Tian Fang
Sharp Monocular View Synthesis in Less Than a Second
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:We present SHARP, an approach to photorealistic view synthesis from a single image. Given a single photograph, SHARP regresses the parameters of a 3D Gaussian representation of the depicted scene. This is done in less than a second on a standard GPU via a single feedforward pass through a neural network. The 3D Gaussian representation produced by SHARP can then be rendered in real time, yielding high-resolution photorealistic images for nearby views. The representation is metric, with absolute scale, supporting metric camera movements. Experimental results demonstrate that SHARP delivers robust zero-shot generalization across datasets. It sets a new state of the art on multiple datasets, reducing LPIPS by 25-34% and DISTS by 21-43% versus the best prior model, while lowering the synthesis time by three orders of magnitude. Code and weights are provided at https://github.com/apple/ml-sharp
Matrix3D: Large Photogrammetry Model All-in-One
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:We present Matrix3D, a unified model that performs several photogrammetry subtasks, including pose estimation, depth prediction, and novel view synthesis using just the same model. Matrix3D utilizes a multi-modal diffusion transformer (DiT) to integrate transformations across several modalities, such as images, camera parameters, and depth maps. The key to Matrix3D's large-scale multi-modal training lies in the incorporation of a mask learning strategy. This enables full-modality model training even with partially complete data, such as bi-modality data of image-pose and image-depth pairs, thus significantly increases the pool of available training data. Matrix3D demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in pose estimation and novel view synthesis tasks. Additionally, it offers fine-grained control through multi-round interactions, making it an innovative tool for 3D content creation. Project page: https://nju-3dv.github.io/projects/matrix3d.
Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of YOLOv11, YOLOv10, YOLOv9, YOLOv8 and YOLOv5 on Object Detection of Power Equipment
Nov 28, 2024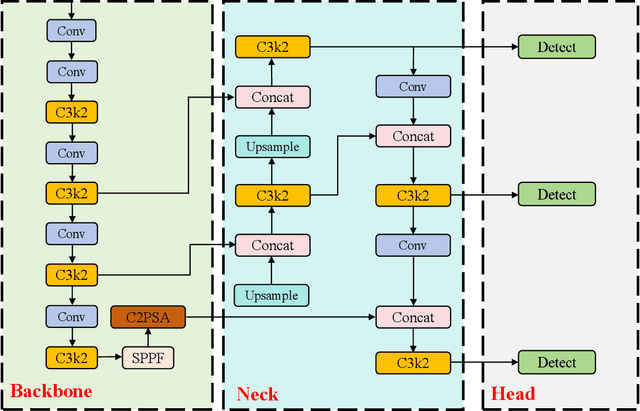


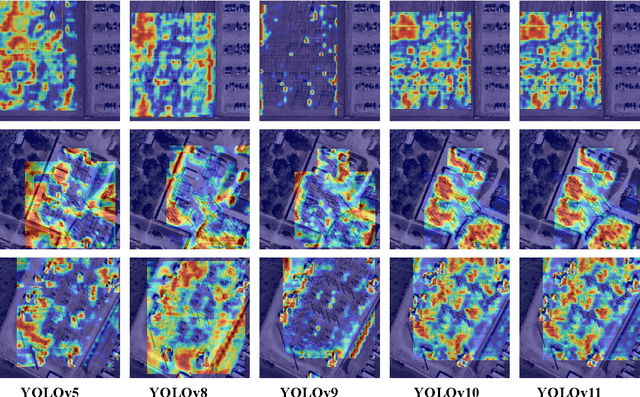
Abstract:With the rapid development of global industrial production, the demand for reliability in power equipment has been continuously increasing. Ensuring the stability of power system operations requires accurate methods to detect potential faults in power equipment, thereby guaranteeing the normal supply of electrical energy. In this article, the performance of YOLOv5, YOLOv8, YOLOv9, YOLOv10, and the state-of-the-art YOLOv11 methods was comprehensively evaluated for power equipment object detection. Experimental results demonstrate that the mean average precision (mAP) on a public dataset for power equipment was 54.4%, 55.5%, 43.8%, 48.0%, and 57.2%, respectively, with the YOLOv11 achieving the highest detection performance. Moreover, the YOLOv11 outperformed other methods in terms of recall rate and exhibited superior performance in reducing false detections. In conclusion, the findings indicate that the YOLOv11 model provides a reliable and effective solution for power equipment object detection, representing a promising approach to enhancing the operational reliability of power systems.
Affine-based Deformable Attention and Selective Fusion for Semi-dense Matching
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Identifying robust and accurate correspondences across images is a fundamental problem in computer vision that enables various downstream tasks. Recent semi-dense matching methods emphasize the effectiveness of fusing relevant cross-view information through Transformer. In this paper, we propose several improvements upon this paradigm. Firstly, we introduce affine-based local attention to model cross-view deformations. Secondly, we present selective fusion to merge local and global messages from cross attention. Apart from network structure, we also identify the importance of enforcing spatial smoothness in loss design, which has been omitted by previous works. Based on these augmentations, our network demonstrate strong matching capacity under different settings. The full version of our network achieves state-of-the-art performance among semi-dense matching methods at a similar cost to LoFTR, while the slim version reaches LoFTR baseline's performance with only 15% computation cost and 18% parameters.
Direct2.5: Diverse Text-to-3D Generation via Multi-view 2.5D Diffusion
Nov 27, 2023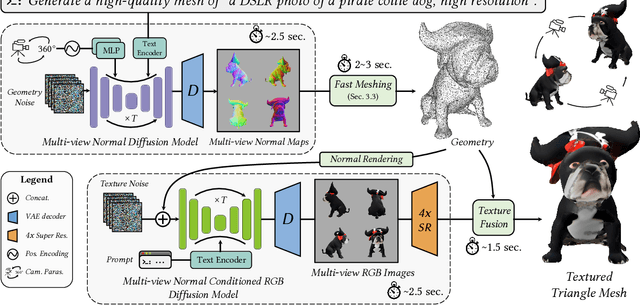


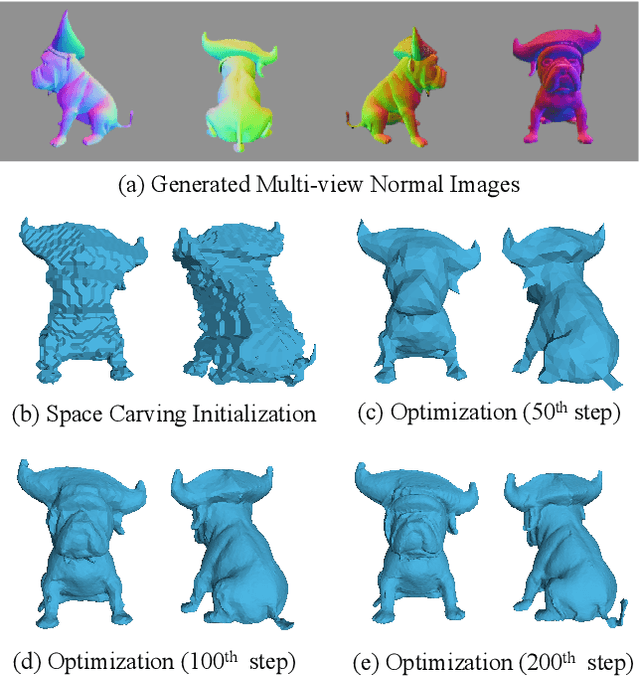
Abstract:Recent advances in generative AI have unveiled significant potential for the creation of 3D content. However, current methods either apply a pre-trained 2D diffusion model with the time-consuming score distillation sampling (SDS), or a direct 3D diffusion model trained on limited 3D data losing generation diversity. In this work, we approach the problem by employing a multi-view 2.5D diffusion fine-tuned from a pre-trained 2D diffusion model. The multi-view 2.5D diffusion directly models the structural distribution of 3D data, while still maintaining the strong generalization ability of the original 2D diffusion model, filling the gap between 2D diffusion-based and direct 3D diffusion-based methods for 3D content generation. During inference, multi-view normal maps are generated using the 2.5D diffusion, and a novel differentiable rasterization scheme is introduced to fuse the almost consistent multi-view normal maps into a consistent 3D model. We further design a normal-conditioned multi-view image generation module for fast appearance generation given the 3D geometry. Our method is a one-pass diffusion process and does not require any SDS optimization as post-processing. We demonstrate through extensive experiments that, our direct 2.5D generation with the specially-designed fusion scheme can achieve diverse, mode-seeking-free, and high-fidelity 3D content generation in only 10 seconds. Project page: https://nju-3dv.github.io/projects/direct25.
JointNet: Extending Text-to-Image Diffusion for Dense Distribution Modeling
Oct 10, 2023


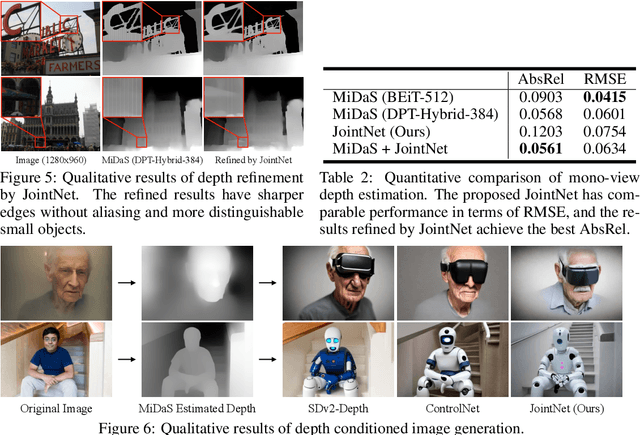
Abstract:We introduce JointNet, a novel neural network architecture for modeling the joint distribution of images and an additional dense modality (e.g., depth maps). JointNet is extended from a pre-trained text-to-image diffusion model, where a copy of the original network is created for the new dense modality branch and is densely connected with the RGB branch. The RGB branch is locked during network fine-tuning, which enables efficient learning of the new modality distribution while maintaining the strong generalization ability of the large-scale pre-trained diffusion model. We demonstrate the effectiveness of JointNet by using RGBD diffusion as an example and through extensive experiments, showcasing its applicability in a variety of applications, including joint RGBD generation, dense depth prediction, depth-conditioned image generation, and coherent tile-based 3D panorama generation.
NeILF++: Inter-Reflectable Light Fields for Geometry and Material Estimation
Mar 30, 2023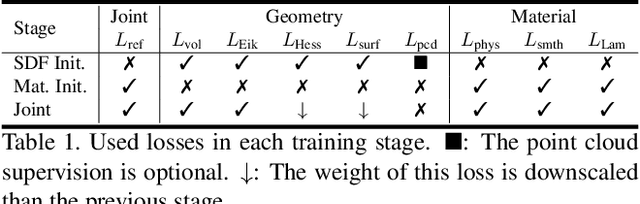
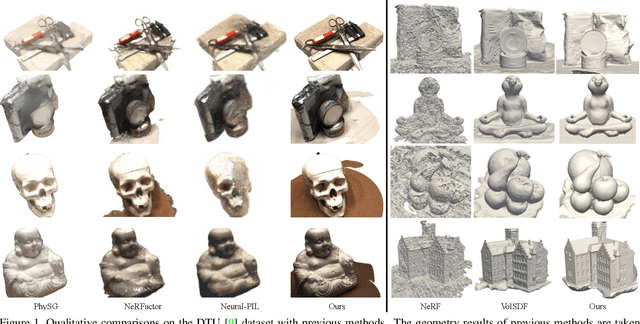
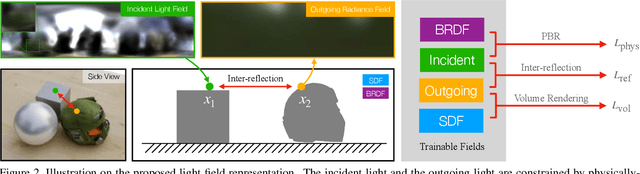
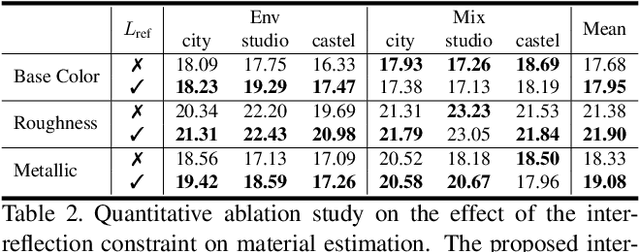
Abstract:We present a novel differentiable rendering framework for joint geometry, material, and lighting estimation from multi-view images. In contrast to previous methods which assume a simplified environment map or co-located flashlights, in this work, we formulate the lighting of a static scene as one neural incident light field (NeILF) and one outgoing neural radiance field (NeRF). The key insight of the proposed method is the union of the incident and outgoing light fields through physically-based rendering and inter-reflections between surfaces, making it possible to disentangle the scene geometry, material, and lighting from image observations in a physically-based manner. The proposed incident light and inter-reflection framework can be easily applied to other NeRF systems. We show that our method can not only decompose the outgoing radiance into incident lights and surface materials, but also serve as a surface refinement module that further improves the reconstruction detail of the neural surface. We demonstrate on several datasets that the proposed method is able to achieve state-of-the-art results in terms of geometry reconstruction quality, material estimation accuracy, and the fidelity of novel view rendering.
ASpanFormer: Detector-Free Image Matching with Adaptive Span Transformer
Aug 30, 2022
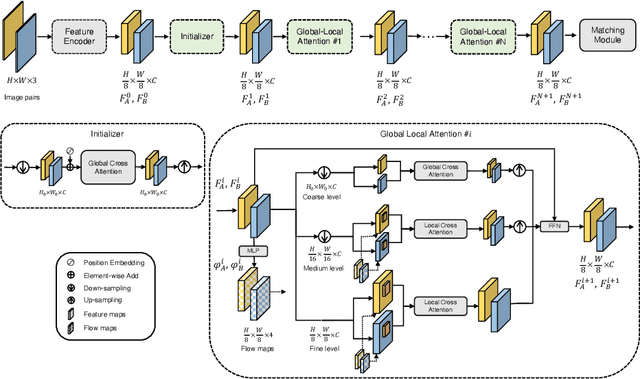
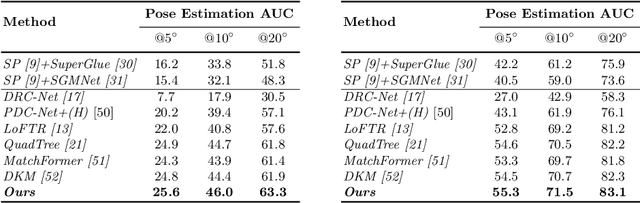
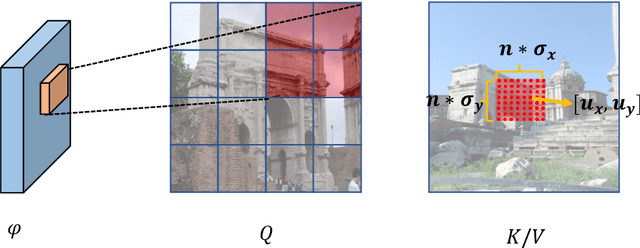
Abstract:Generating robust and reliable correspondences across images is a fundamental task for a diversity of applications. To capture context at both global and local granularity, we propose ASpanFormer, a Transformer-based detector-free matcher that is built on hierarchical attention structure, adopting a novel attention operation which is capable of adjusting attention span in a self-adaptive manner. To achieve this goal, first, flow maps are regressed in each cross attention phase to locate the center of search region. Next, a sampling grid is generated around the center, whose size, instead of being empirically configured as fixed, is adaptively computed from a pixel uncertainty estimated along with the flow map. Finally, attention is computed across two images within derived regions, referred to as attention span. By these means, we are able to not only maintain long-range dependencies, but also enable fine-grained attention among pixels of high relevance that compensates essential locality and piece-wise smoothness in matching tasks. State-of-the-art accuracy on a wide range of evaluation benchmarks validates the strong matching capability of our method.
Critical Regularizations for Neural Surface Reconstruction in the Wild
Jun 07, 2022
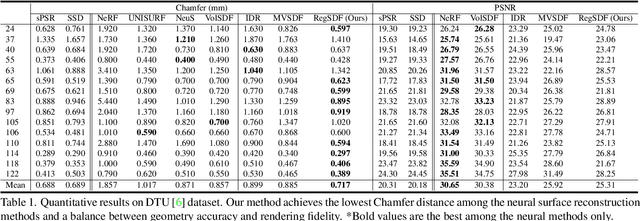
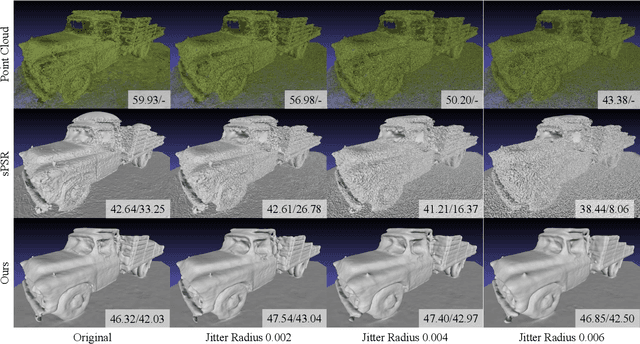
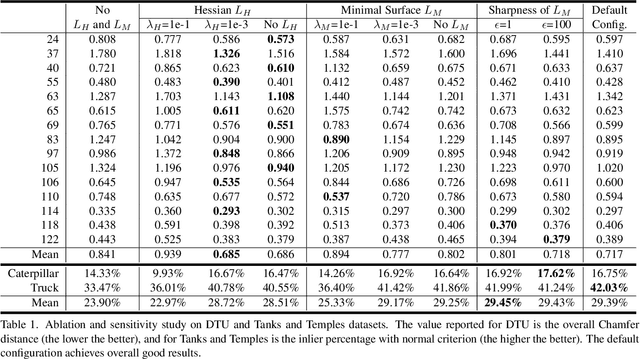
Abstract:Neural implicit functions have recently shown promising results on surface reconstructions from multiple views. However, current methods still suffer from excessive time complexity and poor robustness when reconstructing unbounded or complex scenes. In this paper, we present RegSDF, which shows that proper point cloud supervisions and geometry regularizations are sufficient to produce high-quality and robust reconstruction results. Specifically, RegSDF takes an additional oriented point cloud as input, and optimizes a signed distance field and a surface light field within a differentiable rendering framework. We also introduce the two critical regularizations for this optimization. The first one is the Hessian regularization that smoothly diffuses the signed distance values to the entire distance field given noisy and incomplete input. And the second one is the minimal surface regularization that compactly interpolates and extrapolates the missing geometry. Extensive experiments are conducted on DTU, BlendedMVS, and Tanks and Temples datasets. Compared with recent neural surface reconstruction approaches, RegSDF is able to reconstruct surfaces with fine details even for open scenes with complex topologies and unstructured camera trajectories.
NeILF: Neural Incident Light Field for Physically-based Material Estimation
Mar 18, 2022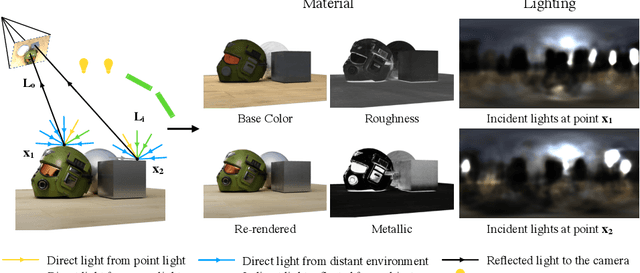
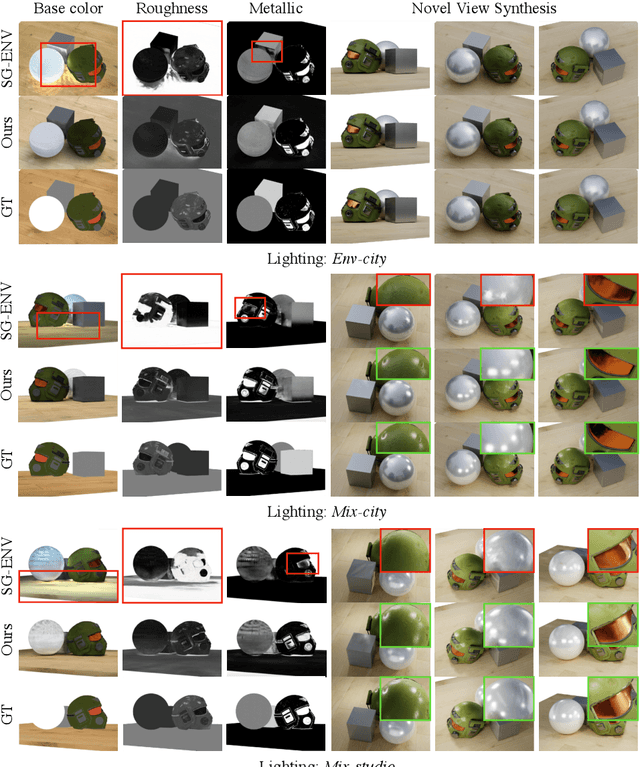
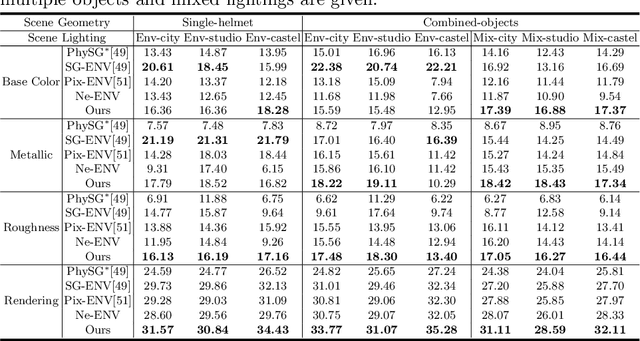
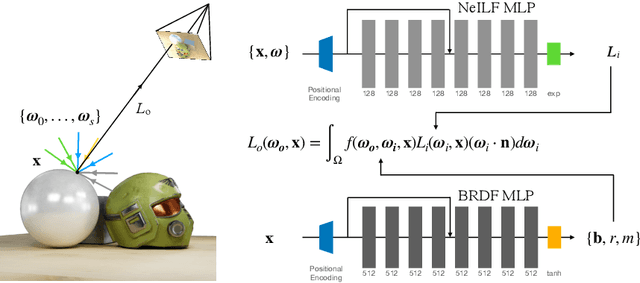

Abstract:We present a differentiable rendering framework for material and lighting estimation from multi-view images and a reconstructed geometry. In the framework, we represent scene lightings as the Neural Incident Light Field (NeILF) and material properties as the surface BRDF modelled by multi-layer perceptrons. Compared with recent approaches that approximate scene lightings as the 2D environment map, NeILF is a fully 5D light field that is capable of modelling illuminations of any static scenes. In addition, occlusions and indirect lights can be handled naturally by the NeILF representation without requiring multiple bounces of ray tracing, making it possible to estimate material properties even for scenes with complex lightings and geometries. We also propose a smoothness regularization and a Lambertian assumption to reduce the material-lighting ambiguity during the optimization. Our method strictly follows the physically-based rendering equation, and jointly optimizes material and lighting through the differentiable rendering process. We have intensively evaluated the proposed method on our in-house synthetic dataset, the DTU MVS dataset, and real-world BlendedMVS scenes. Our method is able to outperform previous methods by a significant margin in terms of novel view rendering quality, setting a new state-of-the-art for image-based material and lighting estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge