Jiahao Bu
Tsinghua University
Hunyuan-TurboS: Advancing Large Language Models through Mamba-Transformer Synergy and Adaptive Chain-of-Thought
May 21, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) rapidly advance, we introduce Hunyuan-TurboS, a novel large hybrid Transformer-Mamba Mixture of Experts (MoE) model. It synergistically combines Mamba's long-sequence processing efficiency with Transformer's superior contextual understanding. Hunyuan-TurboS features an adaptive long-short chain-of-thought (CoT) mechanism, dynamically switching between rapid responses for simple queries and deep "thinking" modes for complex problems, optimizing computational resources. Architecturally, this 56B activated (560B total) parameter model employs 128 layers (Mamba2, Attention, FFN) with an innovative AMF/MF block pattern. Faster Mamba2 ensures linear complexity, Grouped-Query Attention minimizes KV cache, and FFNs use an MoE structure. Pre-trained on 16T high-quality tokens, it supports a 256K context length and is the first industry-deployed large-scale Mamba model. Our comprehensive post-training strategy enhances capabilities via Supervised Fine-Tuning (3M instructions), a novel Adaptive Long-short CoT Fusion method, Multi-round Deliberation Learning for iterative improvement, and a two-stage Large-scale Reinforcement Learning process targeting STEM and general instruction-following. Evaluations show strong performance: overall top 7 rank on LMSYS Chatbot Arena with a score of 1356, outperforming leading models like Gemini-2.0-Flash-001 (1352) and o4-mini-2025-04-16 (1345). TurboS also achieves an average of 77.9% across 23 automated benchmarks. Hunyuan-TurboS balances high performance and efficiency, offering substantial capabilities at lower inference costs than many reasoning models, establishing a new paradigm for efficient large-scale pre-trained models.
Hunyuan-Large: An Open-Source MoE Model with 52 Billion Activated Parameters by Tencent
Nov 05, 2024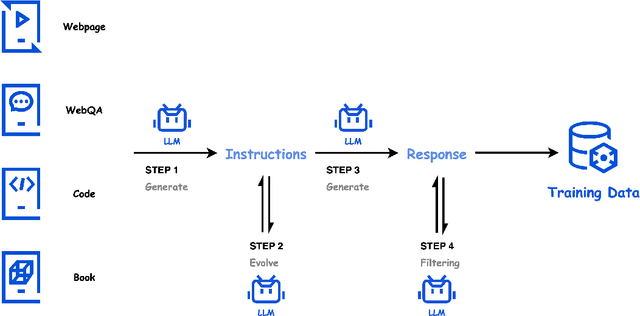
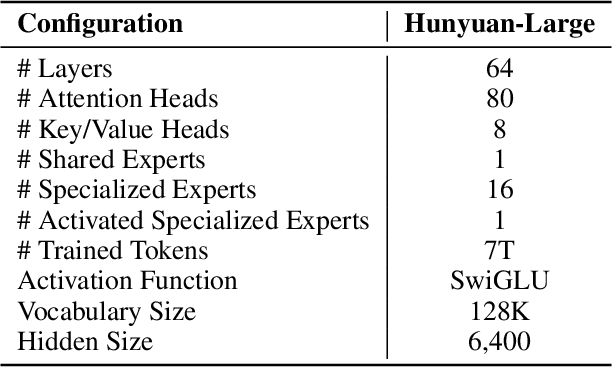
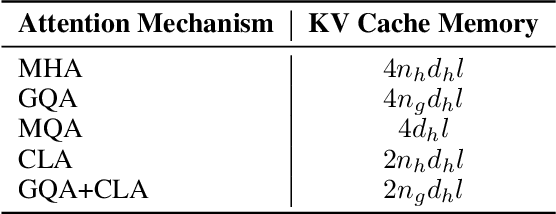
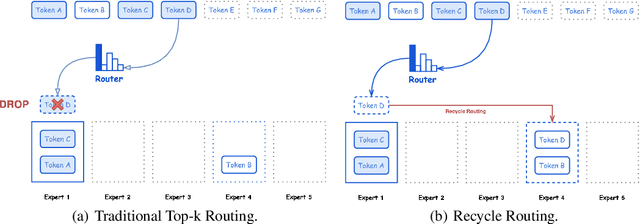
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Hunyuan-Large, which is currently the largest open-source Transformer-based mixture of experts model, with a total of 389 billion parameters and 52 billion activation parameters, capable of handling up to 256K tokens. We conduct a thorough evaluation of Hunyuan-Large's superior performance across various benchmarks including language understanding and generation, logical reasoning, mathematical problem-solving, coding, long-context, and aggregated tasks, where it outperforms LLama3.1-70B and exhibits comparable performance when compared to the significantly larger LLama3.1-405B model. Key practice of Hunyuan-Large include large-scale synthetic data that is orders larger than in previous literature, a mixed expert routing strategy, a key-value cache compression technique, and an expert-specific learning rate strategy. Additionally, we also investigate the scaling laws and learning rate schedule of mixture of experts models, providing valuable insights and guidances for future model development and optimization. The code and checkpoints of Hunyuan-Large are released to facilitate future innovations and applications. Codes: https://github.com/Tencent/Hunyuan-Large Models: https://huggingface.co/tencent/Tencent-Hunyuan-Large
ASAP: A Chinese Review Dataset Towards Aspect Category Sentiment Analysis and Rating Prediction
Mar 11, 2021



Abstract:Sentiment analysis has attracted increasing attention in e-commerce. The sentiment polarities underlying user reviews are of great value for business intelligence. Aspect category sentiment analysis (ACSA) and review rating prediction (RP) are two essential tasks to detect the fine-to-coarse sentiment polarities. %Considering the sentiment of the aspects(ACSA) and the overall review rating(RP) simultaneously has the potential to improve the overall performance. ACSA and RP are highly correlated and usually employed jointly in real-world e-commerce scenarios. While most public datasets are constructed for ACSA and RP separately, which may limit the further exploitation of both tasks. To address the problem and advance related researches, we present a large-scale Chinese restaurant review dataset \textbf{ASAP} including $46,730$ genuine reviews from a leading online-to-offline (O2O) e-commerce platform in China. Besides a $5$-star scale rating, each review is manually annotated according to its sentiment polarities towards $18$ pre-defined aspect categories. We hope the release of the dataset could shed some light on the fields of sentiment analysis. Moreover, we propose an intuitive yet effective joint model for ACSA and RP. Experimental results demonstrate that the joint model outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on both tasks.
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection via Variational Auto-Encoder for Seasonal KPIs in Web Applications
Feb 12, 2018



Abstract:To ensure undisrupted business, large Internet companies need to closely monitor various KPIs (e.g., Page Views, number of online users, and number of orders) of its Web applications, to accurately detect anomalies and trigger timely troubleshooting/mitigation. However, anomaly detection for these seasonal KPIs with various patterns and data quality has been a great challenge, especially without labels. In this paper, we proposed Donut, an unsupervised anomaly detection algorithm based on VAE. Thanks to a few of our key techniques, Donut greatly outperforms a state-of-arts supervised ensemble approach and a baseline VAE approach, and its best F-scores range from 0.75 to 0.9 for the studied KPIs from a top global Internet company. We come up with a novel KDE interpretation of reconstruction for Donut, making it the first VAE-based anomaly detection algorithm with solid theoretical explanation.
Person Re-identification Meets Image Search
Feb 07, 2015
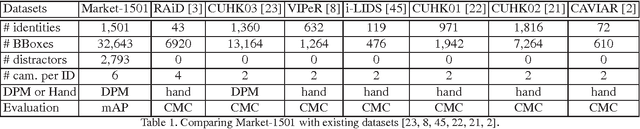
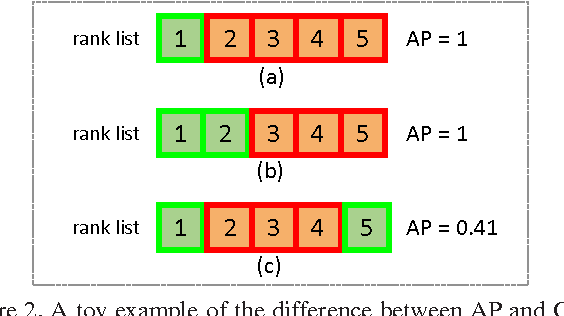
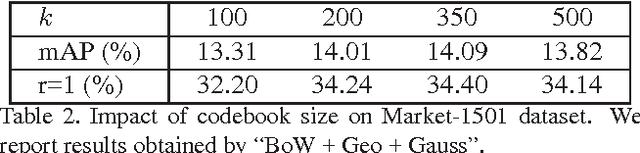
Abstract:For long time, person re-identification and image search are two separately studied tasks. However, for person re-identification, the effectiveness of local features and the "query-search" mode make it well posed for image search techniques. In the light of recent advances in image search, this paper proposes to treat person re-identification as an image search problem. Specifically, this paper claims two major contributions. 1) By designing an unsupervised Bag-of-Words representation, we are devoted to bridging the gap between the two tasks by integrating techniques from image search in person re-identification. We show that our system sets up an effective yet efficient baseline that is amenable to further supervised/unsupervised improvements. 2) We contribute a new high quality dataset which uses DPM detector and includes a number of distractor images. Our dataset reaches closer to realistic settings, and new perspectives are provided. Compared with approaches that rely on feature-feature match, our method is faster by over two orders of magnitude. Moreover, on three datasets, we report competitive results compared with the state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge