James Fishbaugh
Segmentation-Renormalized Deep Feature Modulation for Unpaired Image Harmonization
Feb 16, 2021



Abstract:Deep networks are now ubiquitous in large-scale multi-center imaging studies. However, the direct aggregation of images across sites is contraindicated for downstream statistical and deep learning-based image analysis due to inconsistent contrast, resolution, and noise. To this end, in the absence of paired data, variations of Cycle-consistent Generative Adversarial Networks have been used to harmonize image sets between a source and target domain. Importantly, these methods are prone to instability, contrast inversion, intractable manipulation of pathology, and steganographic mappings which limit their reliable adoption in real-world medical imaging. In this work, based on an underlying assumption that morphological shape is consistent across imaging sites, we propose a segmentation-renormalized image translation framework to reduce inter-scanner heterogeneity while preserving anatomical layout. We replace the affine transformations used in the normalization layers within generative networks with trainable scale and shift parameters conditioned on jointly learned anatomical segmentation embeddings to modulate features at every level of translation. We evaluate our methodologies against recent baselines across several imaging modalities (T1w MRI, FLAIR MRI, and OCT) on datasets with and without lesions. Segmentation-renormalization for translation GANs yields superior image harmonization as quantified by Inception distances, demonstrates improved downstream utility via post-hoc segmentation accuracy, and improved robustness to translation perturbation and self-adversarial attacks.
Self-supervised Denoising via Diffeomorphic Template Estimation: Application to Optical Coherence Tomography
Aug 18, 2020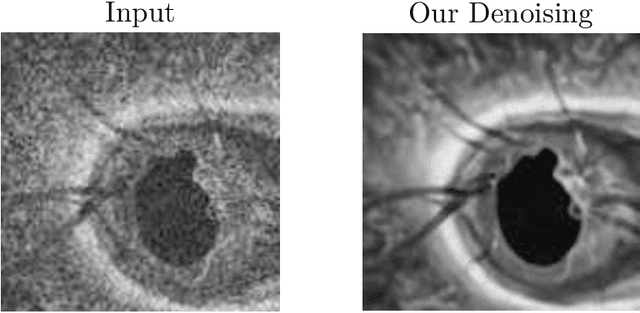
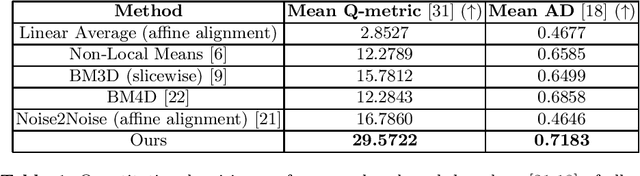
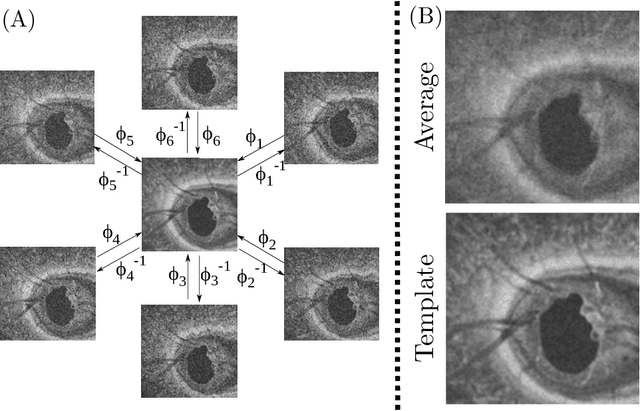
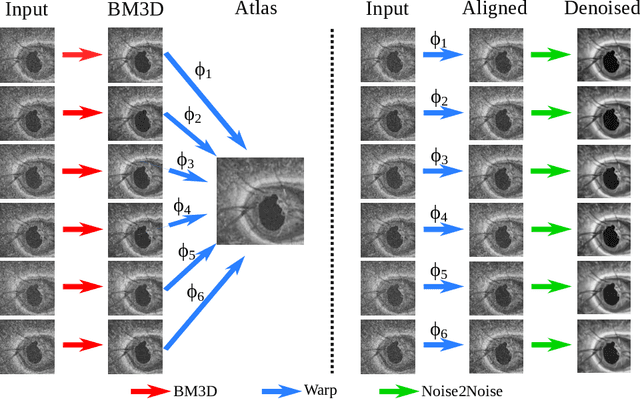
Abstract:Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is pervasive in both the research and clinical practice of Ophthalmology. However, OCT images are strongly corrupted by noise, limiting their interpretation. Current OCT denoisers leverage assumptions on noise distributions or generate targets for training deep supervised denoisers via averaging of repeat acquisitions. However, recent self-supervised advances allow the training of deep denoising networks using only repeat acquisitions without clean targets as ground truth, reducing the burden of supervised learning. Despite the clear advantages of self-supervised methods, their use is precluded as OCT shows strong structural deformations even between sequential scans of the same subject due to involuntary eye motion. Further, direct nonlinear alignment of repeats induces correlation of the noise between images. In this paper, we propose a joint diffeomorphic template estimation and denoising framework which enables the use of self-supervised denoising for motion deformed repeat acquisitions, without empirically registering their noise realizations. Strong qualitative and quantitative improvements are achieved in denoising OCT images, with generic utility in any imaging modality amenable to multiple exposures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge