Jiacheng Ruan
Wisdom of the Crowd: Reinforcement Learning from Coevolutionary Collective Feedback
Aug 17, 2025



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has significantly enhanced the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), but its reliance on expensive human-labeled data or complex reward models severely limits scalability. While existing self-feedback methods aim to address this problem, they are constrained by the capabilities of a single model, which can lead to overconfidence in incorrect answers, reward hacking, and even training collapse. To this end, we propose Reinforcement Learning from Coevolutionary Collective Feedback (RLCCF), a novel RL framework that enables multi-model collaborative evolution without external supervision. Specifically, RLCCF optimizes the ability of a model collective by maximizing its Collective Consistency (CC), which jointly trains a diverse ensemble of LLMs and provides reward signals by voting on collective outputs. Moreover, each model's vote is weighted by its Self-Consistency (SC) score, ensuring that more confident models contribute more to the collective decision. Benefiting from the diverse output distributions and complementary abilities of multiple LLMs, RLCCF enables the model collective to continuously enhance its reasoning ability through coevolution. Experiments on four mainstream open-source LLMs across four mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our framework yields significant performance gains, achieving an average relative improvement of 16.72\% in accuracy. Notably, RLCCF not only improves the performance of individual models but also enhances the group's majority-voting accuracy by 4.51\%, demonstrating its ability to extend the collective capability boundary of the model collective.
EIAD: Explainable Industrial Anomaly Detection Via Multi-Modal Large Language Models
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Industrial Anomaly Detection (IAD) is critical to ensure product quality during manufacturing. Although existing zero-shot defect segmentation and detection methods have shown effectiveness, they cannot provide detailed descriptions of the defects. Furthermore, the application of large multi-modal models in IAD remains in its infancy, facing challenges in balancing question-answering (QA) performance and mask-based grounding capabilities, often owing to overfitting during the fine-tuning process. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach that introduces a dedicated multi-modal defect localization module to decouple the dialog functionality from the core feature extraction. This decoupling is achieved through independent optimization objectives and tailored learning strategies. Additionally, we contribute to the first multi-modal industrial anomaly detection training dataset, named Defect Detection Question Answering (DDQA), encompassing a wide range of defect types and industrial scenarios. Unlike conventional datasets that rely on GPT-generated data, DDQA ensures authenticity and reliability and offers a robust foundation for model training. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method, Explainable Industrial Anomaly Detection Assistant (EIAD), achieves outstanding performance in defect detection and localization tasks. It not only significantly enhances accuracy but also improves interpretability. These advancements highlight the potential of EIAD for practical applications in industrial settings.
ReviewAgents: Bridging the Gap Between Human and AI-Generated Paper Reviews
Mar 11, 2025



Abstract:Academic paper review is a critical yet time-consuming task within the research community. With the increasing volume of academic publications, automating the review process has become a significant challenge. The primary issue lies in generating comprehensive, accurate, and reasoning-consistent review comments that align with human reviewers' judgments. In this paper, we address this challenge by proposing ReviewAgents, a framework that leverages large language models (LLMs) to generate academic paper reviews. We first introduce a novel dataset, Review-CoT, consisting of 142k review comments, designed for training LLM agents. This dataset emulates the structured reasoning process of human reviewers-summarizing the paper, referencing relevant works, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and generating a review conclusion. Building upon this, we train LLM reviewer agents capable of structured reasoning using a relevant-paper-aware training method. Furthermore, we construct ReviewAgents, a multi-role, multi-LLM agent review framework, to enhance the review comment generation process. Additionally, we propose ReviewBench, a benchmark for evaluating the review comments generated by LLMs. Our experimental results on ReviewBench demonstrate that while existing LLMs exhibit a certain degree of potential for automating the review process, there remains a gap when compared to human-generated reviews. Moreover, our ReviewAgents framework further narrows this gap, outperforming advanced LLMs in generating review comments.
VLRMBench: A Comprehensive and Challenging Benchmark for Vision-Language Reward Models
Mar 10, 2025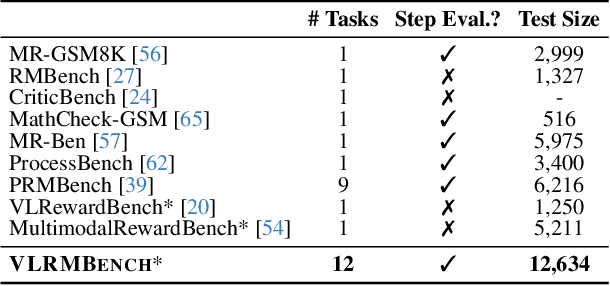
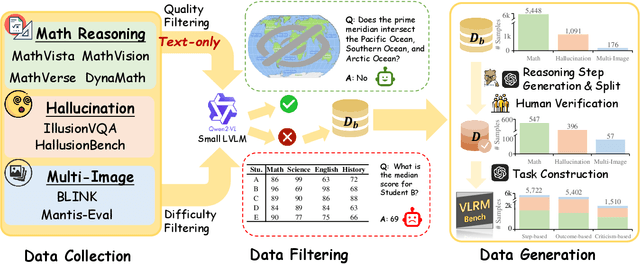
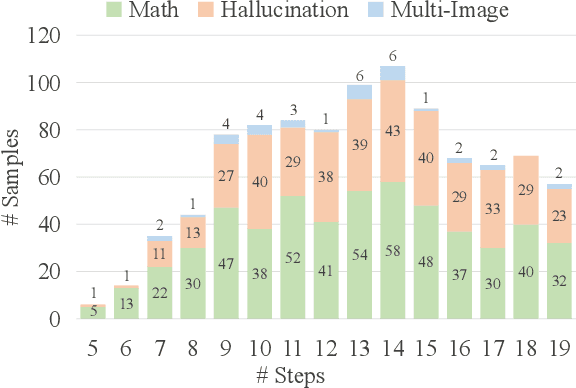
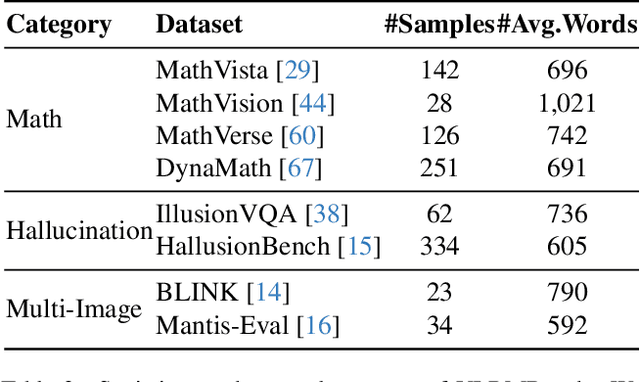
Abstract:Although large visual-language models (LVLMs) have demonstrated strong performance in multimodal tasks, errors may occasionally arise due to biases during the reasoning process. Recently, reward models (RMs) have become increasingly pivotal in the reasoning process. Specifically, process RMs evaluate each reasoning step, outcome RMs focus on the assessment of reasoning results, and critique RMs perform error analysis on the entire reasoning process, followed by corrections. However, existing benchmarks for vision-language RMs (VLRMs) typically assess only a single aspect of their capabilities (e.g., distinguishing between two answers), thus limiting the all-round evaluation and restricting the development of RMs in the visual-language domain. To address this gap, we propose a comprehensive and challenging benchmark, dubbed as VLRMBench, encompassing 12,634 questions. VLRMBench is constructed based on three distinct types of datasets, covering mathematical reasoning, hallucination understanding, and multi-image understanding. We design 12 tasks across three major categories, focusing on evaluating VLRMs in the aspects of process understanding, outcome judgment, and critique generation. Extensive experiments are conducted on 21 open-source models and 5 advanced closed-source models, highlighting the challenges posed by VLRMBench. For instance, in the `Forecasting Future', a binary classification task, the advanced GPT-4o achieves only a 76.0% accuracy. Additionally, we perform comprehensive analytical studies, offering valuable insights for the future development of VLRMs. We anticipate that VLRMBench will serve as a pivotal benchmark in advancing VLRMs. Code and datasets will be available at https://github.com/JCruan519/VLRMBench.
From Motion Signals to Insights: A Unified Framework for Student Behavior Analysis and Feedback in Physical Education Classes
Mar 09, 2025



Abstract:Analyzing student behavior in educational scenarios is crucial for enhancing teaching quality and student engagement. Existing AI-based models often rely on classroom video footage to identify and analyze student behavior. While these video-based methods can partially capture and analyze student actions, they struggle to accurately track each student's actions in physical education classes, which take place in outdoor, open spaces with diverse activities, and are challenging to generalize to the specialized technical movements involved in these settings. Furthermore, current methods typically lack the ability to integrate specialized pedagogical knowledge, limiting their ability to provide in-depth insights into student behavior and offer feedback for optimizing instructional design. To address these limitations, we propose a unified end-to-end framework that leverages human activity recognition technologies based on motion signals, combined with advanced large language models, to conduct more detailed analyses and feedback of student behavior in physical education classes. Our framework begins with the teacher's instructional designs and the motion signals from students during physical education sessions, ultimately generating automated reports with teaching insights and suggestions for improving both learning and class instructions. This solution provides a motion signal-based approach for analyzing student behavior and optimizing instructional design tailored to physical education classes. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework can accurately identify student behaviors and produce meaningful pedagogical insights.
FTII-Bench: A Comprehensive Multimodal Benchmark for Flow Text with Image Insertion
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:Benefiting from the revolutionary advances in large language models (LLMs) and foundational vision models, large vision-language models (LVLMs) have also made significant progress. However, current benchmarks focus on tasks that evaluating only a single aspect of LVLM capabilities (e.g., recognition, detection, understanding). These tasks fail to fully demonstrate LVLMs' potential in complex application scenarios. To comprehensively assess the performance of existing LVLMs, we propose a more challenging task called the Flow Text with Image Insertion task (FTII). This task requires LVLMs to simultaneously possess outstanding abilities in image comprehension, instruction understanding, and long-text interpretation. Specifically, given several text paragraphs and a set of candidate images, as the text paragraphs accumulate, the LVLMs are required to select the most suitable image from the candidates to insert after the corresponding paragraph. Constructing a benchmark for such a task is highly challenging, particularly in determining the sequence of flowing text and images. To address this challenge, we turn to professional news reports, which naturally contain a gold standard for image-text sequences. Based on this, we introduce the Flow Text with Image Insertion Benchmark (FTII-Bench), which includes 318 high-quality Chinese image-text news articles and 307 high-quality English image-text news articles, covering 10 different news domains. Using these 625 high-quality articles, we construct problems of two different types with multiple levels of difficulty. Furthermore, we establish two different evaluation pipelines based on the CLIP model and existing LVLMs. We evaluate 9 open-source and 2 closed-source LVLMs as well as 2 CLIP-based models. Results indicate that even the most advanced models (e.g., GPT-4o) face significant challenges when tackling the FTII task.
Understanding Robustness of Parameter-Efficient Tuning for Image Classification
Oct 13, 2024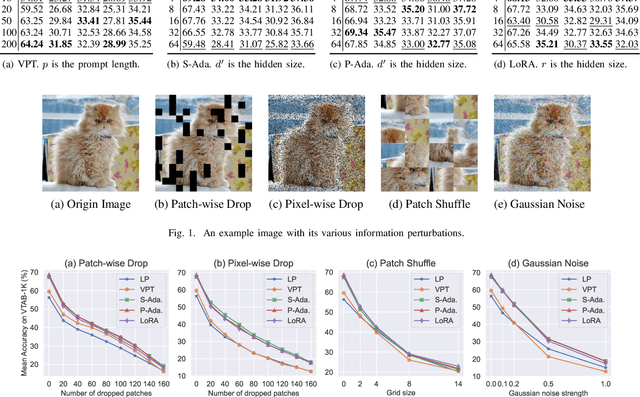
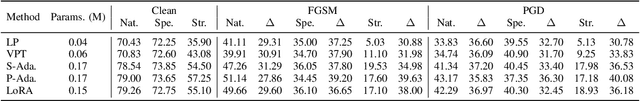
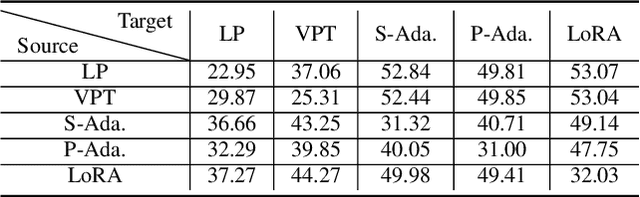
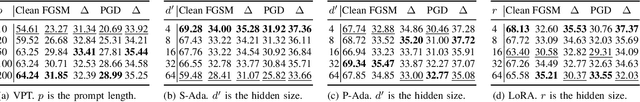
Abstract:Parameter-efficient tuning (PET) techniques calibrate the model's predictions on downstream tasks by freezing the pre-trained models and introducing a small number of learnable parameters. However, despite the numerous PET methods proposed, their robustness has not been thoroughly investigated. In this paper, we systematically explore the robustness of four classical PET techniques (e.g., VPT, Adapter, AdaptFormer, and LoRA) under both white-box attacks and information perturbations. For white-box attack scenarios, we first analyze the performance of PET techniques using FGSM and PGD attacks. Subsequently, we further explore the transferability of adversarial samples and the impact of learnable parameter quantities on the robustness of PET methods. Under information perturbation attacks, we introduce four distinct perturbation strategies, including Patch-wise Drop, Pixel-wise Drop, Patch Shuffle, and Gaussian Noise, to comprehensively assess the robustness of these PET techniques in the presence of information loss. Via these extensive studies, we enhance the understanding of the robustness of PET methods, providing valuable insights for improving their performance in computer vision applications. The code is available at https://github.com/JCruan519/PETRobustness.
MM-CamObj: A Comprehensive Multimodal Dataset for Camouflaged Object Scenarios
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:Large visual-language models (LVLMs) have achieved great success in multiple applications. However, they still encounter challenges in complex scenes, especially those involving camouflaged objects. This is primarily due to the lack of samples related to camouflaged scenes in the training dataset. To mitigate this issue, we construct the MM-CamObj dataset for the first time, comprising two subsets: CamObj-Align and CamObj-Instruct. Specifically, CamObj-Align contains 11,363 image-text pairs, and it is designed for VL alignment and injecting rich knowledge of camouflaged scenes into LVLMs. CamObj-Instruct is collected for fine-tuning the LVLMs with improved instruction-following capabilities, and it includes 11,363 images and 68,849 conversations with diverse instructions. Based on the MM-CamObj dataset, we propose the CamObj-Llava, an LVLM specifically designed for addressing tasks in camouflaged scenes. To facilitate our model's effective acquisition of knowledge about camouflaged objects and scenes, we introduce a curriculum learning strategy with six distinct modes. Additionally, we construct the CamObj-Bench to evaluate the existing LVLMs' capabilities of understanding, recognition, localization and count in camouflage scenes. This benchmark includes 600 images and 7 tasks, with a total of 9,449 questions. Extensive experiments are conducted on the CamObj-Bench with CamObj-Llava, 8 existing open-source and 3 closed-source LVLMs. Surprisingly, the results indicate that our model achieves a 25.84% improvement in 4 out of 7 tasks compared to GPT-4o. Code and datasets will be available at https://github.com/JCruan519/MM-CamObj.
LLaMA-MoE: Building Mixture-of-Experts from LLaMA with Continual Pre-training
Jun 24, 2024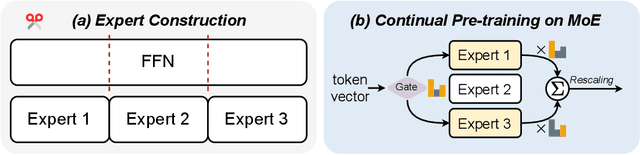


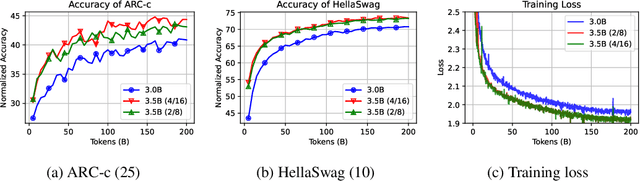
Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) has gained increasing popularity as a promising framework for scaling up large language models (LLMs). However, training MoE from scratch in a large-scale setting still suffers from data-hungry and instability problems. Motivated by this limit, we investigate building MoE models from existing dense large language models. Specifically, based on the well-known LLaMA-2 7B model, we obtain an MoE model by: (1) Expert Construction, which partitions the parameters of original Feed-Forward Networks (FFNs) into multiple experts; (2) Continual Pre-training, which further trains the transformed MoE model and additional gate networks. In this paper, we comprehensively explore different methods for expert construction and various data sampling strategies for continual pre-training. After these stages, our LLaMA-MoE models could maintain language abilities and route the input tokens to specific experts with part of the parameters activated. Empirically, by training 200B tokens, LLaMA-MoE-3.5B models significantly outperform dense models that contain similar activation parameters. The source codes and models are available at https://github.com/pjlab-sys4nlp/llama-moe .
Dynamic Data Mixing Maximizes Instruction Tuning for Mixture-of-Experts
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models have shown remarkable capability in instruction tuning, especially when the number of tasks scales. However, previous methods simply merge all training tasks (e.g. creative writing, coding, and mathematics) and apply fixed sampling weights, without considering the importance of different tasks as the model training state changes. In this way, the most helpful data cannot be effectively distinguished, leading to suboptimal model performance. To reduce the potential redundancies of datasets, we make the first attempt and propose a novel dynamic data mixture for MoE instruction tuning. Specifically, inspired by MoE's token routing preference, we build dataset-level representations and then capture the subtle differences among datasets. Finally, we propose to dynamically adjust the sampling weight of datasets by their inter-redundancies, thus maximizing global performance under a limited training budget. The experimental results on two MoE models demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on both downstream knowledge \& reasoning tasks and open-ended queries. Code and models are available at https://github.com/Spico197/MoE-SFT .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge