Huaijiang Zhu
Should We Learn Contact-Rich Manipulation Policies from Sampling-Based Planners?
Dec 12, 2024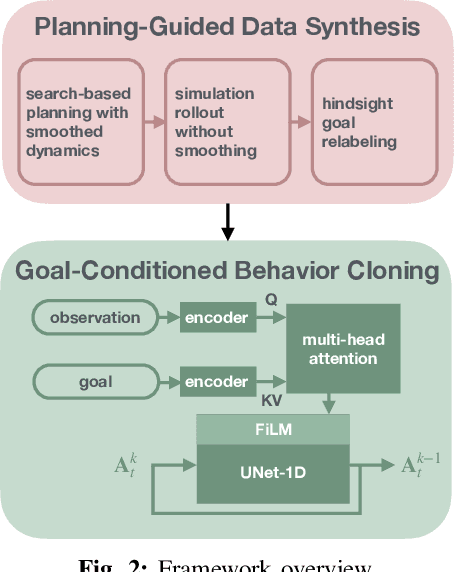
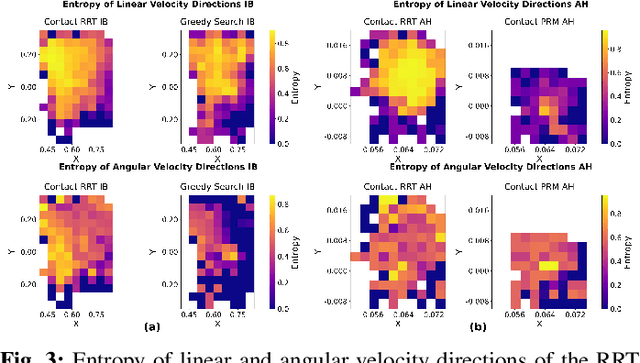

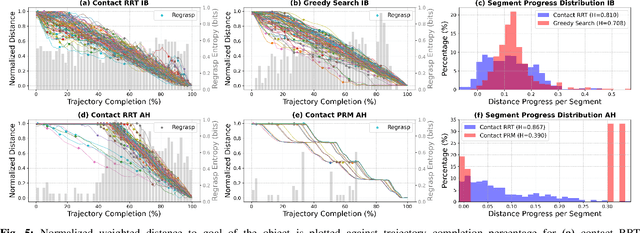
Abstract:The tremendous success of behavior cloning (BC) in robotic manipulation has been largely confined to tasks where demonstrations can be effectively collected through human teleoperation. However, demonstrations for contact-rich manipulation tasks that require complex coordination of multiple contacts are difficult to collect due to the limitations of current teleoperation interfaces. We investigate how to leverage model-based planning and optimization to generate training data for contact-rich dexterous manipulation tasks. Our analysis reveals that popular sampling-based planners like rapidly exploring random tree (RRT), while efficient for motion planning, produce demonstrations with unfavorably high entropy. This motivates modifications to our data generation pipeline that prioritizes demonstration consistency while maintaining solution diversity. Combined with a diffusion-based goal-conditioned BC approach, our method enables effective policy learning and zero-shot transfer to hardware for two challenging contact-rich manipulation tasks.
Is Linear Feedback on Smoothed Dynamics Sufficient for Stabilizing Contact-Rich Plans?
Nov 14, 2024



Abstract:Designing planners and controllers for contact-rich manipulation is extremely challenging as contact violates the smoothness conditions that many gradient-based controller synthesis tools assume. Contact smoothing approximates a non-smooth system with a smooth one, allowing one to use these synthesis tools more effectively. However, applying classical control synthesis methods to smoothed contact dynamics remains relatively under-explored. This paper analyzes the efficacy of linear controller synthesis using differential simulators based on contact smoothing. We introduce natural baselines for leveraging contact smoothing to compute (a) open-loop plans robust to uncertain conditions and/or dynamics, and (b) feedback gains to stabilize around open-loop plans. Using robotic bimanual whole-body manipulation as a testbed, we perform extensive empirical experiments on over 300 trajectories and analyze why LQR seems insufficient for stabilizing contact-rich plans. The video summarizing this paper and hardware experiments is found here: https://youtu.be/HLaKi6qbwQg?si=_zCAmBBD6rGSitm9.
Efficient Search and Learning for Agile Locomotion on Stepping Stones
Mar 06, 2024



Abstract:Legged robots have become capable of performing highly dynamic maneuvers in the past few years. However, agile locomotion in highly constrained environments such as stepping stones is still a challenge. In this paper, we propose a combination of model-based control, search, and learning to design efficient control policies for agile locomotion on stepping stones. In our framework, we use nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC) to generate whole-body motions for a given contact plan. To efficiently search for an optimal contact plan, we propose to use Monte Carlo tree search (MCTS). While the combination of MCTS and NMPC can quickly find a feasible plan for a given environment (a few seconds), it is not yet suitable to be used as a reactive policy. Hence, we generate a dataset for optimal goal-conditioned policy for a given scene and learn it through supervised learning. In particular, we leverage the power of diffusion models in handling multi-modality in the dataset. We test our proposed framework on a scenario where our quadruped robot Solo12 successfully jumps to different goals in a highly constrained environment.
MPC with Sensor-Based Online Cost Adaptation
Sep 20, 2022



Abstract:Model predictive control is a powerful tool to generate complex motions for robots. However, it often requires solving non-convex problems online to produce rich behaviors, which is computationally expensive and not always practical in real time. Additionally, direct integration of high dimensional sensor data (e.g. RGB-D images) in the feedback loop is challenging with current state-space methods. This paper aims to address both issues. It introduces a model predictive control scheme, where a neural network constantly updates the cost function of a quadratic program based on sensory inputs, aiming to minimize a general non-convex task loss without solving a non-convex problem online. By updating the cost, the robot is able to adapt to changes in the environment directly from sensor measurement without requiring a new cost design. Furthermore, since the quadratic program can be solved efficiently with hard constraints, a safe deployment on the robot is ensured. Experiments with a wide variety of reaching tasks on an industrial robot manipulator demonstrate that our method can efficiently solve complex non-convex problems with high-dimensional visual sensory inputs, while still being robust to external disturbances.
Efficient Object Manipulation Planning with Monte Carlo Tree Search
Jun 17, 2022



Abstract:This paper presents an efficient approach to object manipulation planning using Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) to find contact sequences and an efficient ADMM-based trajectory optimization algorithm to evaluate the dynamic feasibility of candidate contact sequences. To accelerate MCTS, we propose a methodology to learn a goal-conditioned policy-value network used to direct the search towards promising nodes. Further, manipulation-specific heuristics enable to drastically reduce the search space. Systematic object manipulation experiments in a physics simulator demonstrate the efficiency of our approach. In particular, our approach scales favorably for long manipulation sequences thanks to the learned policy-value network, significantly improving planning success rate.
Enabling Remote Whole-Body Control with 5G Edge Computing
Aug 19, 2020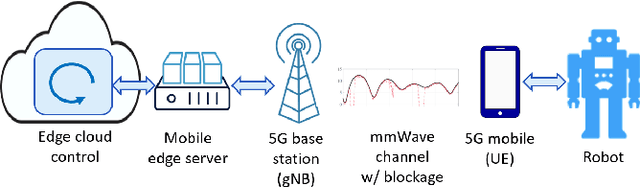
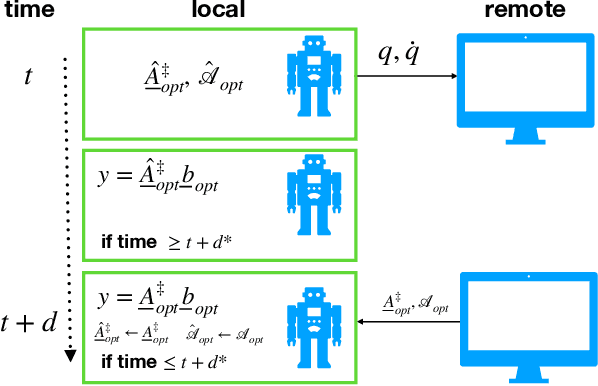
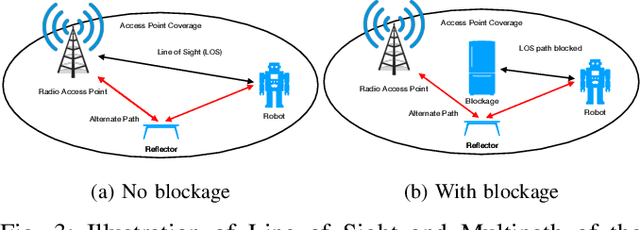
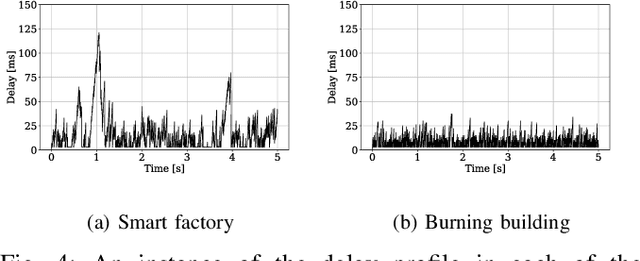
Abstract:Real-world applications require light-weight, energy-efficient, fully autonomous robots. Yet, increasing autonomy is oftentimes synonymous with escalating computational requirements. It might thus be desirable to offload intensive computation--not only sensing and planning, but also low-level whole-body control--to remote servers in order to reduce on-board computational needs. Fifth Generation (5G) wireless cellular technology, with its low latency and high bandwidth capabilities, has the potential to unlock cloud-based high performance control of complex robots. However, state-of-the-art control algorithms for legged robots can only tolerate very low control delays, which even ultra-low latency 5G edge computing can sometimes fail to achieve. In this work, we investigate the problem of cloud-based whole-body control of legged robots over a 5G link. We propose a novel approach that consists of a standard optimization-based controller on the network edge and a local linear, approximately optimal controller that significantly reduces on-board computational needs while increasing robustness to delay and possible loss of communication. Simulation experiments on humanoid balancing and walking tasks that includes a realistic 5G communication model demonstrate significant improvement of the reliability of robot locomotion under jitter and delays likely to experienced in 5G wireless links.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge