Jiaxiang Shang
Animus3D: Text-driven 3D Animation via Motion Score Distillation
Dec 14, 2025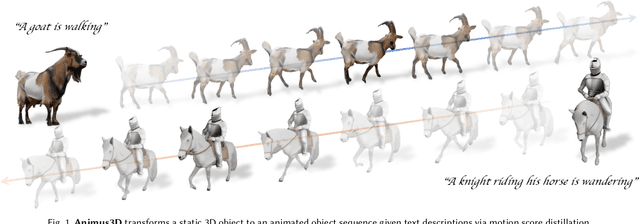
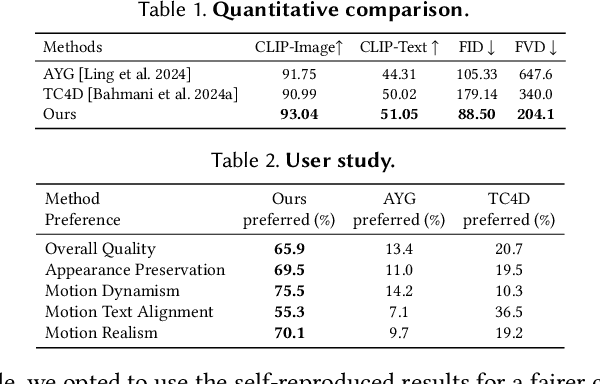
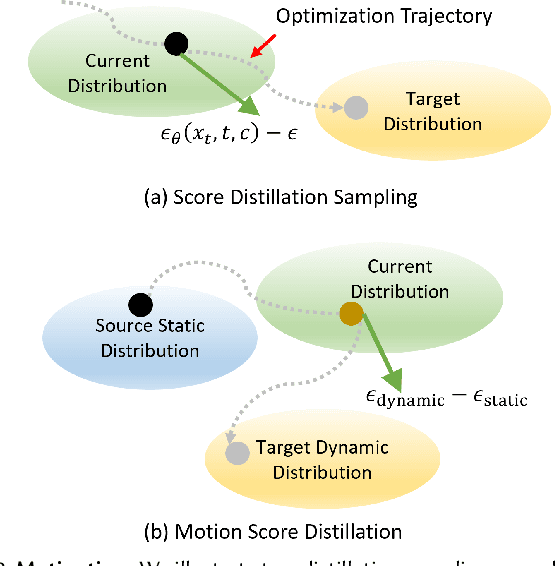
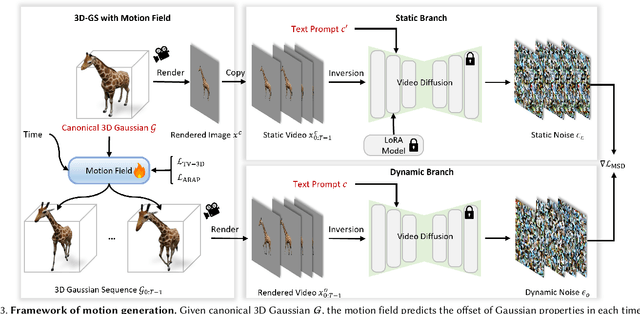
Abstract:We present Animus3D, a text-driven 3D animation framework that generates motion field given a static 3D asset and text prompt. Previous methods mostly leverage the vanilla Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) objective to distill motion from pretrained text-to-video diffusion, leading to animations with minimal movement or noticeable jitter. To address this, our approach introduces a novel SDS alternative, Motion Score Distillation (MSD). Specifically, we introduce a LoRA-enhanced video diffusion model that defines a static source distribution rather than pure noise as in SDS, while another inversion-based noise estimation technique ensures appearance preservation when guiding motion. To further improve motion fidelity, we incorporate explicit temporal and spatial regularization terms that mitigate geometric distortions across time and space. Additionally, we propose a motion refinement module to upscale the temporal resolution and enhance fine-grained details, overcoming the fixed-resolution constraints of the underlying video model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Animus3D successfully animates static 3D assets from diverse text prompts, generating significantly more substantial and detailed motion than state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining high visual integrity. Code will be released at https://qiisun.github.io/animus3d_page.
Sketch2Human: Deep Human Generation with Disentangled Geometry and Appearance Control
Apr 24, 2024Abstract:Geometry- and appearance-controlled full-body human image generation is an interesting but challenging task. Existing solutions are either unconditional or dependent on coarse conditions (e.g., pose, text), thus lacking explicit geometry and appearance control of body and garment. Sketching offers such editing ability and has been adopted in various sketch-based face generation and editing solutions. However, directly adapting sketch-based face generation to full-body generation often fails to produce high-fidelity and diverse results due to the high complexity and diversity in the pose, body shape, and garment shape and texture. Recent geometrically controllable diffusion-based methods mainly rely on prompts to generate appearance and it is hard to balance the realism and the faithfulness of their results to the sketch when the input is coarse. This work presents Sketch2Human, the first system for controllable full-body human image generation guided by a semantic sketch (for geometry control) and a reference image (for appearance control). Our solution is based on the latent space of StyleGAN-Human with inverted geometry and appearance latent codes as input. Specifically, we present a sketch encoder trained with a large synthetic dataset sampled from StyleGAN-Human's latent space and directly supervised by sketches rather than real images. Considering the entangled information of partial geometry and texture in StyleGAN-Human and the absence of disentangled datasets, we design a novel training scheme that creates geometry-preserved and appearance-transferred training data to tune a generator to achieve disentangled geometry and appearance control. Although our method is trained with synthetic data, it can handle hand-drawn sketches as well. Qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate the superior performance of our method to state-of-the-art methods.
VMNet: Voxel-Mesh Network for Geodesic-Aware 3D Semantic Segmentation
Jul 29, 2021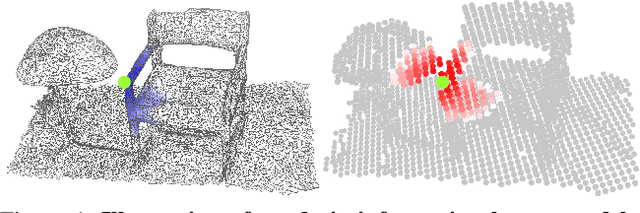
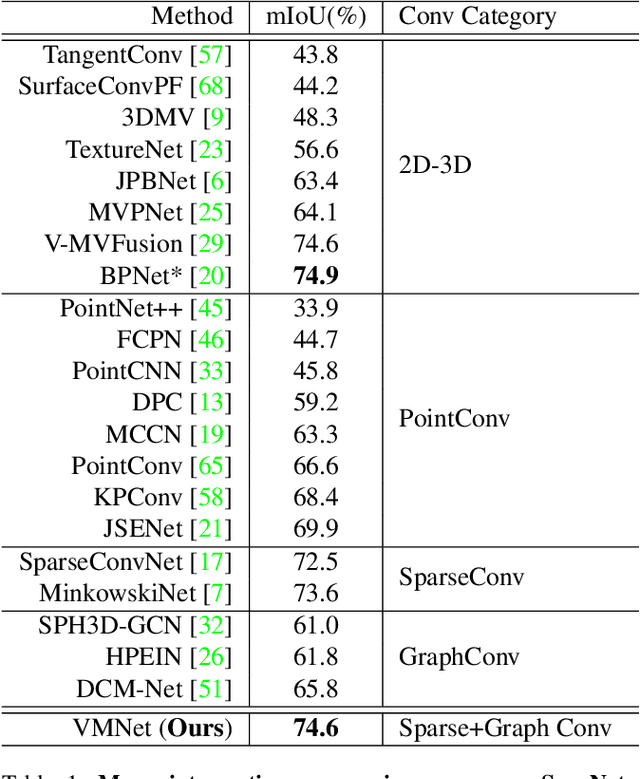
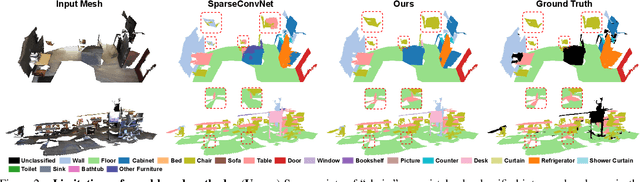
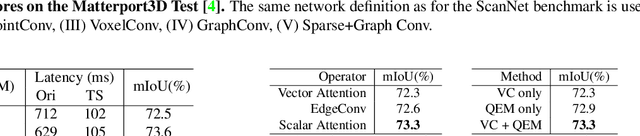
Abstract:In recent years, sparse voxel-based methods have become the state-of-the-arts for 3D semantic segmentation of indoor scenes, thanks to the powerful 3D CNNs. Nevertheless, being oblivious to the underlying geometry, voxel-based methods suffer from ambiguous features on spatially close objects and struggle with handling complex and irregular geometries due to the lack of geodesic information. In view of this, we present Voxel-Mesh Network (VMNet), a novel 3D deep architecture that operates on the voxel and mesh representations leveraging both the Euclidean and geodesic information. Intuitively, the Euclidean information extracted from voxels can offer contextual cues representing interactions between nearby objects, while the geodesic information extracted from meshes can help separate objects that are spatially close but have disconnected surfaces. To incorporate such information from the two domains, we design an intra-domain attentive module for effective feature aggregation and an inter-domain attentive module for adaptive feature fusion. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of VMNet: specifically, on the challenging ScanNet dataset for large-scale segmentation of indoor scenes, it outperforms the state-of-the-art SparseConvNet and MinkowskiNet (74.6% vs 72.5% and 73.6% in mIoU) with a simpler network structure (17M vs 30M and 38M parameters). Code release: https://github.com/hzykent/VMNet
Learning Discriminative Feature with CRF for Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation
Aug 04, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel network, called discriminative feature network (DFNet), to address the unsupervised video object segmentation task. To capture the inherent correlation among video frames, we learn discriminative features (D-features) from the input images that reveal feature distribution from a global perspective. The D-features are then used to establish correspondence with all features of test image under conditional random field (CRF) formulation, which is leveraged to enforce consistency between pixels. The experiments verify that DFNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods by a large margin with a mean IoU score of 83.4% and ranks first on the DAVIS-2016 leaderboard while using much fewer parameters and achieving much more efficient performance in the inference phase. We further evaluate DFNet on the FBMS dataset and the video saliency dataset ViSal, reaching a new state-of-the-art. To further demonstrate the generalizability of our framework, DFNet is also applied to the image object co-segmentation task. We perform experiments on a challenging dataset PASCAL-VOC and observe the superiority of DFNet. The thorough experiments verify that DFNet is able to capture and mine the underlying relations of images and discover the common foreground objects.
Self-Supervised Monocular 3D Face Reconstruction by Occlusion-Aware Multi-view Geometry Consistency
Jul 24, 2020



Abstract:Recent learning-based approaches, in which models are trained by single-view images have shown promising results for monocular 3D face reconstruction, but they suffer from the ill-posed face pose and depth ambiguity issue. In contrast to previous works that only enforce 2D feature constraints, we propose a self-supervised training architecture by leveraging the multi-view geometry consistency, which provides reliable constraints on face pose and depth estimation. We first propose an occlusion-aware view synthesis method to apply multi-view geometry consistency to self-supervised learning. Then we design three novel loss functions for multi-view consistency, including the pixel consistency loss, the depth consistency loss, and the facial landmark-based epipolar loss. Our method is accurate and robust, especially under large variations of expressions, poses, and illumination conditions. Comprehensive experiments on the face alignment and 3D face reconstruction benchmarks have demonstrated superiority over state-of-the-art methods. Our code and model are released in https://github.com/jiaxiangshang/MGCNet.
Joint Semantic Segmentation and Boundary Detection using Iterative Pyramid Contexts
Apr 16, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we present a joint multi-task learning framework for semantic segmentation and boundary detection. The critical component in the framework is the iterative pyramid context module (PCM), which couples two tasks and stores the shared latent semantics to interact between the two tasks. For semantic boundary detection, we propose the novel spatial gradient fusion to suppress nonsemantic edges. As semantic boundary detection is the dual task of semantic segmentation, we introduce a loss function with boundary consistency constraint to improve the boundary pixel accuracy for semantic segmentation. Our extensive experiments demonstrate superior performance over state-of-the-art works, not only in semantic segmentation but also in semantic boundary detection. In particular, a mean IoU score of 81:8% on Cityscapes test set is achieved without using coarse data or any external data for semantic segmentation. For semantic boundary detection, we improve over previous state-of-the-art works by 9.9% in terms of AP and 6:8% in terms of MF(ODS).
Compositional Human Pose Regression
Aug 02, 2017



Abstract:Regression based methods are not performing as well as detection based methods for human pose estimation. A central problem is that the structural information in the pose is not well exploited in the previous regression methods. In this work, we propose a structure-aware regression approach. It adopts a reparameterized pose representation using bones instead of joints. It exploits the joint connection structure to define a compositional loss function that encodes the long range interactions in the pose. It is simple, effective, and general for both 2D and 3D pose estimation in a unified setting. Comprehensive evaluation validates the effectiveness of our approach. It significantly advances the state-of-the-art on Human3.6M and is competitive with state-of-the-art results on MPII.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge