Huaixiao Tou
MVP: Multi-Stage Vision-Language Pre-Training via Multi-Level Semantic Alignment
Jan 29, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a Multi-stage Vision-language Pre-training (MVP) framework to learn cross-modality representation via multi-level semantic alignment. We introduce concepts in both modalities to construct two-level semantic representations for language and vision. Based on the multi-level input, we train the cross-modality model in two stages, namely, uni-modal learning and cross-modal learning. The former stage enforces within-modality interactions to learn multi-level semantics for each single modality. The latter stage enforces interactions across modalities via both coarse-grain and fine-grain semantic alignment tasks. Image-text matching and masked language modeling are then used to further optimize the pre-training model. Our model generates the-state-of-the-art results on several vision and language tasks.
Knowledge Perceived Multi-modal Pretraining in E-commerce
Aug 20, 2021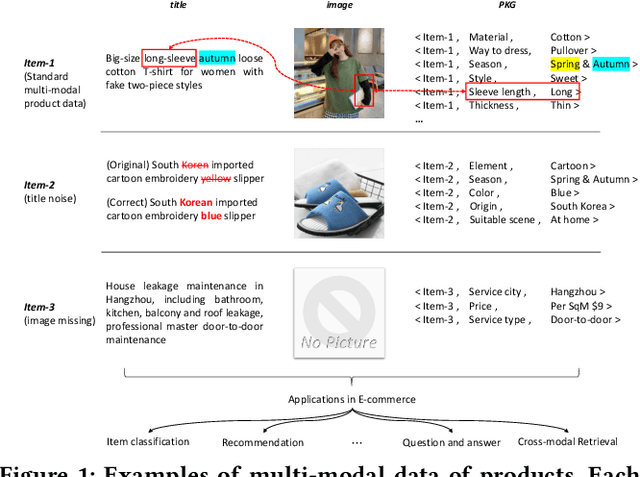
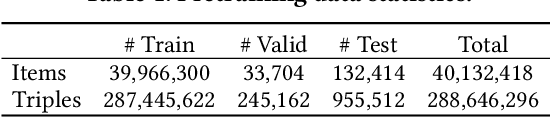
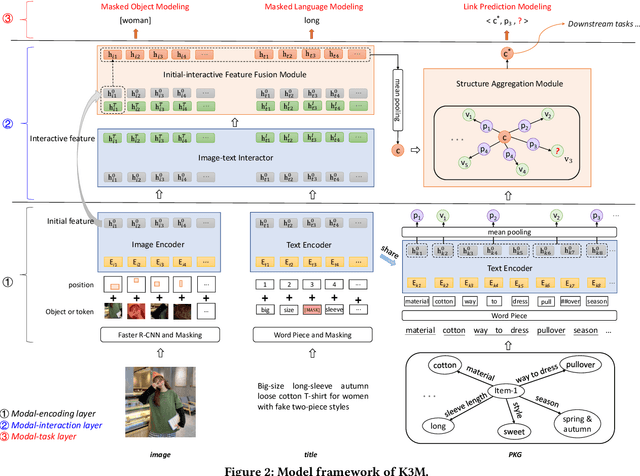
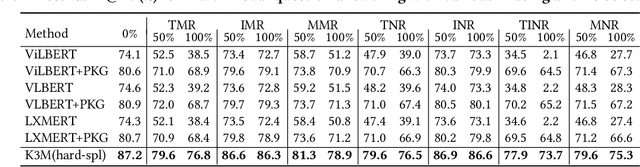
Abstract:In this paper, we address multi-modal pretraining of product data in the field of E-commerce. Current multi-modal pretraining methods proposed for image and text modalities lack robustness in the face of modality-missing and modality-noise, which are two pervasive problems of multi-modal product data in real E-commerce scenarios. To this end, we propose a novel method, K3M, which introduces knowledge modality in multi-modal pretraining to correct the noise and supplement the missing of image and text modalities. The modal-encoding layer extracts the features of each modality. The modal-interaction layer is capable of effectively modeling the interaction of multiple modalities, where an initial-interactive feature fusion model is designed to maintain the independence of image modality and text modality, and a structure aggregation module is designed to fuse the information of image, text, and knowledge modalities. We pretrain K3M with three pretraining tasks, including masked object modeling (MOM), masked language modeling (MLM), and link prediction modeling (LPM). Experimental results on a real-world E-commerce dataset and a series of product-based downstream tasks demonstrate that K3M achieves significant improvements in performances than the baseline and state-of-the-art methods when modality-noise or modality-missing exists.
AliCG: Fine-grained and Evolvable Conceptual Graph Construction for Semantic Search at Alibaba
Jun 03, 2021



Abstract:Conceptual graphs, which is a particular type of Knowledge Graphs, play an essential role in semantic search. Prior conceptual graph construction approaches typically extract high-frequent, coarse-grained, and time-invariant concepts from formal texts. In real applications, however, it is necessary to extract less-frequent, fine-grained, and time-varying conceptual knowledge and build taxonomy in an evolving manner. In this paper, we introduce an approach to implementing and deploying the conceptual graph at Alibaba. Specifically, We propose a framework called AliCG which is capable of a) extracting fine-grained concepts by a novel bootstrapping with alignment consensus approach, b) mining long-tail concepts with a novel low-resource phrase mining approach, c) updating the graph dynamically via a concept distribution estimation method based on implicit and explicit user behaviors. We have deployed the framework at Alibaba UC Browser. Extensive offline evaluation as well as online A/B testing demonstrate the efficacy of our approach.
OntoED: Low-resource Event Detection with Ontology Embedding
May 27, 2021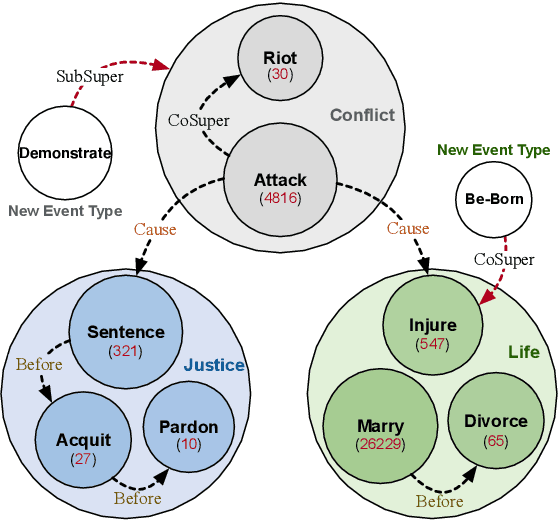

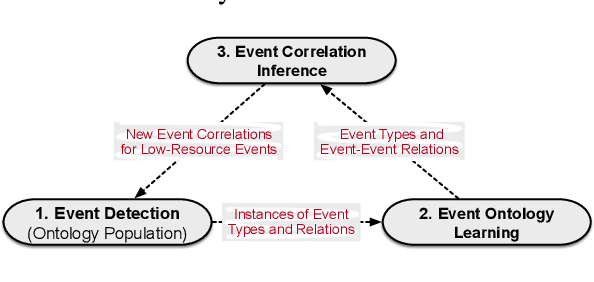
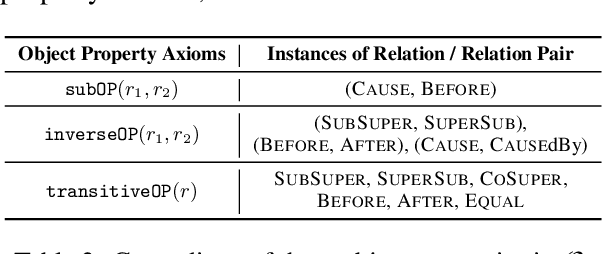
Abstract:Event Detection (ED) aims to identify event trigger words from a given text and classify it into an event type. Most of current methods to ED rely heavily on training instances, and almost ignore the correlation of event types. Hence, they tend to suffer from data scarcity and fail to handle new unseen event types. To address these problems, we formulate ED as a process of event ontology population: linking event instances to pre-defined event types in event ontology, and propose a novel ED framework entitled OntoED with ontology embedding. We enrich event ontology with linkages among event types, and further induce more event-event correlations. Based on the event ontology, OntoED can leverage and propagate correlation knowledge, particularly from data-rich to data-poor event types. Furthermore, OntoED can be applied to new unseen event types, by establishing linkages to existing ones. Experiments indicate that OntoED is more predominant and robust than previous approaches to ED, especially in data-scarce scenarios.
Text-guided Legal Knowledge Graph Reasoning
Apr 06, 2021



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the prosperity of legal artificial intelligence with the development of technologies. In this paper, we propose a novel legal application of legal provision prediction (LPP), which aims to predict the related legal provisions of affairs. We formulate this task as a challenging knowledge graph completion problem, which requires not only text understanding but also graph reasoning. To this end, we propose a novel text-guided graph reasoning approach. We collect amounts of real-world legal provision data from the Guangdong government service website and construct a legal dataset called LegalLPP. Extensive experimental results on the dataset show that our approach achieves better performance compared with baselines. The code and dataset are available in \url{https://github.com/zjunlp/LegalPP} for reproducibility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge