Gadi Wollstein
Dueling Deep Q-Network for Unsupervised Inter-frame Eye Movement Correction in Optical Coherence Tomography Volumes
Jul 03, 2020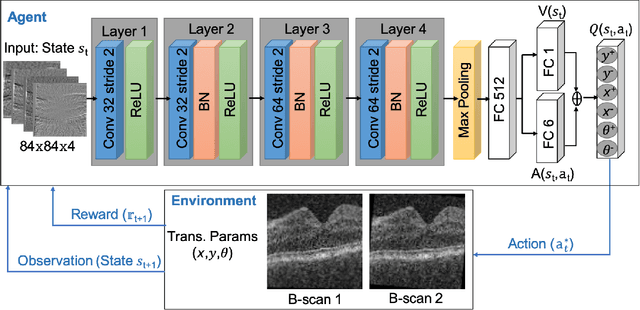
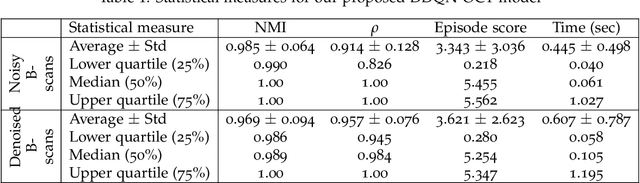
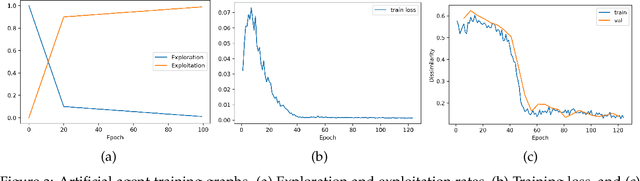
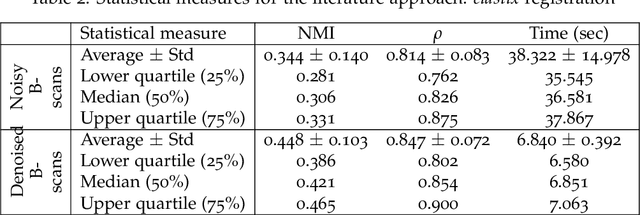
Abstract:In optical coherence tomography (OCT) volumes of retina, the sequential acquisition of the individual slices makes this modality prone to motion artifacts, misalignments between adjacent slices being the most noticeable. Any distortion in OCT volumes can bias structural analysis and influence the outcome of longitudinal studies. On the other hand, presence of speckle noise that is characteristic of this imaging modality, leads to inaccuracies when traditional registration techniques are employed. Also, the lack of a well-defined ground truth makes supervised deep-learning techniques ill-posed to tackle the problem. In this paper, we tackle these issues by using deep reinforcement learning to correct inter-frame movements in an unsupervised manner. Specifically, we use dueling deep Q-network to train an artificial agent to find the optimal policy, i.e. a sequence of actions, that best improves the alignment by maximizing the sum of reward signals. Instead of relying on the ground-truth of transformation parameters to guide the rewarding system, for the first time, we use a combination of intensity based image similarity metrics. Further, to avoid the agent bias towards speckle noise, we ensure the agent can see retinal layers as part of the interacting environment. For quantitative evaluation, we simulate the eye movement artifacts by applying 2D rigid transformations on individual B-scans. The proposed model achieves an average of 0.985 and 0.914 for normalized mutual information and correlation coefficient, respectively. We also compare our model with elastix intensity based medical image registration approach, where significant improvement is achieved by our model for both noisy and denoised volumes.
Inference of visual field test performance from OCT volumes using deep learning
Aug 26, 2019

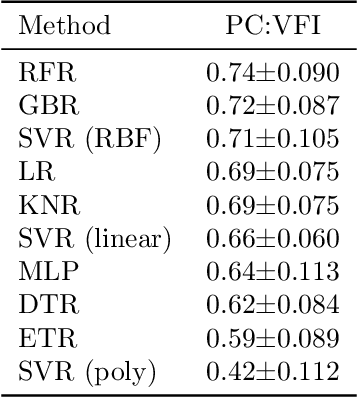

Abstract:Visual field tests (VFT) are pivotal for glaucoma diagnosis and conducted regularly to monitor disease progression. Here we address the question to what degree aggregate VFT measurements such as Visual Field Index (VFI) and Mean Deviation (MD) can be inferred from Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) scans of the Optic Nerve Head (ONH) or the macula. Accurate inference of VFT measurements from OCT could reduce examination time and cost. We propose a novel 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for this task and compare its accuracy with classical machine learning (ML) algorithms trained on common, segmentation-based OCT, features employed for glaucoma diagnostics. Peak accuracies were achieved on ONH scans when inferring VFI with a Pearson Correlation (PC) of 0.88$\pm$0.035 for the CNN and a significantly lower (p $<$ 0.01) PC of 0.74$\pm$0.090 for the best performing, classical ML algorithm - a Random Forest regressor. Estimation of MD was equally accurate with a PC of 0.88$\pm$0.023 on ONH scans for the CNN.
A feature agnostic approach for glaucoma detection in OCT volumes
Aug 15, 2018
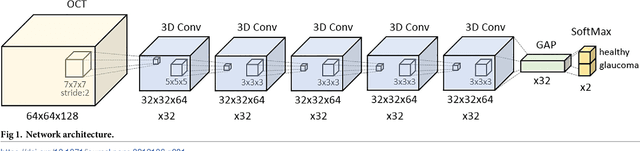
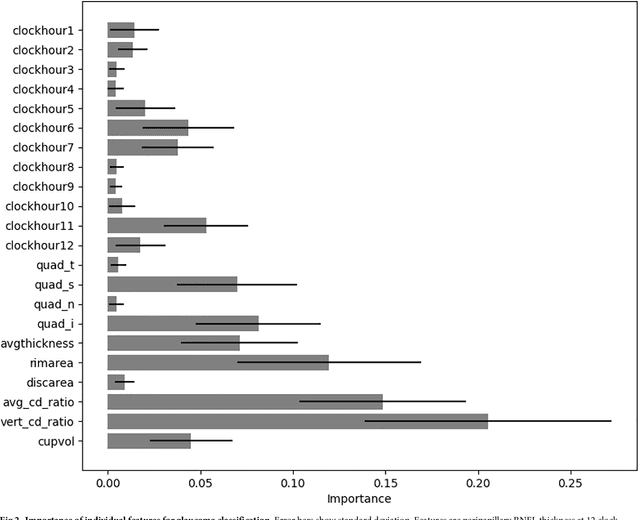
Abstract:Optical coherence tomography (OCT) based measurements of retinal layer thickness, such as the retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) and the ganglion cell with inner plexiform layer (GCIPL) are commonly used for the diagnosis and monitoring of glaucoma. Previously, machine learning techniques have utilized segmentation-based imaging features such as the peripapillary RNFL thickness and the cup-to-disc ratio. Here, we propose a deep learning technique that classifies eyes as healthy or glaucomatous directly from raw, unsegmented OCT volumes of the optic nerve head (ONH) using a 3D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). We compared the accuracy of this technique with various feature-based machine learning algorithms and demonstrated the superiority of the proposed deep learning based method. Logistic regression was found to be the best performing classical machine learning technique with an AUC of 0.89. In direct comparison, the deep learning approach achieved a substantially higher AUC of 0.94 with the additional advantage of providing insight into which regions of an OCT volume are important for glaucoma detection. Computing Class Activation Maps (CAM), we found that the CNN identified neuroretinal rim and optic disc cupping as well as the lamina cribrosa (LC) and its surrounding areas as the regions significantly associated with the glaucoma classification. These regions anatomically correspond to the well established and commonly used clinical markers for glaucoma diagnosis such as increased cup volume, cup diameter, and neuroretinal rim thinning at the superior and inferior segments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge