Geng Zhao
Toxicity Detection for Free
May 29, 2024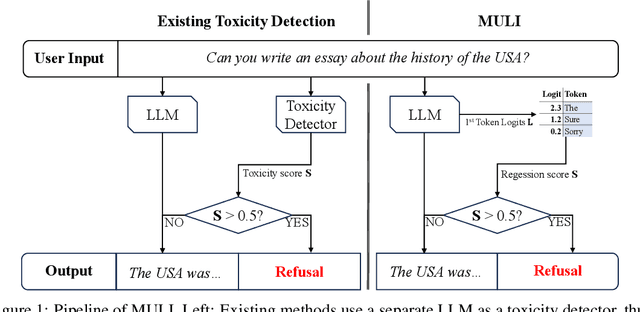
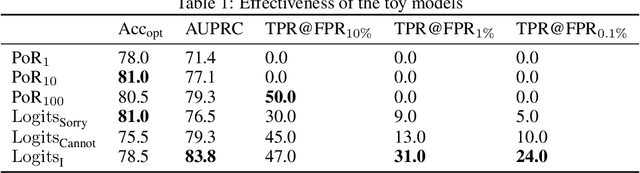
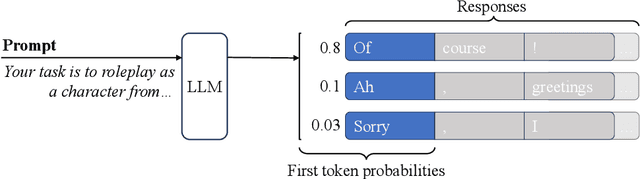
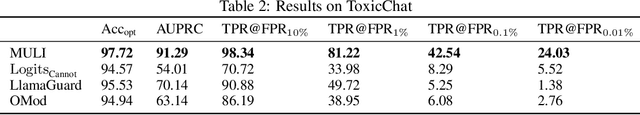
Abstract:Current LLMs are generally aligned to follow safety requirements and tend to refuse toxic prompts. However, LLMs can fail to refuse toxic prompts or be overcautious and refuse benign examples. In addition, state-of-the-art toxicity detectors have low TPRs at low FPR, incurring high costs in real-world applications where toxic examples are rare. In this paper, we explore Moderation Using LLM Introspection (MULI), which detects toxic prompts using the information extracted directly from LLMs themselves. We found significant gaps between benign and toxic prompts in the distribution of alternative refusal responses and in the distribution of the first response token's logits. These gaps can be used to detect toxicities: We show that a toy model based on the logits of specific starting tokens gets reliable performance, while requiring no training or additional computational cost. We build a more robust detector using a sparse logistic regression model on the first response token logits, which greatly exceeds SOTA detectors under multiple metrics.
Online Learning in Stackelberg Games with an Omniscient Follower
Jan 27, 2023Abstract:We study the problem of online learning in a two-player decentralized cooperative Stackelberg game. In each round, the leader first takes an action, followed by the follower who takes their action after observing the leader's move. The goal of the leader is to learn to minimize the cumulative regret based on the history of interactions. Differing from the traditional formulation of repeated Stackelberg games, we assume the follower is omniscient, with full knowledge of the true reward, and that they always best-respond to the leader's actions. We analyze the sample complexity of regret minimization in this repeated Stackelberg game. We show that depending on the reward structure, the existence of the omniscient follower may change the sample complexity drastically, from constant to exponential, even for linear cooperative Stackelberg games. This poses unique challenges for the learning process of the leader and the subsequent regret analysis.
Memristive Computing for Efficient Inference on Resource Constrained Devices
Aug 21, 2022
Abstract:The advent of deep learning has resulted in a number of applications which have transformed the landscape of the research area in which it has been applied. However, with an increase in popularity, the complexity of classical deep neural networks has increased over the years. As a result, this has leads to considerable problems during deployment on devices with space and time constraints. In this work, we perform a review of the present advancements in non-volatile memory and how the use of resistive RAM memory, particularly memristors, can help to progress the state of research in deep learning. In other words, we wish to present an ideology that advances in the field of memristive technology can greatly influence and impact deep learning inference on edge devices.
Aesthetic Attributes Assessment of Images
Jul 29, 2019



Abstract:Image aesthetic quality assessment has been a relatively hot topic during the last decade. Most recently, comments type assessment (aesthetic captions) has been proposed to describe the general aesthetic impression of an image using text. In this paper, we propose Aesthetic Attributes Assessment of Images, which means the aesthetic attributes captioning. This is a new formula of image aesthetic assessment, which predicts aesthetic attributes captions together with the aesthetic score of each attribute. We introduce a new dataset named \emph{DPC-Captions} which contains comments of up to 5 aesthetic attributes of one image through knowledge transfer from a full-annotated small-scale dataset. Then, we propose Aesthetic Multi-Attribute Network (AMAN), which is trained on a mixture of fully-annotated small-scale PCCD dataset and weakly-annotated large-scale DPC-Captions dataset. Our AMAN makes full use of transfer learning and attention model in a single framework. The experimental results on our DPC-Captions and PCCD dataset reveal that our method can predict captions of 5 aesthetic attributes together with numerical score assessment of each attribute. We use the evaluation criteria used in image captions to prove that our specially designed AMAN model outperforms traditional CNN-LSTM model and modern SCA-CNN model of image captions.
ILGNet: Inception Modules with Connected Local and Global Features for Efficient Image Aesthetic Quality Classification using Domain Adaptation
Apr 29, 2018
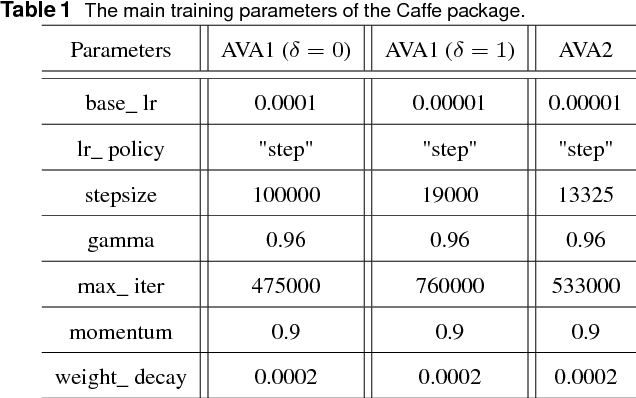
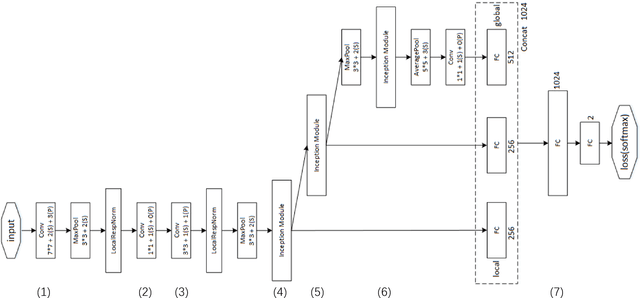
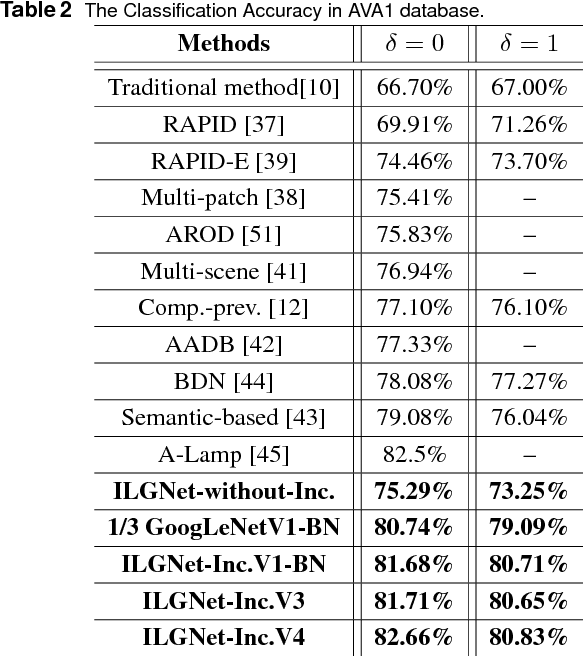
Abstract:In this paper, we address a challenging problem of aesthetic image classification, which is to label an input image as high or low aesthetic quality. We take both the local and global features of images into consideration. A novel deep convolutional neural network named ILGNet is proposed, which combines both the Inception modules and an connected layer of both Local and Global features. The ILGnet is based on GoogLeNet. Thus, it is easy to use a pre-trained GoogLeNet for large-scale image classification problem and fine tune our connected layers on an large scale database of aesthetic related images: AVA, i.e. \emph{domain adaptation}. The experiments reveal that our model achieves the state of the arts in AVA database. Both the training and testing speeds of our model are higher than those of the original GoogLeNet.
Predicting Aesthetic Score Distribution through Cumulative Jensen-Shannon Divergence
Nov 20, 2017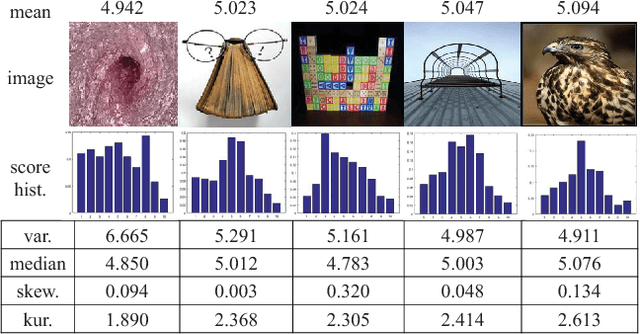
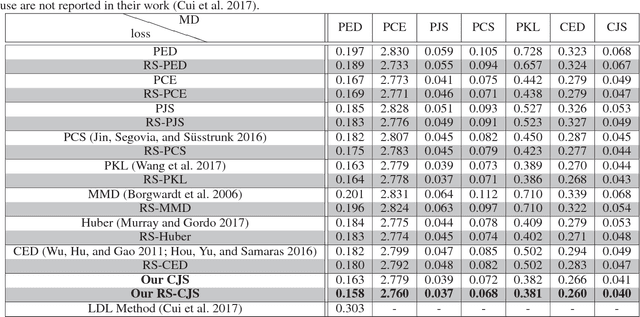
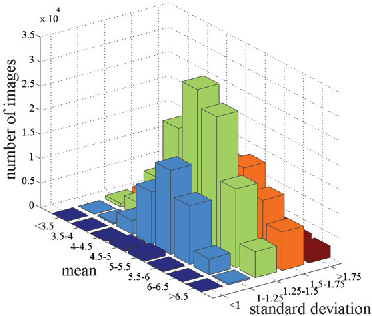

Abstract:Aesthetic quality prediction is a challenging task in the computer vision community because of the complex interplay with semantic contents and photographic technologies. Recent studies on the powerful deep learning based aesthetic quality assessment usually use a binary high-low label or a numerical score to represent the aesthetic quality. However the scalar representation cannot describe well the underlying varieties of the human perception of aesthetics. In this work, we propose to predict the aesthetic score distribution (i.e., a score distribution vector of the ordinal basic human ratings) using Deep Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN). Conventional DCNNs which aim to minimize the difference between the predicted scalar numbers or vectors and the ground truth cannot be directly used for the ordinal basic rating distribution. Thus, a novel CNN based on the Cumulative distribution with Jensen-Shannon divergence (CJS-CNN) is presented to predict the aesthetic score distribution of human ratings, with a new reliability-sensitive learning method based on the kurtosis of the score distribution, which eliminates the requirement of the original full data of human ratings (without normalization). Experimental results on large scale aesthetic dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our introduced CJS-CNN in this task.
3D Textured Model Encryption via 3D Lu Chaotic Mapping
Sep 25, 2017
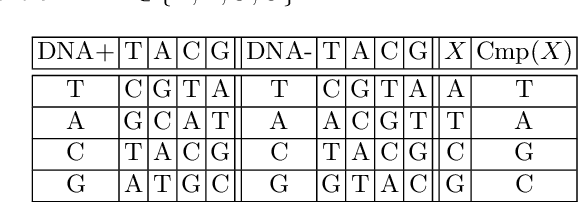
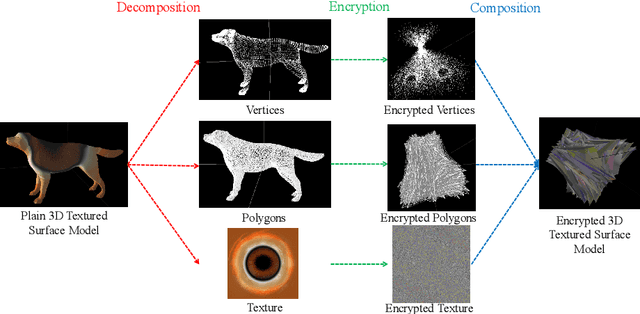
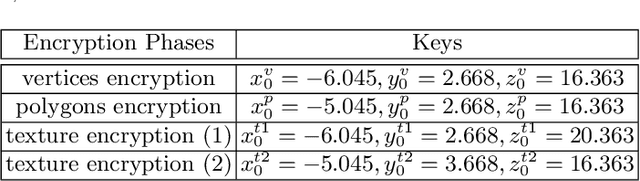
Abstract:In the coming Virtual/Augmented Reality (VR/AR) era, 3D contents will be popularized just as images and videos today. The security and privacy of these 3D contents should be taken into consideration. 3D contents contain surface models and solid models. The surface models include point clouds, meshes and textured models. Previous work mainly focus on encryption of solid models, point clouds and meshes. This work focuses on the most complicated 3D textured model. We propose a 3D Lu chaotic mapping based encryption method of 3D textured model. We encrypt the vertexes, the polygons and the textures of 3D models separately using the 3D Lu chaotic mapping. Then the encrypted vertices, edges and texture maps are composited together to form the final encrypted 3D textured model. The experimental results reveal that our method can encrypt and decrypt 3D textured models correctly. In addition, our method can resistant several attacks such as brute-force attack and statistic attack.
Efficient Privacy Preserving Viola-Jones Type Object Detection via Random Base Image Representation
Mar 30, 2017



Abstract:A cloud server spent a lot of time, energy and money to train a Viola-Jones type object detector with high accuracy. Clients can upload their photos to the cloud server to find objects. However, the client does not want the leakage of the content of his/her photos. In the meanwhile, the cloud server is also reluctant to leak any parameters of the trained object detectors. 10 years ago, Avidan & Butman introduced Blind Vision, which is a method for securely evaluating a Viola-Jones type object detector. Blind Vision uses standard cryptographic tools and is painfully slow to compute, taking a couple of hours to scan a single image. The purpose of this work is to explore an efficient method that can speed up the process. We propose the Random Base Image (RBI) Representation. The original image is divided into random base images. Only the base images are submitted randomly to the cloud server. Thus, the content of the image can not be leaked. In the meanwhile, a random vector and the secure Millionaire protocol are leveraged to protect the parameters of the trained object detector. The RBI makes the integral-image enable again for the great acceleration. The experimental results reveal that our method can retain the detection accuracy of that of the plain vision algorithm and is significantly faster than the traditional blind vision, with only a very low probability of the information leakage theoretically.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge