Hiroshi Ishikawa
BrainDecoder: Style-Based Visual Decoding of EEG Signals
Sep 09, 2024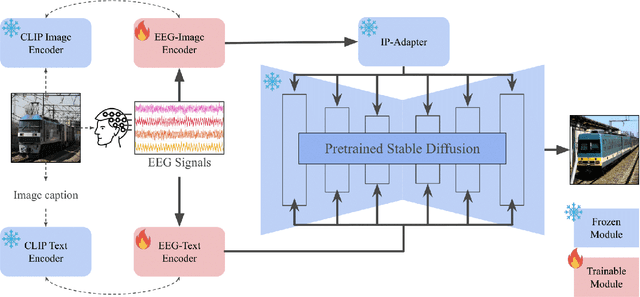

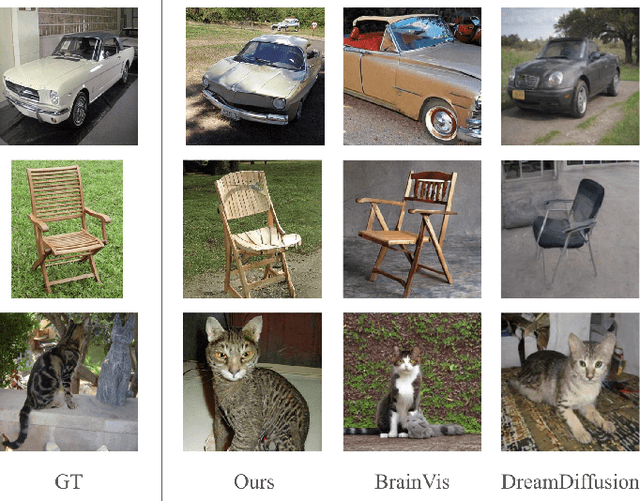
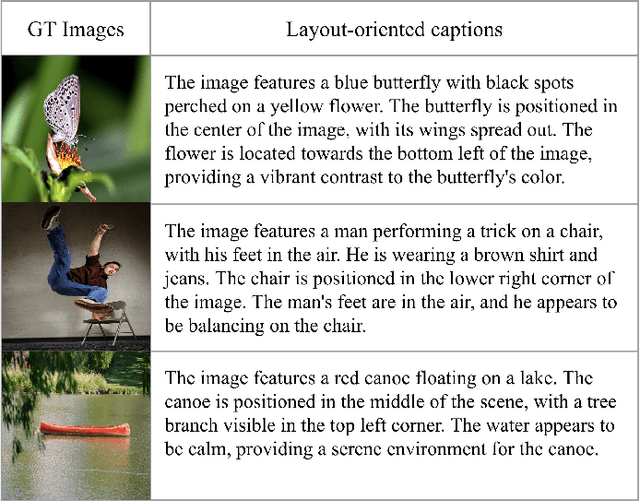
Abstract:Decoding neural representations of visual stimuli from electroencephalography (EEG) offers valuable insights into brain activity and cognition. Recent advancements in deep learning have significantly enhanced the field of visual decoding of EEG, primarily focusing on reconstructing the semantic content of visual stimuli. In this paper, we present a novel visual decoding pipeline that, in addition to recovering the content, emphasizes the reconstruction of the style, such as color and texture, of images viewed by the subject. Unlike previous methods, this ``style-based'' approach learns in the CLIP spaces of image and text separately, facilitating a more nuanced extraction of information from EEG signals. We also use captions for text alignment simpler than previously employed, which we find work better. Both quantitative and qualitative evaluations show that our method better preserves the style of visual stimuli and extracts more fine-grained semantic information from neural signals. Notably, it achieves significant improvements in quantitative results and sets a new state-of-the-art on the popular Brain2Image dataset.
Data-Dependent Higher-Order Clique Selection for Artery-Vein Segmentation by Energy Minimization
Dec 13, 2023Abstract:We propose a novel segmentation method based on energy minimization of higher-order potentials. We introduce higher-order terms into the energy to incorporate prior knowledge on the shape of the segments. The terms encourage certain sets of pixels to be entirely in one segment or the other. The sets can for instance be smooth curves in order to help delineate pulmonary vessels, which are known to run in almost straight lines. The higher-order terms can be converted to submodular first-order terms by adding auxiliary variables, which can then be globally minimized using graph cuts. We also determine the weight of these terms, or the degree of the aforementioned encouragement, in a principled way by learning from training data with the ground truth. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in a real-world application in fully-automatic pulmonary artery-vein segmentation in CT images.
P2Net: A Post-Processing Network for Refining Semantic Segmentation of LiDAR Point Cloud based on Consistency of Consecutive Frames
Dec 01, 2022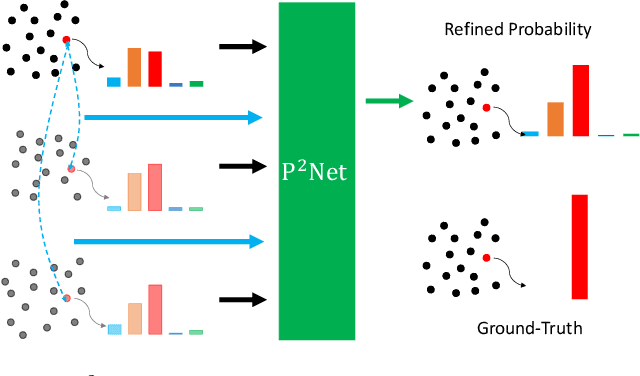
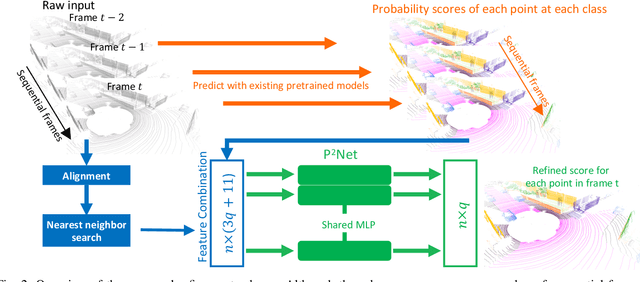
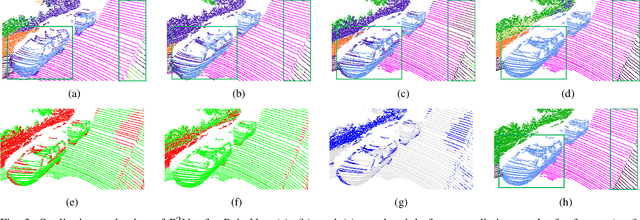
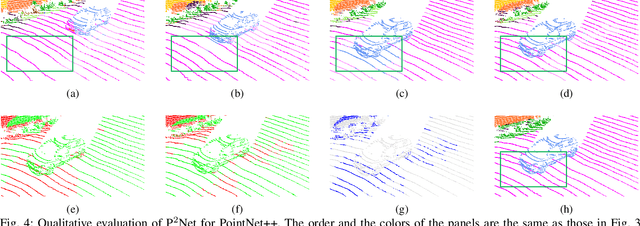
Abstract:We present a lightweight post-processing method to refine the semantic segmentation results of point cloud sequences. Most existing methods usually segment frame by frame and encounter the inherent ambiguity of the problem: based on a measurement in a single frame, labels are sometimes difficult to predict even for humans. To remedy this problem, we propose to explicitly train a network to refine these results predicted by an existing segmentation method. The network, which we call the P2Net, learns the consistency constraints between coincident points from consecutive frames after registration. We evaluate the proposed post-processing method both qualitatively and quantitatively on the SemanticKITTI dataset that consists of real outdoor scenes. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated by comparing the results predicted by two representative networks with and without the refinement by the post-processing network. Specifically, qualitative visualization validates the key idea that labels of the points that are difficult to predict can be corrected with P2Net. Quantitatively, overall mIoU is improved from 10.5% to 11.7% for PointNet [1] and from 10.8% to 15.9% for PointNet++ [2].
Uncertainty guided semi-supervised segmentation of retinal layers in OCT images
Mar 02, 2021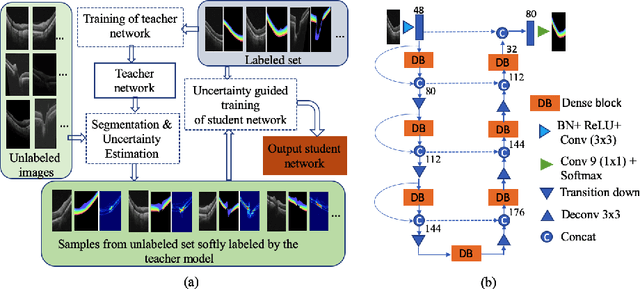
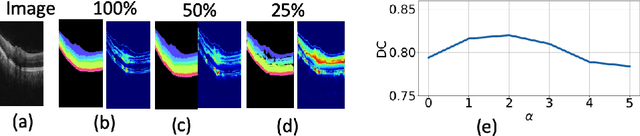
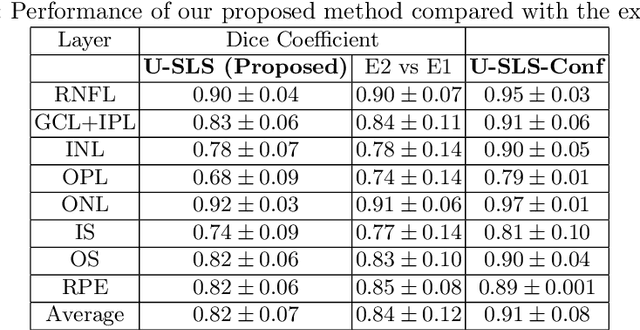
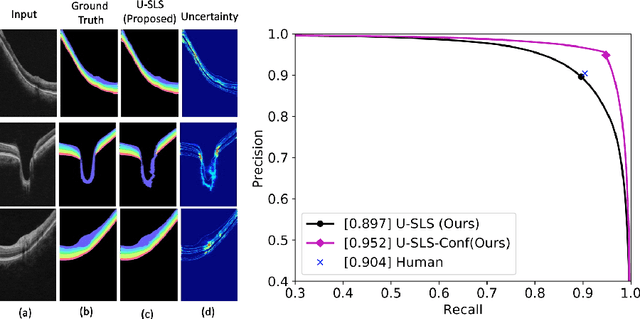
Abstract:Deep convolutional neural networks have shown outstanding performance in medical image segmentation tasks. The usual problem when training supervised deep learning methods is the lack of labeled data which is time-consuming and costly to obtain. In this paper, we propose a novel uncertainty-guided semi-supervised learning based on a student-teacher approach for training the segmentation network using limited labeled samples and a large number of unlabeled images. First, a teacher segmentation model is trained from the labeled samples using Bayesian deep learning. The trained model is used to generate soft segmentation labels and uncertainty maps for the unlabeled set. The student model is then updated using the softly segmented samples and the corresponding pixel-wise confidence of the segmentation quality estimated from the uncertainty of the teacher model using a newly designed loss function. Experimental results on a retinal layer segmentation task show that the proposed method improves the segmentation performance in comparison to the fully supervised approach and is on par with the expert annotator. The proposed semi-supervised segmentation framework is a key contribution and applicable for biomedical image segmentation across various imaging modalities where access to annotated medical images is challenging
* MICCAI,19
Self-supervised Denoising via Diffeomorphic Template Estimation: Application to Optical Coherence Tomography
Aug 18, 2020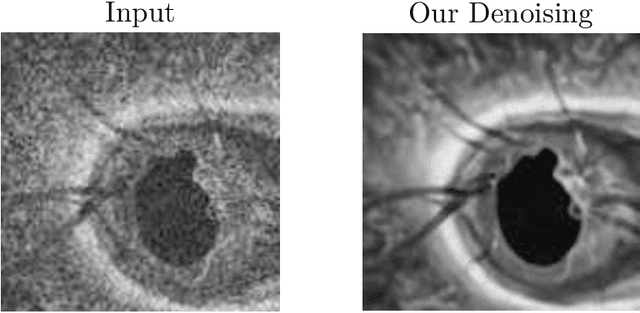
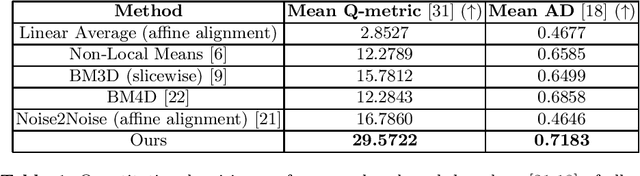
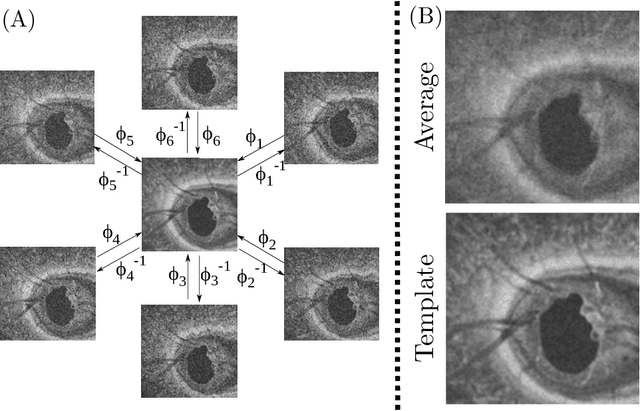
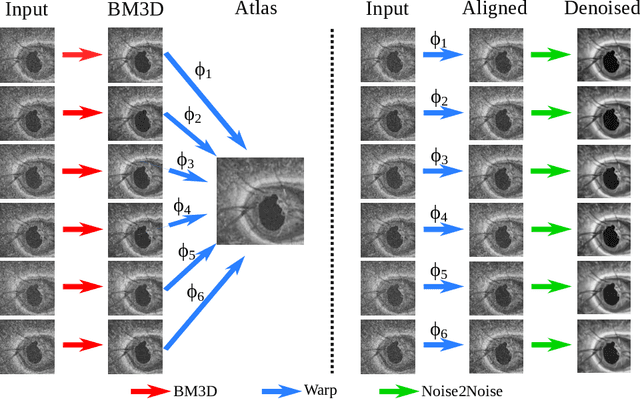
Abstract:Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is pervasive in both the research and clinical practice of Ophthalmology. However, OCT images are strongly corrupted by noise, limiting their interpretation. Current OCT denoisers leverage assumptions on noise distributions or generate targets for training deep supervised denoisers via averaging of repeat acquisitions. However, recent self-supervised advances allow the training of deep denoising networks using only repeat acquisitions without clean targets as ground truth, reducing the burden of supervised learning. Despite the clear advantages of self-supervised methods, their use is precluded as OCT shows strong structural deformations even between sequential scans of the same subject due to involuntary eye motion. Further, direct nonlinear alignment of repeats induces correlation of the noise between images. In this paper, we propose a joint diffeomorphic template estimation and denoising framework which enables the use of self-supervised denoising for motion deformed repeat acquisitions, without empirically registering their noise realizations. Strong qualitative and quantitative improvements are achieved in denoising OCT images, with generic utility in any imaging modality amenable to multiple exposures.
Dueling Deep Q-Network for Unsupervised Inter-frame Eye Movement Correction in Optical Coherence Tomography Volumes
Jul 03, 2020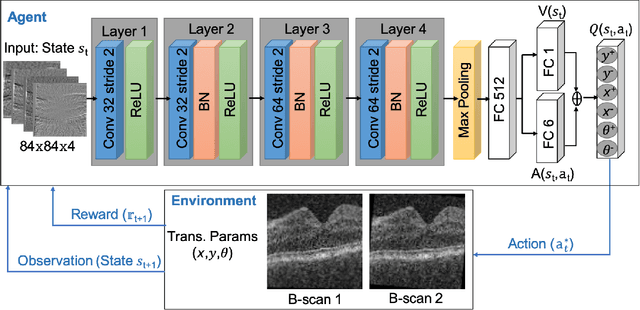
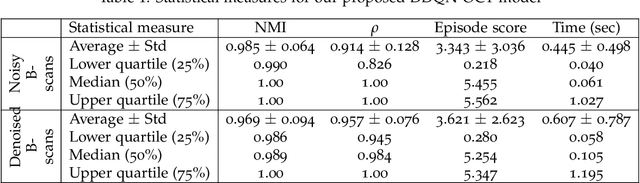
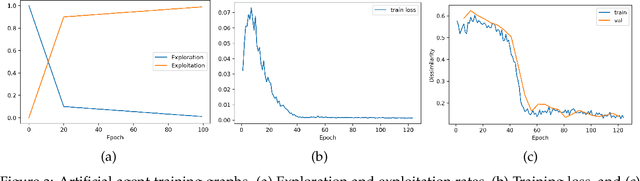
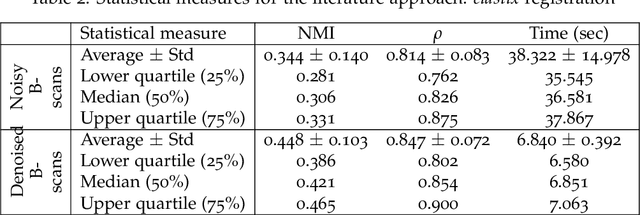
Abstract:In optical coherence tomography (OCT) volumes of retina, the sequential acquisition of the individual slices makes this modality prone to motion artifacts, misalignments between adjacent slices being the most noticeable. Any distortion in OCT volumes can bias structural analysis and influence the outcome of longitudinal studies. On the other hand, presence of speckle noise that is characteristic of this imaging modality, leads to inaccuracies when traditional registration techniques are employed. Also, the lack of a well-defined ground truth makes supervised deep-learning techniques ill-posed to tackle the problem. In this paper, we tackle these issues by using deep reinforcement learning to correct inter-frame movements in an unsupervised manner. Specifically, we use dueling deep Q-network to train an artificial agent to find the optimal policy, i.e. a sequence of actions, that best improves the alignment by maximizing the sum of reward signals. Instead of relying on the ground-truth of transformation parameters to guide the rewarding system, for the first time, we use a combination of intensity based image similarity metrics. Further, to avoid the agent bias towards speckle noise, we ensure the agent can see retinal layers as part of the interacting environment. For quantitative evaluation, we simulate the eye movement artifacts by applying 2D rigid transformations on individual B-scans. The proposed model achieves an average of 0.985 and 0.914 for normalized mutual information and correlation coefficient, respectively. We also compare our model with elastix intensity based medical image registration approach, where significant improvement is achieved by our model for both noisy and denoised volumes.
Inference of visual field test performance from OCT volumes using deep learning
Aug 26, 2019

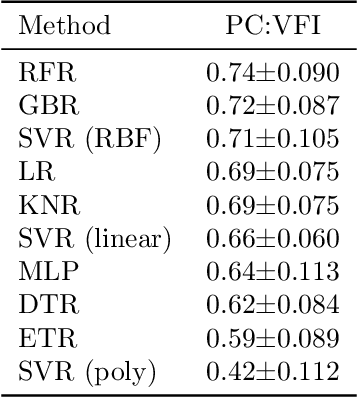

Abstract:Visual field tests (VFT) are pivotal for glaucoma diagnosis and conducted regularly to monitor disease progression. Here we address the question to what degree aggregate VFT measurements such as Visual Field Index (VFI) and Mean Deviation (MD) can be inferred from Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) scans of the Optic Nerve Head (ONH) or the macula. Accurate inference of VFT measurements from OCT could reduce examination time and cost. We propose a novel 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for this task and compare its accuracy with classical machine learning (ML) algorithms trained on common, segmentation-based OCT, features employed for glaucoma diagnostics. Peak accuracies were achieved on ONH scans when inferring VFI with a Pearson Correlation (PC) of 0.88$\pm$0.035 for the CNN and a significantly lower (p $<$ 0.01) PC of 0.74$\pm$0.090 for the best performing, classical ML algorithm - a Random Forest regressor. Estimation of MD was equally accurate with a PC of 0.88$\pm$0.023 on ONH scans for the CNN.
A feature agnostic approach for glaucoma detection in OCT volumes
Aug 15, 2018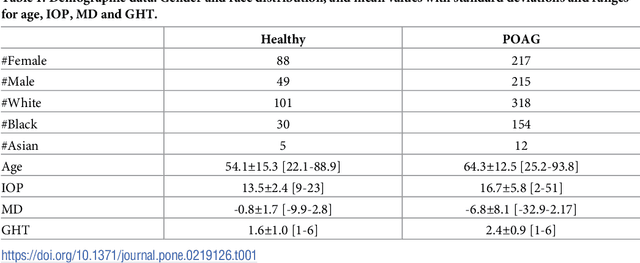
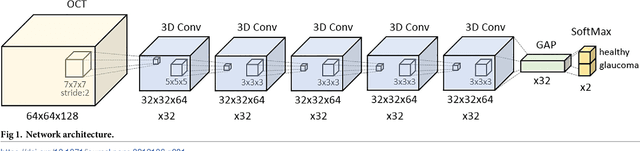
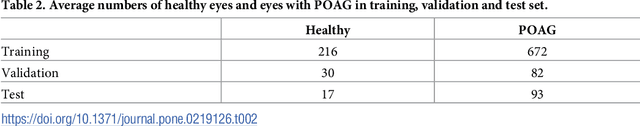
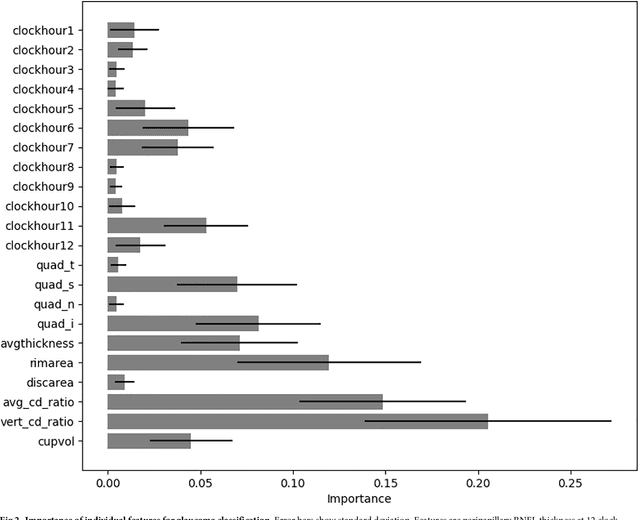
Abstract:Optical coherence tomography (OCT) based measurements of retinal layer thickness, such as the retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) and the ganglion cell with inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) are commonly used for the diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma. Previously, machine learning techniques have utilized segmentation-based imaging features such as the peripapillary RNFL thickness and the cup-to-disc ratio. Here, we propose a deep learning technique that classifies eyes as healthy or glaucomatous directly from raw, unsegmented OCT volumes of the optic nerve head (ONH) using a 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). We compared the accuracy of this technique with various feature-based machine learning algorithms and demonstrated the superiority of the proposed deep learning based method. Logistic regression was found to be the best performing classical machine learning technique with an AUC of 0.89. In direct comparison, the deep learning approach achieved a substantially higher AUC of 0.94 with the additional advantage of providing insight into which regions of an OCT volume are important for glaucoma detection. Computing Class Activation Maps (CAM), we found that the CNN identified neuroretinal rim and optic disc cupping as well as the lamina cribrosa (LC) and its surrounding areas as the regions significantly associated with the glaucoma classification. These regions anatomically correspond to the well established and commonly used clinical markers for glaucoma diagnosis such as increased cup volume, cup diameter, and neuroretinal rim thinning at the superior and inferior segments.
Mastering Sketching: Adversarial Augmentation for Structured Prediction
Mar 27, 2017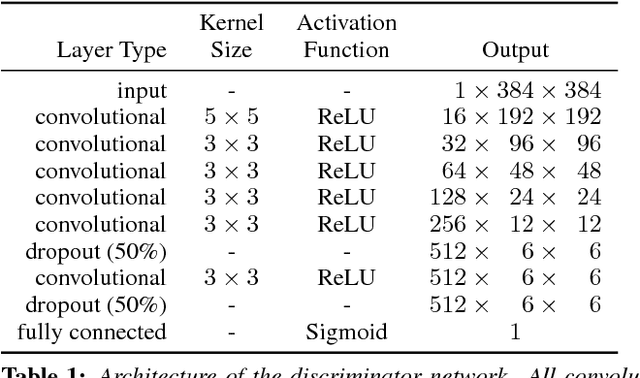
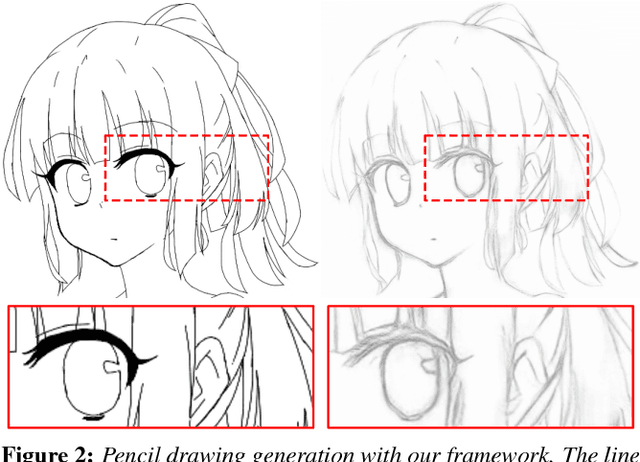


Abstract:We present an integral framework for training sketch simplification networks that convert challenging rough sketches into clean line drawings. Our approach augments a simplification network with a discriminator network, training both networks jointly so that the discriminator network discerns whether a line drawing is a real training data or the output of the simplification network, which in turn tries to fool it. This approach has two major advantages. First, because the discriminator network learns the structure in line drawings, it encourages the output sketches of the simplification network to be more similar in appearance to the training sketches. Second, we can also train the simplification network with additional unsupervised data, using the discriminator network as a substitute teacher. Thus, by adding only rough sketches without simplified line drawings, or only line drawings without the original rough sketches, we can improve the quality of the sketch simplification. We show how our framework can be used to train models that significantly outperform the state of the art in the sketch simplification task, despite using the same architecture for inference. We additionally present an approach to optimize for a single image, which improves accuracy at the cost of additional computation time. Finally, we show that, using the same framework, it is possible to train the network to perform the inverse problem, i.e., convert simple line sketches into pencil drawings, which is not possible using the standard mean squared error loss. We validate our framework with two user tests, where our approach is preferred to the state of the art in sketch simplification 92.3% of the time and obtains 1.2 more points on a scale of 1 to 5.
Representation and Measure of Structural Information
Jun 12, 2008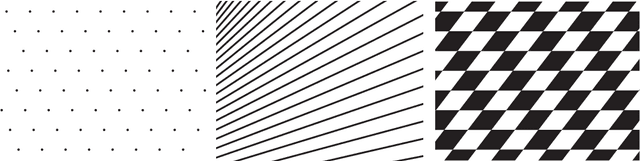


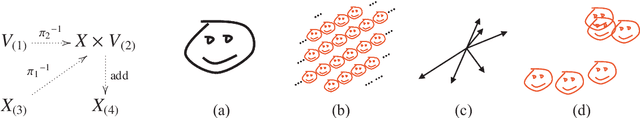
Abstract:We introduce a uniform representation of general objects that captures the regularities with respect to their structure. It allows a representation of a general class of objects including geometric patterns and images in a sparse, modular, hierarchical, and recursive manner. The representation can exploit any computable regularity in objects to compactly describe them, while also being capable of representing random objects as raw data. A set of rules uniformly dictates the interpretation of the representation into raw signal, which makes it possible to ask what pattern a given raw signal contains. Also, it allows simple separation of the information that we wish to ignore from that which we measure, by using a set of maps to delineate the a priori parts of the objects, leaving only the information in the structure. Using the representation, we introduce a measure of information in general objects relative to structures defined by the set of maps. We point out that the common prescription of encoding objects by strings to use Kolmogorov complexity is meaningless when, as often is the case, the encoding is not specified in any way other than that it exists. Noting this, we define the measure directly in terms of the structures of the spaces in which the objects reside. As a result, the measure is defined relative to a set of maps that characterize the structures. It turns out that the measure is equivalent to Kolmogorov complexity when it is defined relative to the maps characterizing the structure of natural numbers. Thus, the formulation gives the larger class of objects a meaningful measure of information that generalizes Kolmogorov complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge