Shravika Mittal
Exposure to Content Written by Large Language Models Can Reduce Stigma Around Opioid Use Disorder in Online Communities
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Widespread stigma, both in the offline and online spaces, acts as a barrier to harm reduction efforts in the context of opioid use disorder (OUD). This stigma is prominently directed towards clinically approved medications for addiction treatment (MAT), people with the condition, and the condition itself. Given the potential of artificial intelligence based technologies in promoting health equity, and facilitating empathic conversations, this work examines whether large language models (LLMs) can help abate OUD-related stigma in online communities. To answer this, we conducted a series of pre-registered randomized controlled experiments, where participants read LLM-generated, human-written, or no responses to help seeking OUD-related content in online communities. The experiment was conducted under two setups, i.e., participants read the responses either once (N = 2,141), or repeatedly for 14 days (N = 107). We found that participants reported the least stigmatized attitudes toward MAT after consuming LLM-generated responses under both the setups. This study offers insights into strategies that can foster inclusive online discourse on OUD, e.g., based on our findings LLMs can be used as an education-based intervention to promote positive attitudes and increase people's propensity toward MAT.
Incomplete Gamma Integrals for Deep Cascade Prediction using Content, Network, and Exogenous Signals
Jun 13, 2021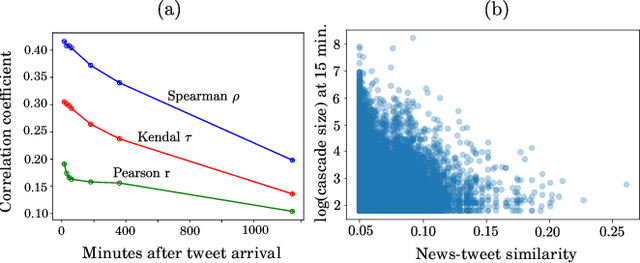
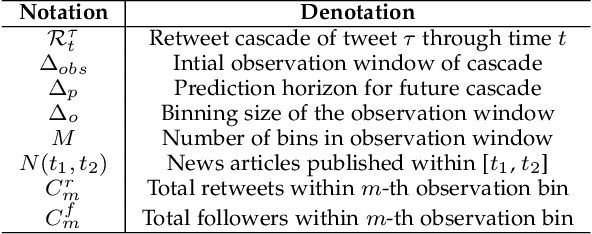
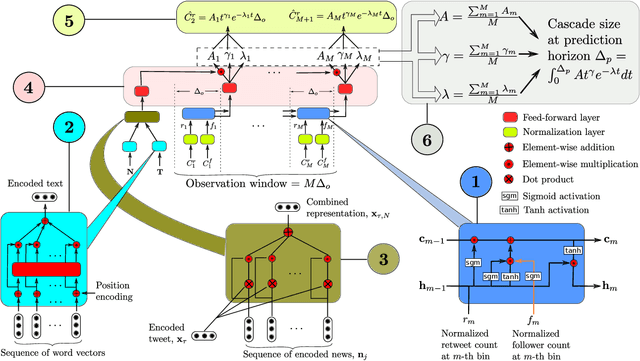
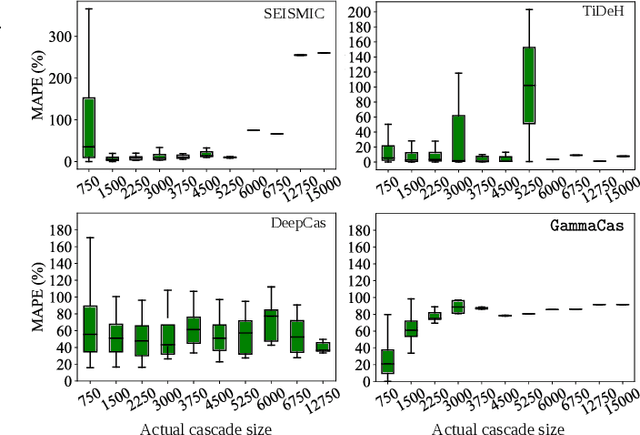
Abstract:The behaviour of information cascades (such as retweets) has been modelled extensively. While point process-based generative models have long been in use for estimating cascade growths, deep learning has greatly enhanced diverse feature integration. We observe two significant temporal signals in cascade data that have not been emphasized or reported to our knowledge. First, the popularity of the cascade root is known to influence cascade size strongly; but the effect falls off rapidly with time. Second, there is a measurable positive correlation between the novelty of the root content (with respect to a streaming external corpus) and the relative size of the resulting cascade. Responding to these observations, we propose GammaCas, a new cascade growth model as a parametric function of time, which combines deep influence signals from content (e.g., tweet text), network features (e.g., followers of the root user), and exogenous event sources (e.g., online news). Specifically, our model processes these signals through a customized recurrent network, whose states then provide the parameters of the cascade rate function, which is integrated over time to predict the cascade size. The network parameters are trained end-to-end using observed cascades. GammaCas outperforms seven recent and diverse baselines significantly on a large-scale dataset of retweet cascades coupled with time-aligned online news -- it beats the best baseline with an 18.98% increase in terms of Kendall's $\tau$ correlation and $35.63$ reduction in Mean Absolute Percentage Error. Extensive ablation and case studies unearth interesting insights regarding retweet cascade dynamics.
Hide and Seek: Outwitting Community Detection Algorithms
Feb 22, 2021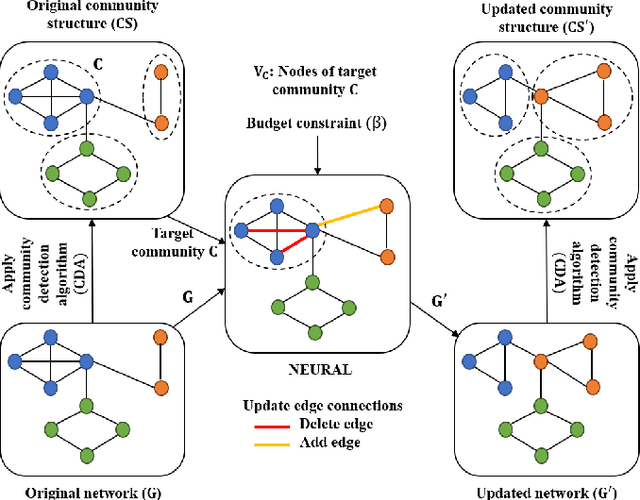
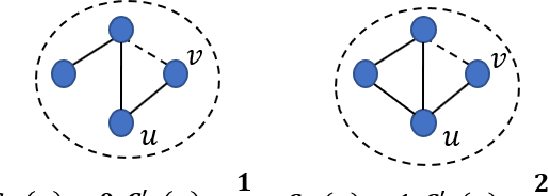
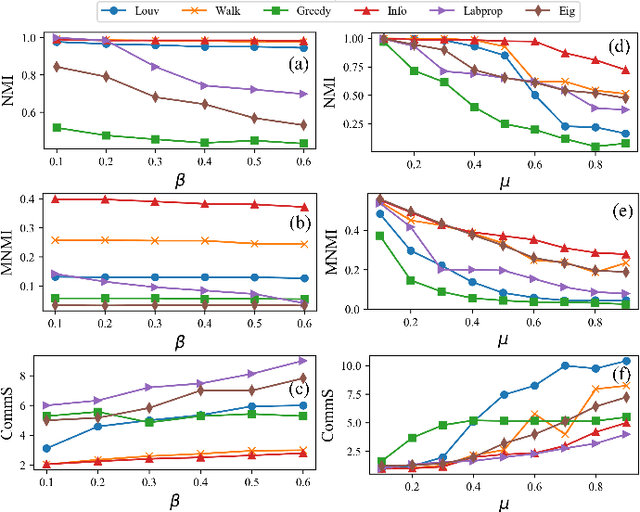
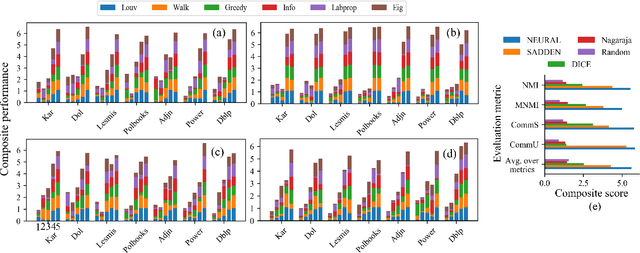
Abstract:Community affiliation of a node plays an important role in determining its contextual position in the network, which may raise privacy concerns when a sensitive node wants to hide its identity in a network. Oftentimes, a target community seeks to protect itself from adversaries so that its constituent members remain hidden inside the network. The current study focuses on hiding such sensitive communities so that the community affiliation of the targeted nodes can be concealed. This leads to the problem of community deception which investigates the avenues of minimally rewiring nodes in a network so that a given target community maximally hides from a community detection algorithm. We formalize the problem of community deception and introduce NEURAL, a novel method that greedily optimizes a node-centric objective function to determine the rewiring strategy. Theoretical settings pose a restriction on the number of strategies that can be employed to optimize the objective function, which in turn reduces the overhead of choosing the best strategy from multiple options. We also show that our objective function is submodular and monotone. When tested on both synthetic and 7 real-world networks, NEURAL is able to deceive 6 widely used community detection algorithms. We benchmark its performance with respect to 4 state-of-the-art methods on 4 evaluation metrics. Additionally, our qualitative analysis of 3 other attributed real-world networks reveals that NEURAL, quite strikingly, captures important meta-information about edges that otherwise could not be inferred by observing only their topological structures.
* 10 tables, 7 figures, 10 main pages, 3 supplementary pages, Accepted in IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems
Judging a Book by its Description : Analyzing Gender Stereotypes in the Man Bookers Prize Winning Fiction
Jul 25, 2018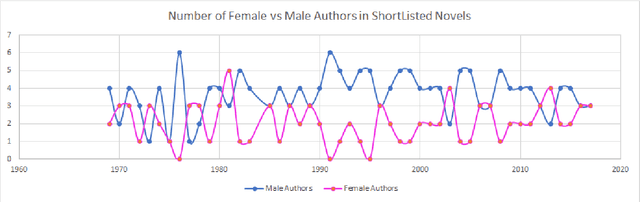
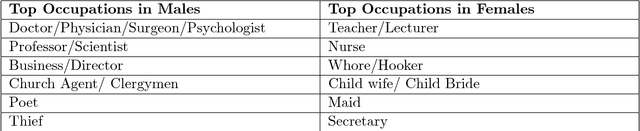
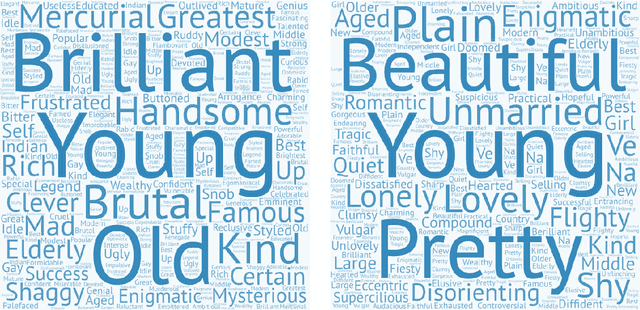

Abstract:The presence of gender stereotypes in many aspects of society is a well-known phenomenon. In this paper, we focus on studying and quantifying such stereotypes and bias in the Man Bookers Prize winning fiction. We consider 275 books shortlisted for Man Bookers Prize between 1969 and 2017. The gender bias is analyzed by semantic modeling of book descriptions on Goodreads. This reveals the pervasiveness of gender bias and stereotype in the books on different features like occupation, introductions and actions associated to the characters in the book.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge