Dipankar Das
GS-Net: Global Self-Attention Guided CNN for Multi-Stage Glaucoma Classification
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:Glaucoma is a common eye disease that leads to irreversible blindness unless timely detected. Hence, glaucoma detection at an early stage is of utmost importance for a better treatment plan and ultimately saving the vision. The recent literature has shown the prominence of CNN-based methods to detect glaucoma from retinal fundus images. However, such methods mainly focus on solving binary classification tasks and have not been thoroughly explored for the detection of different glaucoma stages, which is relatively challenging due to minute lesion size variations and high inter-class similarities. This paper proposes a global self-attention based network called GS-Net for efficient multi-stage glaucoma classification. We introduce a global self-attention module (GSAM) consisting of two parallel attention modules, a channel attention module (CAM) and a spatial attention module (SAM), to learn global feature dependencies across channel and spatial dimensions. The GSAM encourages extracting more discriminative and class-specific features from the fundus images. The experimental results on a publicly available dataset demonstrate that our GS-Net outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Also, the GSAM achieves competitive performance against popular attention modules.
* 5 pages, 3 figures
JU_NLP at HinglishEval: Quality Evaluation of the Low-Resource Code-Mixed Hinglish Text
Jun 16, 2022
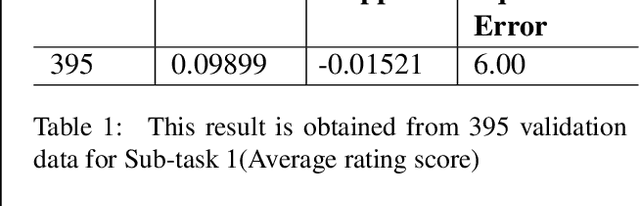
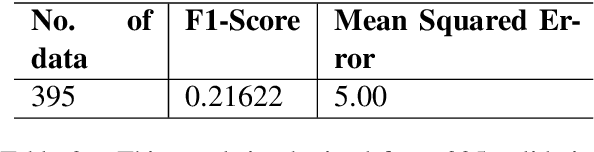
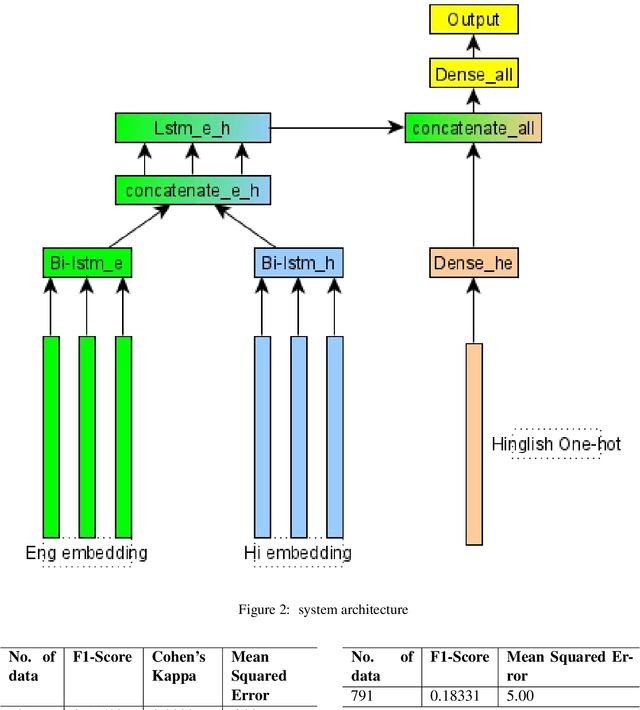
Abstract:In this paper we describe a system submitted to the INLG 2022 Generation Challenge (GenChal) on Quality Evaluation of the Low-Resource Synthetically Generated Code-Mixed Hinglish Text. We implement a Bi-LSTM-based neural network model to predict the Average rating score and Disagreement score of the synthetic Hinglish dataset. In our models, we used word embeddings for English and Hindi data, and one hot encodings for Hinglish data. We achieved a F1 score of 0.11, and mean squared error of 6.0 in the average rating score prediction task. In the task of Disagreement score prediction, we achieve a F1 score of 0.18, and mean squared error of 5.0.
Can Unsupervised Knowledge Transfer from Social Discussions Help Argument Mining?
Mar 24, 2022
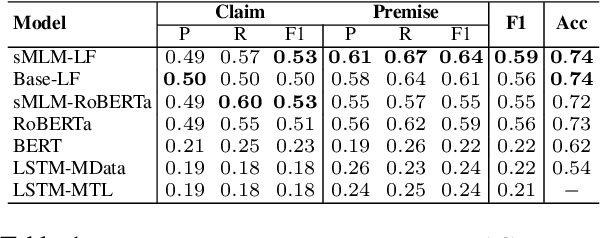
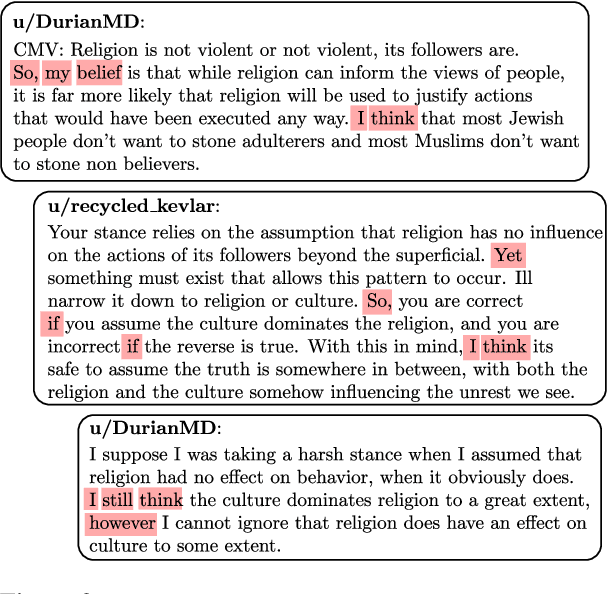
Abstract:Identifying argument components from unstructured texts and predicting the relationships expressed among them are two primary steps of argument mining. The intrinsic complexity of these tasks demands powerful learning models. While pretrained Transformer-based Language Models (LM) have been shown to provide state-of-the-art results over different NLP tasks, the scarcity of manually annotated data and the highly domain-dependent nature of argumentation restrict the capabilities of such models. In this work, we propose a novel transfer learning strategy to overcome these challenges. We utilize argumentation-rich social discussions from the ChangeMyView subreddit as a source of unsupervised, argumentative discourse-aware knowledge by finetuning pretrained LMs on a selectively masked language modeling task. Furthermore, we introduce a novel prompt-based strategy for inter-component relation prediction that compliments our proposed finetuning method while leveraging on the discourse context. Exhaustive experiments show the generalization capability of our method on these two tasks over within-domain as well as out-of-domain datasets, outperforming several existing and employed strong baselines.
AdvCodeMix: Adversarial Attack on Code-Mixed Data
Oct 30, 2021
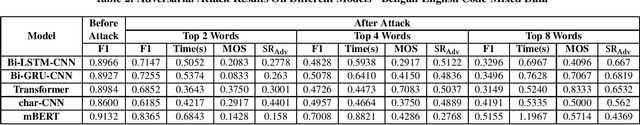

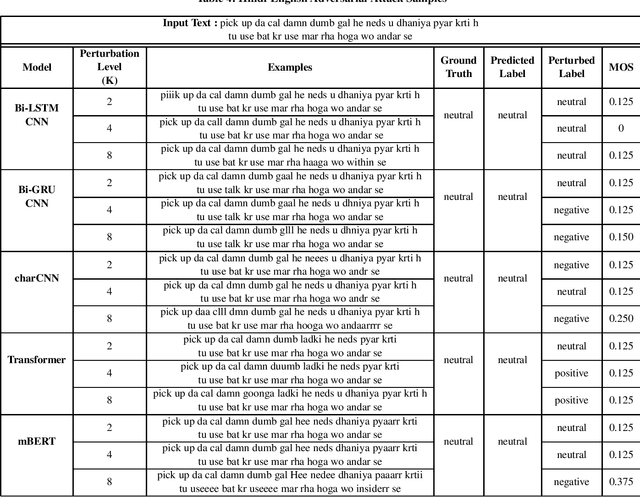
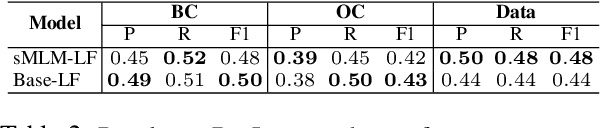
Abstract:Research on adversarial attacks are becoming widely popular in the recent years. One of the unexplored areas where prior research is lacking is the effect of adversarial attacks on code-mixed data. Therefore, in the present work, we have explained the first generalized framework on text perturbation to attack code-mixed classification models in a black-box setting. We rely on various perturbation techniques that preserve the semantic structures of the sentences and also obscure the attacks from the perception of a human user. The present methodology leverages the importance of a token to decide where to attack by employing various perturbation strategies. We test our strategies on various sentiment classification models trained on Bengali-English and Hindi-English code-mixed datasets, and reduce their F1-scores by nearly 51 % and 53 % respectively, which can be further reduced if a larger number of tokens are perturbed in a given sentence.
Incomplete Gamma Integrals for Deep Cascade Prediction using Content, Network, and Exogenous Signals
Jun 13, 2021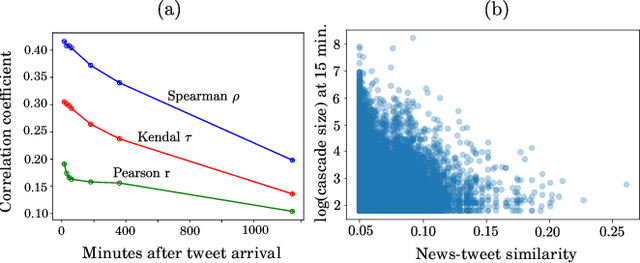
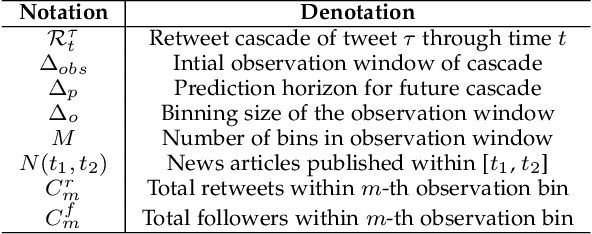
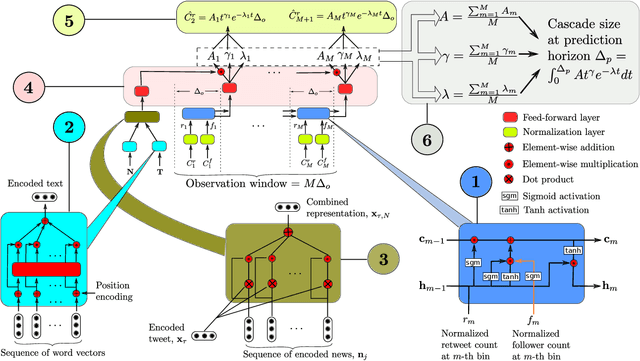
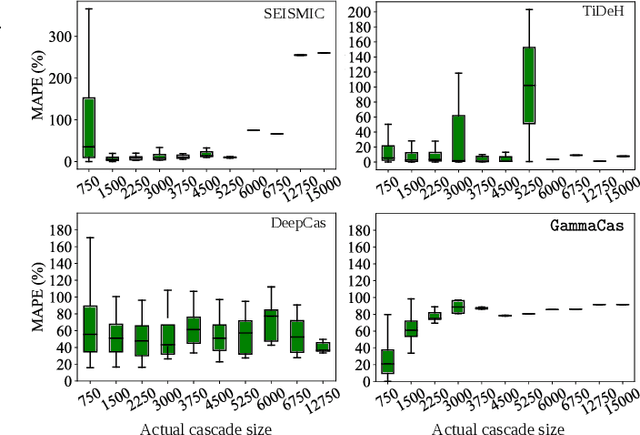
Abstract:The behaviour of information cascades (such as retweets) has been modelled extensively. While point process-based generative models have long been in use for estimating cascade growths, deep learning has greatly enhanced diverse feature integration. We observe two significant temporal signals in cascade data that have not been emphasized or reported to our knowledge. First, the popularity of the cascade root is known to influence cascade size strongly; but the effect falls off rapidly with time. Second, there is a measurable positive correlation between the novelty of the root content (with respect to a streaming external corpus) and the relative size of the resulting cascade. Responding to these observations, we propose GammaCas, a new cascade growth model as a parametric function of time, which combines deep influence signals from content (e.g., tweet text), network features (e.g., followers of the root user), and exogenous event sources (e.g., online news). Specifically, our model processes these signals through a customized recurrent network, whose states then provide the parameters of the cascade rate function, which is integrated over time to predict the cascade size. The network parameters are trained end-to-end using observed cascades. GammaCas outperforms seven recent and diverse baselines significantly on a large-scale dataset of retweet cascades coupled with time-aligned online news -- it beats the best baseline with an 18.98% increase in terms of Kendall's $\tau$ correlation and $35.63$ reduction in Mean Absolute Percentage Error. Extensive ablation and case studies unearth interesting insights regarding retweet cascade dynamics.
JUNLP@Dravidian-CodeMix-FIRE2020: Sentiment Classification of Code-Mixed Tweets using Bi-Directional RNN and Language Tags
Oct 20, 2020


Abstract:Sentiment analysis has been an active area of research in the past two decades and recently, with the advent of social media, there has been an increasing demand for sentiment analysis on social media texts. Since the social media texts are not in one language and are largely code-mixed in nature, the traditional sentiment classification models fail to produce acceptable results. This paper tries to solve this very research problem and uses bi-directional LSTMs along with language tagging, to facilitate sentiment tagging of code-mixed Tamil texts that have been extracted from social media. The presented algorithm, when evaluated on the test data, garnered precision, recall, and F1 scores of 0.59, 0.66, and 0.58 respectively.
JUNLP@SemEval-2020 Task 9:Sentiment Analysis of Hindi-English code mixed data using Grid Search Cross Validation
Sep 02, 2020

Abstract:Code-mixing is a phenomenon which arises mainly in multilingual societies. Multilingual people, who are well versed in their native languages and also English speakers, tend to code-mix using English-based phonetic typing and the insertion of anglicisms in their main language. This linguistic phenomenon poses a great challenge to conventional NLP domains such as Sentiment Analysis, Machine Translation, and Text Summarization, to name a few. In this work, we focus on working out a plausible solution to the domain of Code-Mixed Sentiment Analysis. This work was done as participation in the SemEval-2020 Sentimix Task, where we focused on the sentiment analysis of English-Hindi code-mixed sentences. our username for the submission was "sainik.mahata" and team name was "JUNLP". We used feature extraction algorithms in conjunction with traditional machine learning algorithms such as SVR and Grid Search in an attempt to solve the task. Our approach garnered an f1-score of 66.2\% when tested using metrics prepared by the organizers of the task.
Development of POS tagger for English-Bengali Code-Mixed data
Jul 29, 2020



Abstract:Code-mixed texts are widespread nowadays due to the advent of social media. Since these texts combine two languages to formulate a sentence, it gives rise to various research problems related to Natural Language Processing. In this paper, we try to excavate one such problem, namely, Parts of Speech tagging of code-mixed texts. We have built a system that can POS tag English-Bengali code-mixed data where the Bengali words were written in Roman script. Our approach initially involves the collection and cleaning of English-Bengali code-mixed tweets. These tweets were used as a development dataset for building our system. The proposed system is a modular approach that starts by tagging individual tokens with their respective languages and then passes them to different POS taggers, designed for different languages (English and Bengali, in our case). Tags given by the two systems are later joined together and the final result is then mapped to a universal POS tag set. Our system was checked using 100 manually POS tagged code-mixed sentences and it returned an accuracy of 75.29%
Preparation of Sentiment tagged Parallel Corpus and Testing its effect on Machine Translation
Jul 28, 2020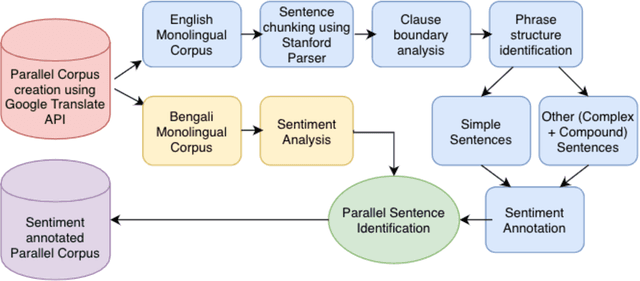
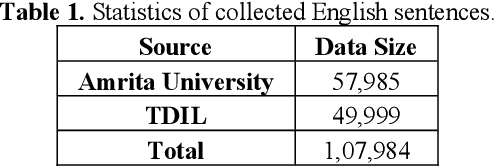

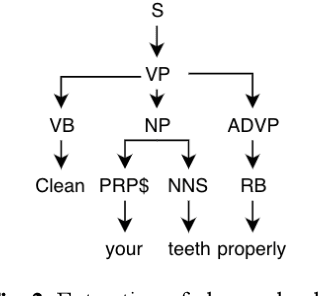
Abstract:In the current work, we explore the enrichment in the machine translation output when the training parallel corpus is augmented with the introduction of sentiment analysis. The paper discusses the preparation of the same sentiment tagged English-Bengali parallel corpus. The preparation of raw parallel corpus, sentiment analysis of the sentences and the training of a Character Based Neural Machine Translation model using the same has been discussed extensively in this paper. The output of the translation model has been compared with a base-line translation model using automated metrics such as BLEU and TER as well as manually.
Investigating Deep Learning Approaches for Hate Speech Detection in Social Media
May 29, 2020



Abstract:The phenomenal growth on the internet has helped in empowering individual's expressions, but the misuse of freedom of expression has also led to the increase of various cyber crimes and anti-social activities. Hate speech is one such issue that needs to be addressed very seriously as otherwise, this could pose threats to the integrity of the social fabrics. In this paper, we proposed deep learning approaches utilizing various embeddings for detecting various types of hate speeches in social media. Detecting hate speech from a large volume of text, especially tweets which contains limited contextual information also poses several practical challenges. Moreover, the varieties in user-generated data and the presence of various forms of hate speech makes it very challenging to identify the degree and intention of the message. Our experiments on three publicly available datasets of different domains shows a significant improvement in accuracy and F1-score.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge