Daoxin Zhang
VLRMBench: A Comprehensive and Challenging Benchmark for Vision-Language Reward Models
Mar 10, 2025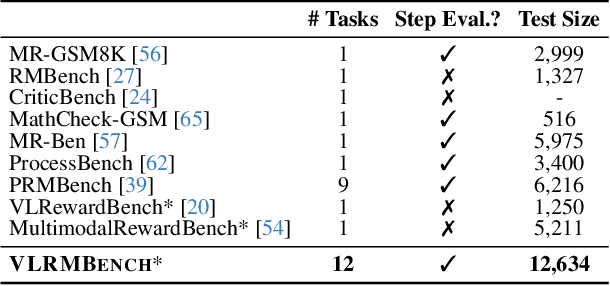
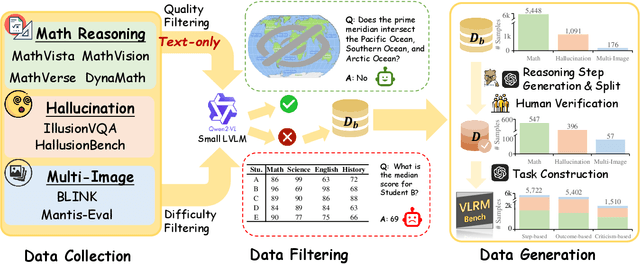
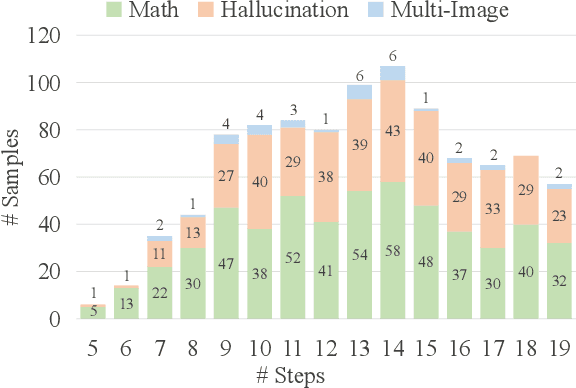
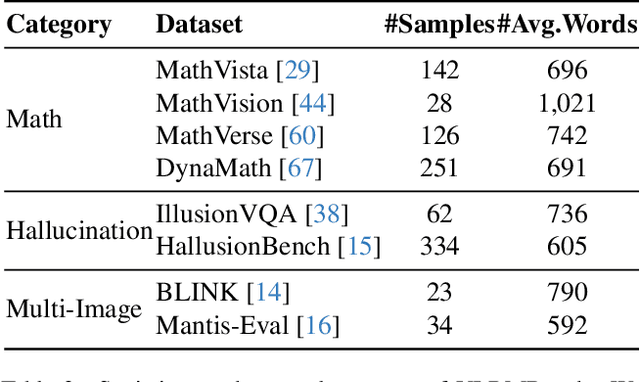
Abstract:Although large visual-language models (LVLMs) have demonstrated strong performance in multimodal tasks, errors may occasionally arise due to biases during the reasoning process. Recently, reward models (RMs) have become increasingly pivotal in the reasoning process. Specifically, process RMs evaluate each reasoning step, outcome RMs focus on the assessment of reasoning results, and critique RMs perform error analysis on the entire reasoning process, followed by corrections. However, existing benchmarks for vision-language RMs (VLRMs) typically assess only a single aspect of their capabilities (e.g., distinguishing between two answers), thus limiting the all-round evaluation and restricting the development of RMs in the visual-language domain. To address this gap, we propose a comprehensive and challenging benchmark, dubbed as VLRMBench, encompassing 12,634 questions. VLRMBench is constructed based on three distinct types of datasets, covering mathematical reasoning, hallucination understanding, and multi-image understanding. We design 12 tasks across three major categories, focusing on evaluating VLRMs in the aspects of process understanding, outcome judgment, and critique generation. Extensive experiments are conducted on 21 open-source models and 5 advanced closed-source models, highlighting the challenges posed by VLRMBench. For instance, in the `Forecasting Future', a binary classification task, the advanced GPT-4o achieves only a 76.0% accuracy. Additionally, we perform comprehensive analytical studies, offering valuable insights for the future development of VLRMs. We anticipate that VLRMBench will serve as a pivotal benchmark in advancing VLRMs. Code and datasets will be available at https://github.com/JCruan519/VLRMBench.
Bridging the Emotional Semantic Gap via Multimodal Relevance Estimation
Feb 03, 2023



Abstract:Human beings have rich ways of emotional expressions, including facial action, voice, and natural languages. Due to the diversity and complexity of different individuals, the emotions expressed by various modalities may be semantically irrelevant. Directly fusing information from different modalities may inevitably make the model subject to the noise from semantically irrelevant modalities. To tackle this problem, we propose a multimodal relevance estimation network to capture the relevant semantics among modalities in multimodal emotions. Specifically, we take advantage of an attention mechanism to reflect the semantic relevance weights of each modality. Moreover, we propose a relevant semantic estimation loss to weakly supervise the semantics of each modality. Furthermore, we make use of contrastive learning to optimize the similarity of category-level modality-relevant semantics across different modalities in feature space, thereby bridging the semantic gap between heterogeneous modalities. In order to better reflect the emotional state in the real interactive scenarios and perform the semantic relevance analysis, we collect a single-label discrete multimodal emotion dataset named SDME, which enables researchers to conduct multimodal semantic relevance research with large category bias. Experiments on continuous and discrete emotion datasets show that our model can effectively capture the relevant semantics, especially for the large deviations in modal semantics. The code and SDME dataset will be publicly available.
Salient Object Ranking with Position-Preserved Attention
Jun 10, 2021



Abstract:Instance segmentation can detect where the objects are in an image, but hard to understand the relationship between them. We pay attention to a typical relationship, relative saliency. A closely related task, salient object detection, predicts a binary map highlighting a visually salient region while hard to distinguish multiple objects. Directly combining two tasks by post-processing also leads to poor performance. There is a lack of research on relative saliency at present, limiting the practical applications such as content-aware image cropping, video summary, and image labeling. In this paper, we study the Salient Object Ranking (SOR) task, which manages to assign a ranking order of each detected object according to its visual saliency. We propose the first end-to-end framework of the SOR task and solve it in a multi-task learning fashion. The framework handles instance segmentation and salient object ranking simultaneously. In this framework, the SOR branch is independent and flexible to cooperate with different detection methods, so that easy to use as a plugin. We also introduce a Position-Preserved Attention (PPA) module tailored for the SOR branch. It consists of the position embedding stage and feature interaction stage. Considering the importance of position in saliency comparison, we preserve absolute coordinates of objects in ROI pooling operation and then fuse positional information with semantic features in the first stage. In the feature interaction stage, we apply the attention mechanism to obtain proposals' contextualized representations to predict their relative ranking orders. Extensive experiments have been conducted on the ASR dataset. Without bells and whistles, our proposed method outperforms the former state-of-the-art method significantly. The code will be released publicly available.
Horizontal-to-Vertical Video Conversion
Jan 11, 2021



Abstract:Alongside the prevalence of mobile videos, the general public leans towards consuming vertical videos on hand-held devices. To revitalize the exposure of horizontal contents, we hereby set forth the exploration of automated horizontal-to-vertical (abbreviated as H2V) video conversion with our proposed H2V framework, accompanied by an accurately annotated H2V-142K dataset. Concretely, H2V framework integrates video shot boundary detection, subject selection and multi-object tracking to facilitate the subject-preserving conversion, wherein the key is subject selection. To achieve so, we propose a Rank-SS module that detects human objects, then selects the subject-to-preserve via exploiting location, appearance, and salient cues. Afterward, the framework automatically crops the video around the subject to produce vertical contents from horizontal sources. To build and evaluate our H2V framework, H2V-142K dataset is densely annotated with subject bounding boxes for 125 videos with 132K frames and 9,500 video covers, upon which we demonstrate superior subject selection performance comparing to traditional salient approaches, and exhibit promising horizontal-to-vertical conversion performance overall. By publicizing this dataset as well as our approach, we wish to pave the way for more valuable endeavors on the horizontal-to-vertical video conversion task.
Single-Shot Bidirectional Pyramid Networks for High-Quality Object Detection
Mar 22, 2018



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed many exciting achievements for object detection using deep learning techniques. Despite achieving significant progresses, most existing detectors are designed to detect objects with relatively low-quality prediction of locations, i.e., often trained with the threshold of Intersection over Union (IoU) set to 0.5 by default, which can yield low-quality or even noisy detections. It remains an open challenge for how to devise and train a high-quality detector that can achieve more precise localization (i.e., IoU$>$0.5) without sacrificing the detection performance. In this paper, we propose a novel single-shot detection framework of Bidirectional Pyramid Networks (BPN) towards high-quality object detection, which consists of two novel components: (i) a Bidirectional Feature Pyramid structure for more effective and robust feature representations; and (ii) a Cascade Anchor Refinement to gradually refine the quality of predesigned anchors for more effective training. Our experiments showed that the proposed BPN achieves the best performances among all the single-stage object detectors on both PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets, especially for high-quality detections.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge