Jeevesh Juneja
Universal Model Routing for Efficient LLM Inference
Feb 12, 2025



Abstract:Large language models' significant advances in capabilities are accompanied by significant increases in inference costs. Model routing is a simple technique for reducing inference cost, wherein one maintains a pool of candidate LLMs, and learns to route each prompt to the smallest feasible LLM. Existing works focus on learning a router for a fixed pool of LLMs. In this paper, we consider the problem of dynamic routing, where new, previously unobserved LLMs are available at test time. We propose a new approach to this problem that relies on representing each LLM as a feature vector, derived based on predictions on a set of representative prompts. Based on this, we detail two effective strategies, relying on cluster-based routing and a learned cluster map respectively. We prove that these strategies are estimates of a theoretically optimal routing rule, and provide an excess risk bound to quantify their errors. Experiments on a range of public benchmarks show the effectiveness of the proposed strategies in routing amongst more than 30 unseen LLMs.
Linear Connectivity Reveals Generalization Strategies
May 24, 2022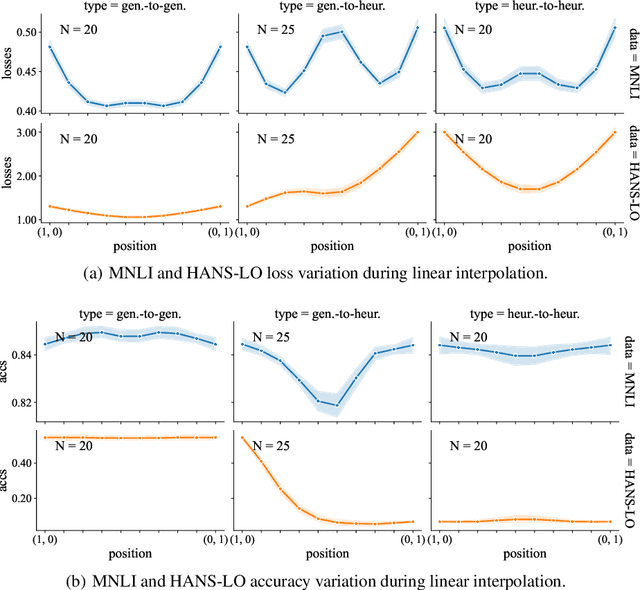
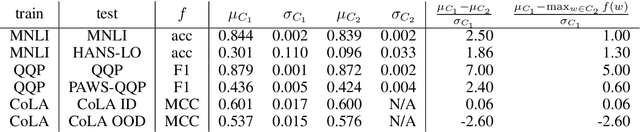
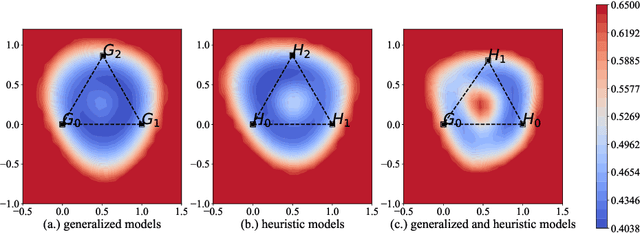
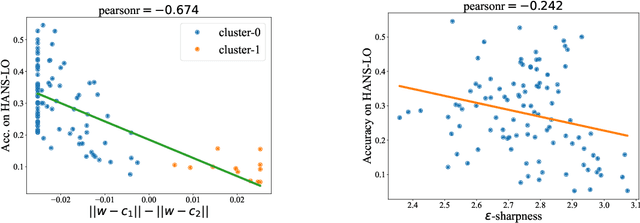
Abstract:It is widely accepted in the mode connectivity literature that when two neural networks are trained similarly on the same data, they are connected by a path through parameter space over which test set accuracy is maintained. Under some circumstances, including transfer learning from pretrained models, these paths are presumed to be linear. In contrast to existing results, we find that among text classifiers (trained on MNLI, QQP, and CoLA), some pairs of finetuned models have large barriers of increasing loss on the linear paths between them. On each task, we find distinct clusters of models which are linearly connected on the test loss surface, but are disconnected from models outside the cluster -- models that occupy separate basins on the surface. By measuring performance on specially-crafted diagnostic datasets, we find that these clusters correspond to different generalization strategies: one cluster behaves like a bag of words model under domain shift, while another cluster uses syntactic heuristics. Our work demonstrates how the geometry of the loss surface can guide models towards different heuristic functions.
Finding patterns in Knowledge Attribution for Transformers
May 04, 2022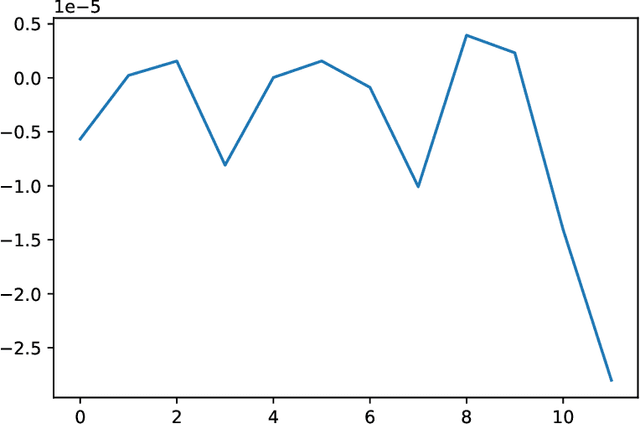
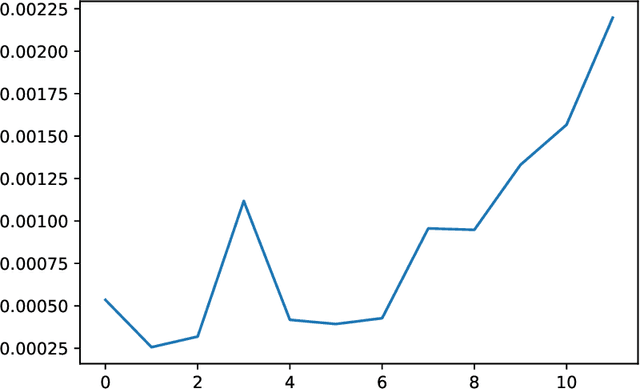
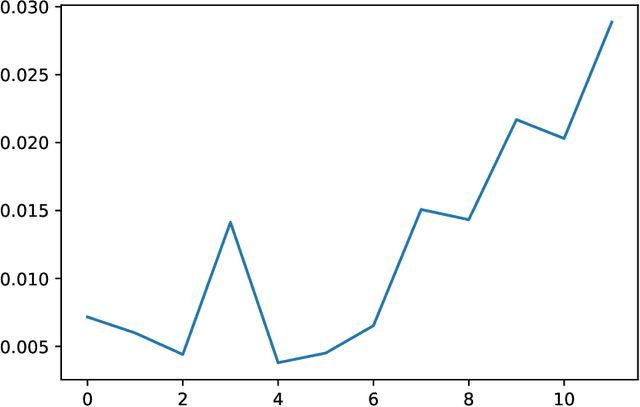
Abstract:We analyze the Knowledge Neurons framework for the attribution of factual and relational knowledge to particular neurons in the transformer network. We use a 12-layer multi-lingual BERT model for our experiments. Our study reveals various interesting phenomena. We observe that mostly factual knowledge can be attributed to middle and higher layers of the network($\ge 6$). Further analysis reveals that the middle layers($6-9$) are mostly responsible for relational information, which is further refined into actual factual knowledge or the "correct answer" in the last few layers($10-12$). Our experiments also show that the model handles prompts in different languages, but representing the same fact, similarly, providing further evidence for effectiveness of multi-lingual pre-training. Applying the attribution scheme for grammatical knowledge, we find that grammatical knowledge is far more dispersed among the neurons than factual knowledge.
Can Unsupervised Knowledge Transfer from Social Discussions Help Argument Mining?
Mar 24, 2022
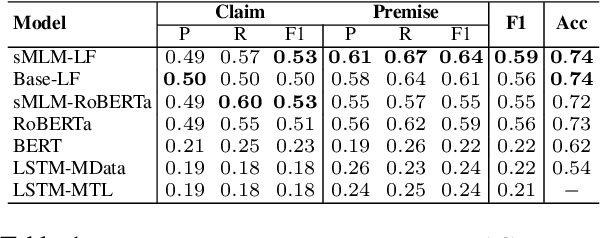
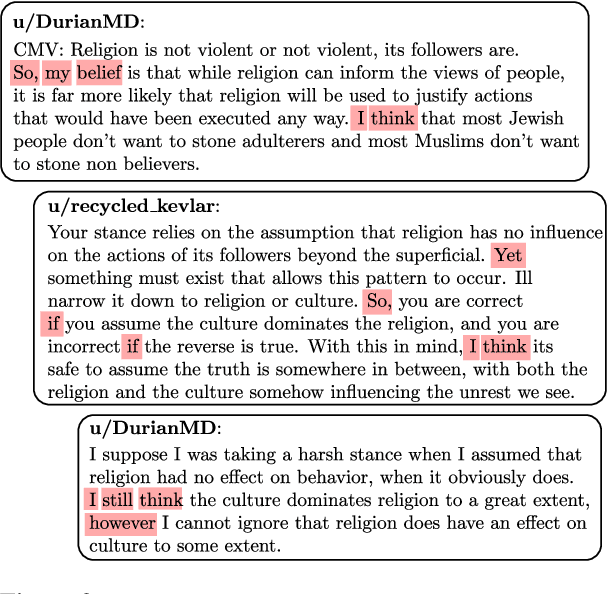
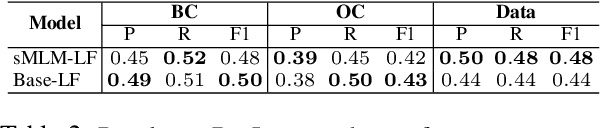
Abstract:Identifying argument components from unstructured texts and predicting the relationships expressed among them are two primary steps of argument mining. The intrinsic complexity of these tasks demands powerful learning models. While pretrained Transformer-based Language Models (LM) have been shown to provide state-of-the-art results over different NLP tasks, the scarcity of manually annotated data and the highly domain-dependent nature of argumentation restrict the capabilities of such models. In this work, we propose a novel transfer learning strategy to overcome these challenges. We utilize argumentation-rich social discussions from the ChangeMyView subreddit as a source of unsupervised, argumentative discourse-aware knowledge by finetuning pretrained LMs on a selectively masked language modeling task. Furthermore, we introduce a novel prompt-based strategy for inter-component relation prediction that compliments our proposed finetuning method while leveraging on the discourse context. Exhaustive experiments show the generalization capability of our method on these two tasks over within-domain as well as out-of-domain datasets, outperforming several existing and employed strong baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge