Hugo Yèche
Towards Foundation Models for Critical Care Time Series
Nov 25, 2024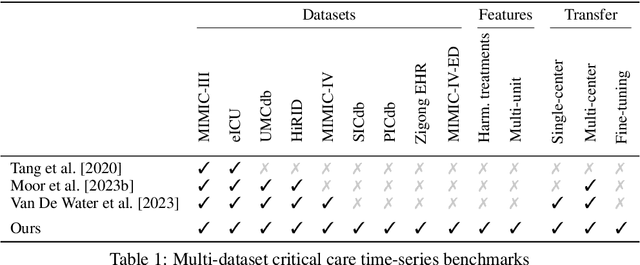
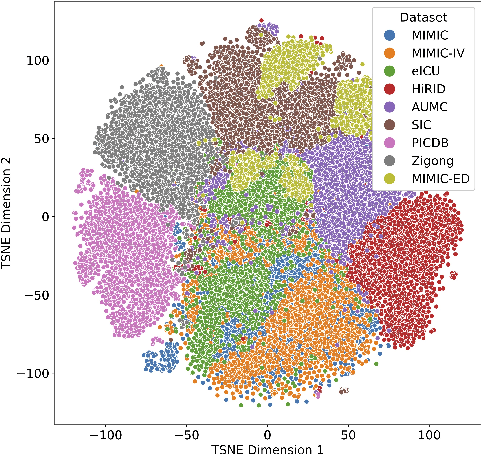
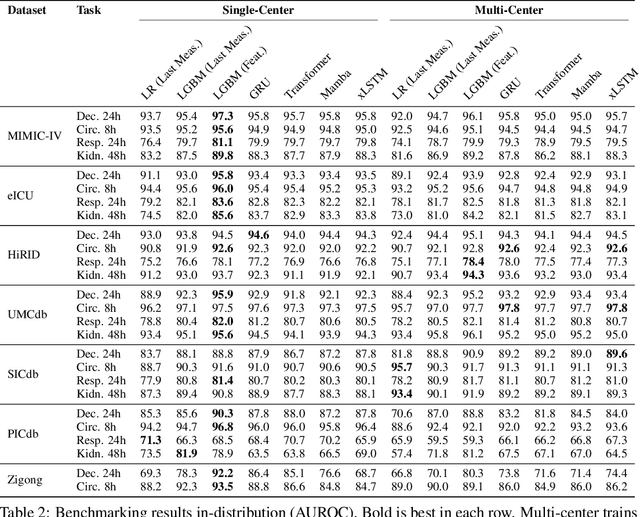
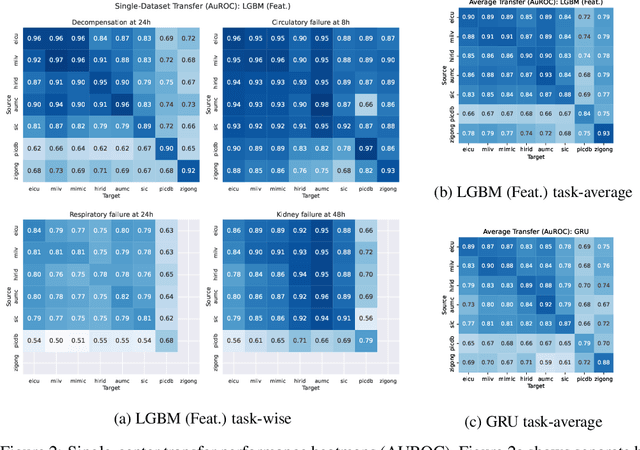
Abstract:Notable progress has been made in generalist medical large language models across various healthcare areas. However, large-scale modeling of in-hospital time series data - such as vital signs, lab results, and treatments in critical care - remains underexplored. Existing datasets are relatively small, but combining them can enhance patient diversity and improve model robustness. To effectively utilize these combined datasets for large-scale modeling, it is essential to address the distribution shifts caused by varying treatment policies, necessitating the harmonization of treatment variables across the different datasets. This work aims to establish a foundation for training large-scale multi-variate time series models on critical care data and to provide a benchmark for machine learning models in transfer learning across hospitals to study and address distribution shift challenges. We introduce a harmonized dataset for sequence modeling and transfer learning research, representing the first large-scale collection to include core treatment variables. Future plans involve expanding this dataset to support further advancements in transfer learning and the development of scalable, generalizable models for critical healthcare applications.
Dynamic Survival Analysis for Early Event Prediction
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:This study advances Early Event Prediction (EEP) in healthcare through Dynamic Survival Analysis (DSA), offering a novel approach by integrating risk localization into alarm policies to enhance clinical event metrics. By adapting and evaluating DSA models against traditional EEP benchmarks, our research demonstrates their ability to match EEP models on a time-step level and significantly improve event-level metrics through a new alarm prioritization scheme (up to 11% AuPRC difference). This approach represents a significant step forward in predictive healthcare, providing a more nuanced and actionable framework for early event prediction and management.
On the Importance of Step-wise Embeddings for Heterogeneous Clinical Time-Series
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in deep learning architectures for sequence modeling have not fully transferred to tasks handling time-series from electronic health records. In particular, in problems related to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU), the state-of-the-art remains to tackle sequence classification in a tabular manner with tree-based methods. Recent findings in deep learning for tabular data are now surpassing these classical methods by better handling the severe heterogeneity of data input features. Given the similar level of feature heterogeneity exhibited by ICU time-series and motivated by these findings, we explore these novel methods' impact on clinical sequence modeling tasks. By jointly using such advances in deep learning for tabular data, our primary objective is to underscore the importance of step-wise embeddings in time-series modeling, which remain unexplored in machine learning methods for clinical data. On a variety of clinically relevant tasks from two large-scale ICU datasets, MIMIC-III and HiRID, our work provides an exhaustive analysis of state-of-the-art methods for tabular time-series as time-step embedding models, showing overall performance improvement. In particular, we evidence the importance of feature grouping in clinical time-series, with significant performance gains when considering features within predefined semantic groups in the step-wise embedding module.
Delphic Offline Reinforcement Learning under Nonidentifiable Hidden Confounding
Jun 01, 2023



Abstract:A prominent challenge of offline reinforcement learning (RL) is the issue of hidden confounding: unobserved variables may influence both the actions taken by the agent and the observed outcomes. Hidden confounding can compromise the validity of any causal conclusion drawn from data and presents a major obstacle to effective offline RL. In the present paper, we tackle the problem of hidden confounding in the nonidentifiable setting. We propose a definition of uncertainty due to hidden confounding bias, termed delphic uncertainty, which uses variation over world models compatible with the observations, and differentiate it from the well-known epistemic and aleatoric uncertainties. We derive a practical method for estimating the three types of uncertainties, and construct a pessimistic offline RL algorithm to account for them. Our method does not assume identifiability of the unobserved confounders, and attempts to reduce the amount of confounding bias. We demonstrate through extensive experiments and ablations the efficacy of our approach on a sepsis management benchmark, as well as on electronic health records. Our results suggest that nonidentifiable hidden confounding bias can be mitigated to improve offline RL solutions in practice.
Laplace-Approximated Neural Additive Models: Improving Interpretability with Bayesian Inference
May 26, 2023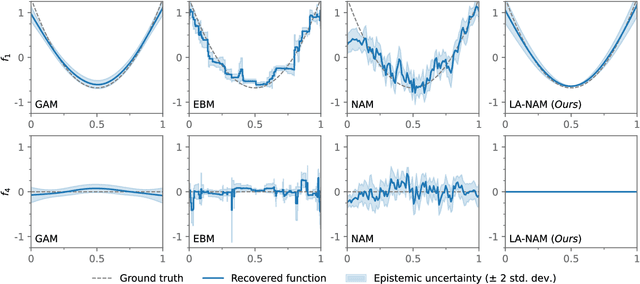
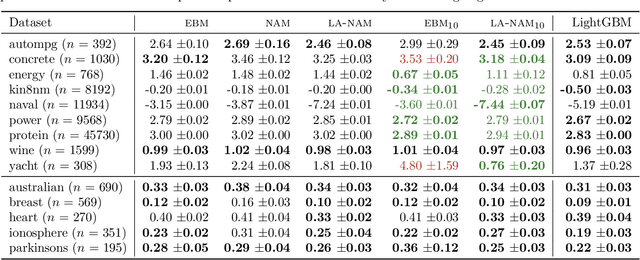
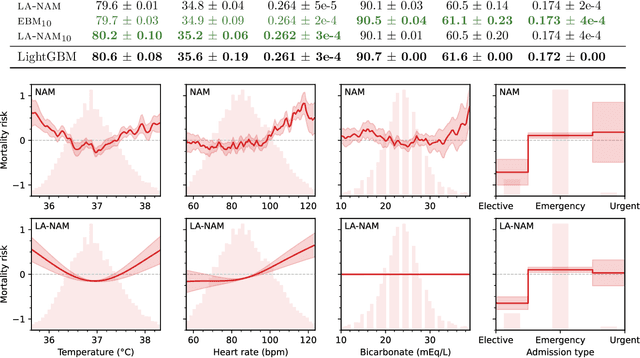
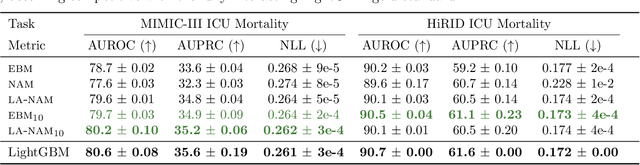
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have found successful applications in many fields, but their black-box nature hinders interpretability. This is addressed by the neural additive model (NAM), in which the network is divided into additive sub-networks, thus making apparent the interaction between input features and predictions. In this paper, we approach the additive structure from a Bayesian perspective and develop a practical Laplace approximation. This enhances interpretability in three primary ways: a) It provides credible intervals for the recovered feature interactions by estimating function-space uncertainty of the sub-networks; b) it yields a tractable estimate of the marginal likelihood, which can be used to perform an implicit selection of features through an empirical Bayes procedure; and c) it can be used to rank feature pairs as candidates for second-order interactions in fine-tuned interaction models. We show empirically that our proposed Laplace-approximated NAM (LA-NAM) improves performance and interpretability on tabular regression and classification datasets and challenging real-world medical tasks.
On the Importance of Clinical Notes in Multi-modal Learning for EHR Data
Dec 06, 2022Abstract:Understanding deep learning model behavior is critical to accepting machine learning-based decision support systems in the medical community. Previous research has shown that jointly using clinical notes with electronic health record (EHR) data improved predictive performance for patient monitoring in the intensive care unit (ICU). In this work, we explore the underlying reasons for these improvements. While relying on a basic attention-based model to allow for interpretability, we first confirm that performance significantly improves over state-of-the-art EHR data models when combining EHR data and clinical notes. We then provide an analysis showing improvements arise almost exclusively from a subset of notes containing broader context on patient state rather than clinician notes. We believe such findings highlight deep learning models for EHR data to be more limited by partially-descriptive data than by modeling choice, motivating a more data-centric approach in the field.
Temporal Label Smoothing for Early Prediction of Adverse Events
Aug 29, 2022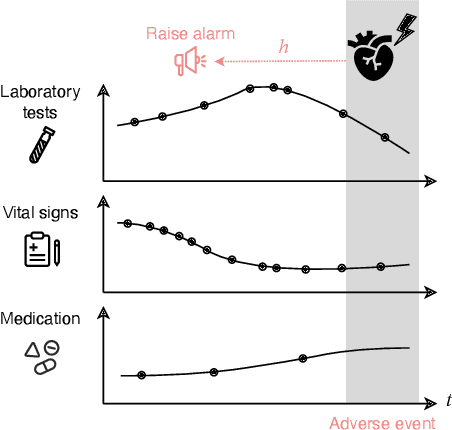

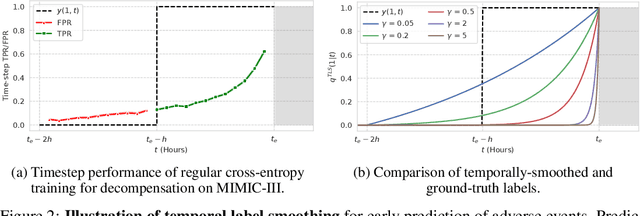
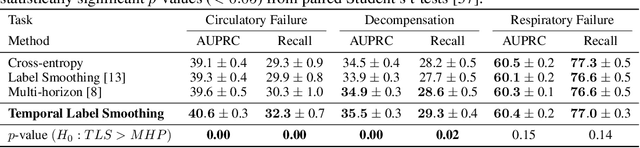
Abstract:Models that can predict adverse events ahead of time with low false-alarm rates are critical to the acceptance of decision support systems in the medical community. This challenging machine learning task remains typically treated as simple binary classification, with few bespoke methods proposed to leverage temporal dependency across samples. We propose Temporal Label Smoothing (TLS), a novel learning strategy that modulates smoothing strength as a function of proximity to the event of interest. This regularization technique reduces model confidence at the class boundary, where the signal is often noisy or uninformative, thus allowing training to focus on clinically informative data points away from this boundary region. From a theoretical perspective, we also show that our method can be framed as an extension of multi-horizon prediction, a learning heuristic proposed in other early prediction work. TLS empirically matches or outperforms considered competing methods on various early prediction benchmark tasks. In particular, our approach significantly improves performance on clinically-relevant metrics such as event recall at low false-alarm rates.
HiRID-ICU-Benchmark -- A Comprehensive Machine Learning Benchmark on High-resolution ICU Data
Nov 18, 2021
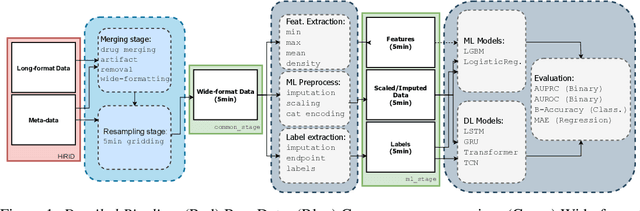
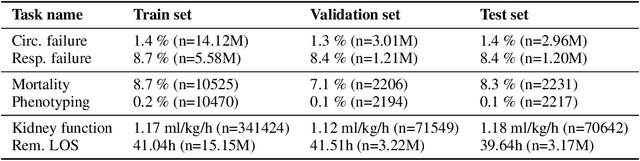
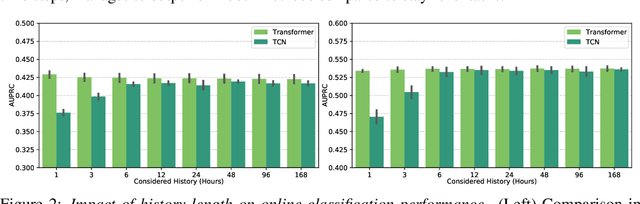
Abstract:The recent success of machine learning methods applied to time series collected from Intensive Care Units (ICU) exposes the lack of standardized machine learning benchmarks for developing and comparing such methods. While raw datasets, such as MIMIC-IV or eICU, can be freely accessed on Physionet, the choice of tasks and pre-processing is often chosen ad-hoc for each publication, limiting comparability across publications. In this work, we aim to improve this situation by providing a benchmark covering a large spectrum of ICU-related tasks. Using the HiRID dataset, we define multiple clinically relevant tasks developed in collaboration with clinicians. In addition, we provide a reproducible end-to-end pipeline to construct both data and labels. Finally, we provide an in-depth analysis of current state-of-the-art sequence modeling methods, highlighting some limitations of deep learning approaches for this type of data. With this benchmark, we hope to give the research community the possibility of a fair comparison of their work.
Neighborhood Contrastive Learning Applied to Online Patient Monitoring
Jun 09, 2021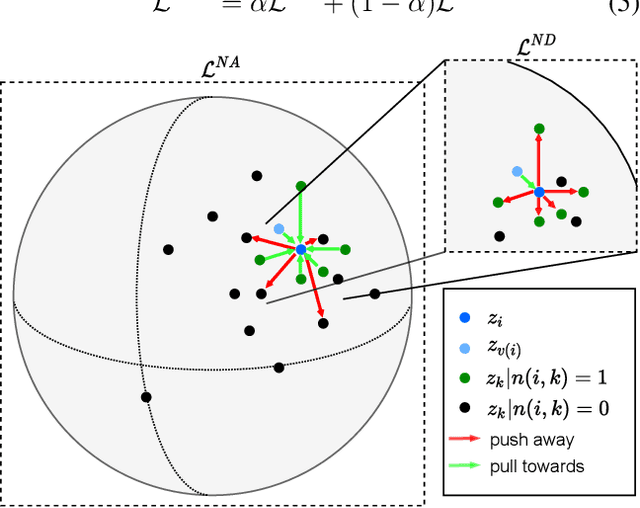
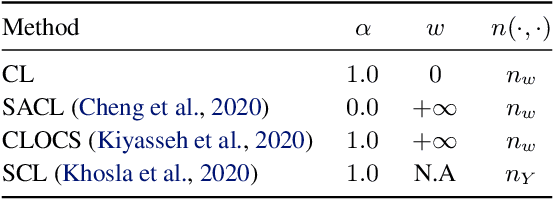
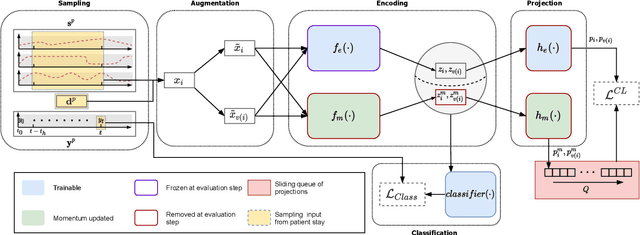
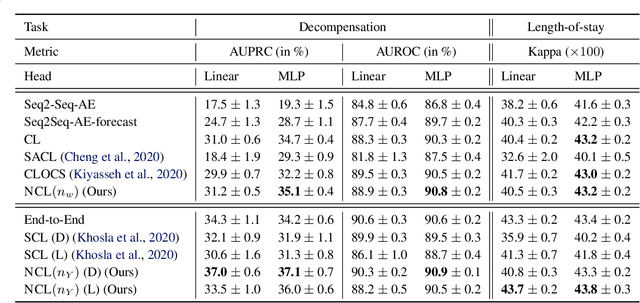
Abstract:Intensive care units (ICU) are increasingly looking towards machine learning for methods to provide online monitoring of critically ill patients. In machine learning, online monitoring is often formulated as a supervised learning problem. Recently, contrastive learning approaches have demonstrated promising improvements over competitive supervised benchmarks. These methods rely on well-understood data augmentation techniques developed for image data which do not apply to online monitoring. In this work, we overcome this limitation by supplementing time-series data augmentation techniques with a novel contrastive learning objective which we call neighborhood contrastive learning (NCL). Our objective explicitly groups together contiguous time segments from each patient while maintaining state-specific information. Our experiments demonstrate a marked improvement over existing work applying contrastive methods to medical time-series.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge