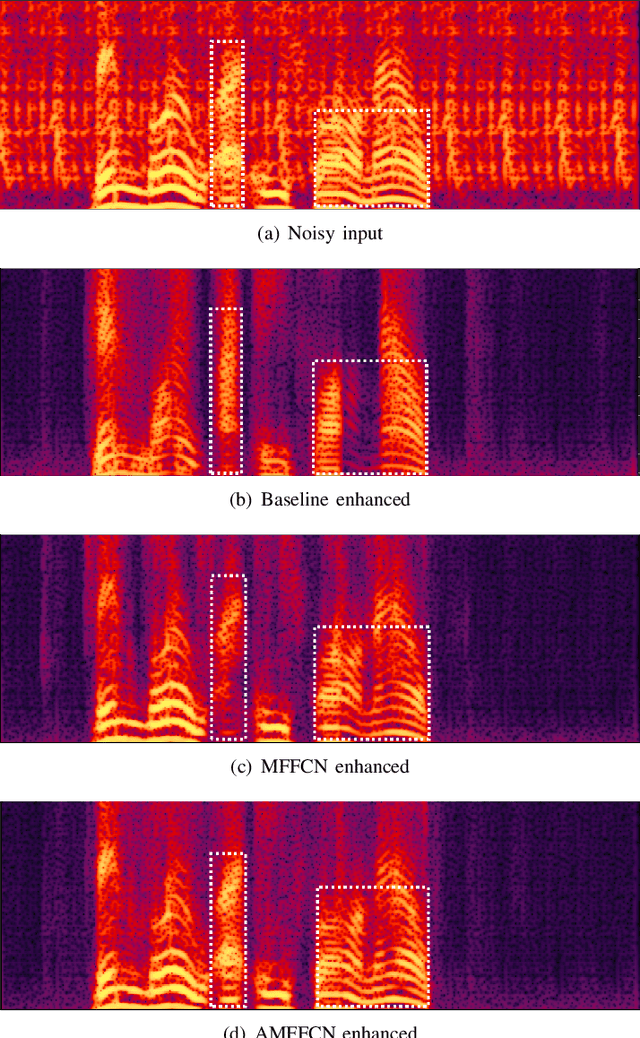
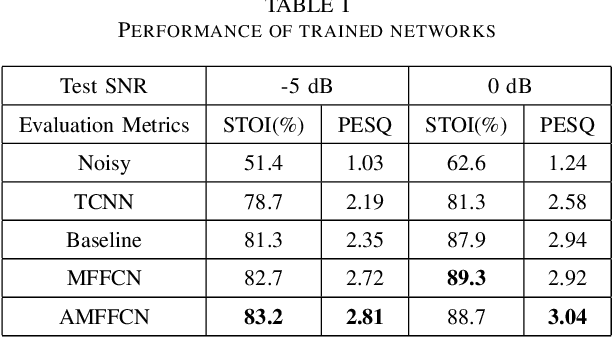
Abstract:Audio-visual speech enhancement system is regarded to be one of promising solutions for isolating and enhancing speech of desired speaker. Conventional methods focus on predicting clean speech spectrum via a naive convolution neural network based encoder-decoder architecture, and these methods a) not adequate to use data fully and effectively, b) cannot process features selectively. The proposed model addresses these drawbacks, by a) applying a model that fuses audio and visual features layer by layer in encoding phase, and that feeds fused audio-visual features to each corresponding decoder layer, and more importantly, b) introducing soft threshold attention into the model to select the informative modality softly. This paper proposes attentional audio-visual multi-layer feature fusion model, in which soft threshold attention unit are applied on feature mapping at every layer of decoder. The proposed model demonstrates the superior performance of the network against the state-of-the-art models.
MFFCN: Multi-layer Feature Fusion Convolution Network for Audio-visual Speech Enhancement
Feb 04, 2021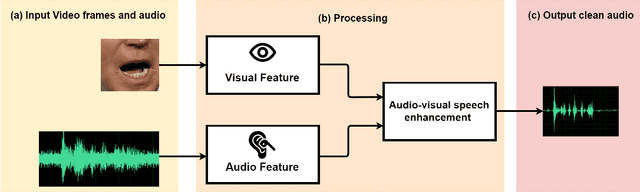
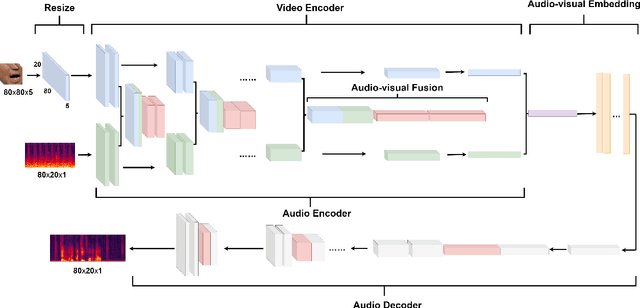
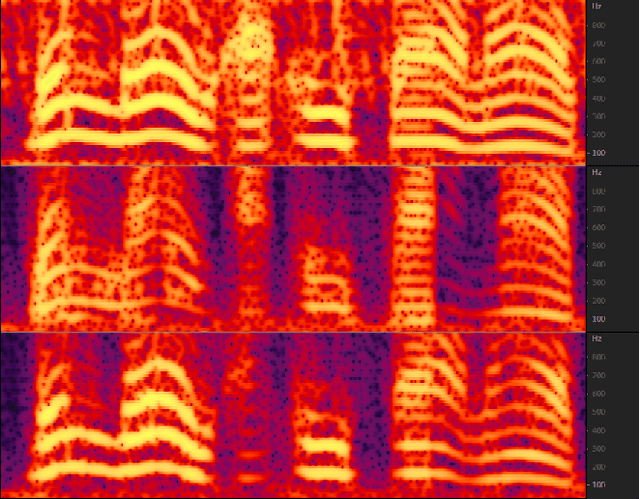
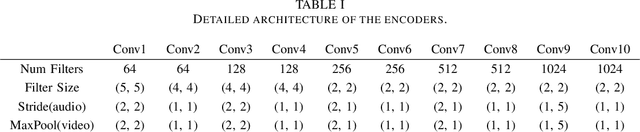
Abstract:The purpose of speech enhancement is to extract target speech signal from a mixture of sounds generated from several sources. Speech enhancement can potentially benefit from the visual information from the target speaker, such as lip move-ment and facial expressions, because the visual aspect of speech isessentially unaffected by acoustic environment. In order to fuse audio and visual information, an audio-visual fusion strategy is proposed, which goes beyond simple feature concatenation and learns to automatically align the two modalities, leading to more powerful representation which increase intelligibility in noisy conditions. The proposed model fuses audio-visual featureslayer by layer, and feed these audio-visual features to each corresponding decoding layer. Experiment results show relative improvement from 6% to 24% on test sets over the audio modalityalone, depending on audio noise level. Moreover, there is a significant increase of PESQ from 1.21 to 2.06 in our -15 dB SNR experiment.
Generative Model for Heterogeneous Inference
Apr 26, 2018



Abstract:Generative models (GMs) such as Generative Adversary Network (GAN) and Variational Auto-Encoder (VAE) have thrived these years and achieved high quality results in generating new samples. Especially in Computer Vision, GMs have been used in image inpainting, denoising and completion, which can be treated as the inference from observed pixels to corrupted pixels. However, images are hierarchically structured which are quite different from many real-world inference scenarios with non-hierarchical features. These inference scenarios contain heterogeneous stochastic variables and irregular mutual dependences. Traditionally they are modeled by Bayesian Network (BN). However, the learning and inference of BN model are NP-hard thus the number of stochastic variables in BN is highly constrained. In this paper, we adapt typical GMs to enable heterogeneous learning and inference in polynomial time.We also propose an extended autoregressive (EAR) model and an EAR with adversary loss (EARA) model and give theoretical results on their effectiveness. Experiments on several BN datasets show that our proposed EAR model achieves the best performance in most cases compared to other GMs. Except for black box analysis, we've also done a serial of experiments on Markov border inference of GMs for white box analysis and give theoretical results.
Using Deep Neural Network Approximate Bayesian Network
Jan 11, 2018



Abstract:We present a new method to approximate posterior probabilities of Bayesian Network using Deep Neural Network. Experiment results on several public Bayesian Network datasets shows that Deep Neural Network is capable of learning joint probability distri- bution of Bayesian Network by learning from a few observation and posterior probability distribution pairs with high accuracy. Compared with traditional approximate method likelihood weighting sampling algorithm, our method is much faster and gains higher accuracy in medium sized Bayesian Network. Another advantage of our method is that our method can be parallelled much easier in GPU without extra effort. We also ex- plored the connection between the accuracy of our model and the number of training examples. The result shows that our model saturate as the number of training examples grow and we don't need many training examples to get reasonably good result. Another contribution of our work is that we have shown discriminative model like Deep Neural Network can approximate generative model like Bayesian Network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge