Feiran Li
Towards Size-invariant Salient Object Detection: A Generic Evaluation and Optimization Approach
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates a fundamental yet underexplored issue in Salient Object Detection (SOD): the size-invariant property for evaluation protocols, particularly in scenarios when multiple salient objects of significantly different sizes appear within a single image. We first present a novel perspective to expose the inherent size sensitivity of existing widely used SOD metrics. Through careful theoretical derivations, we show that the evaluation outcome of an image under current SOD metrics can be essentially decomposed into a sum of several separable terms, with the contribution of each term being directly proportional to its corresponding region size. Consequently, the prediction errors would be dominated by the larger regions, while smaller yet potentially more semantically important objects are often overlooked, leading to biased performance assessments and practical degradation. To address this challenge, a generic Size-Invariant Evaluation (SIEva) framework is proposed. The core idea is to evaluate each separable component individually and then aggregate the results, thereby effectively mitigating the impact of size imbalance across objects. Building upon this, we further develop a dedicated optimization framework (SIOpt), which adheres to the size-invariant principle and significantly enhances the detection of salient objects across a broad range of sizes. Notably, SIOpt is model-agnostic and can be seamlessly integrated with a wide range of SOD backbones. Theoretically, we also present generalization analysis of SOD methods and provide evidence supporting the validity of our new evaluation protocols. Finally, comprehensive experiments speak to the efficacy of our proposed approach. The code is available at https://github.com/Ferry-Li/SI-SOD.
MOL: Joint Estimation of Micro-Expression, Optical Flow, and Landmark via Transformer-Graph-Style Convolution
Jun 17, 2025



Abstract:Facial micro-expression recognition (MER) is a challenging problem, due to transient and subtle micro-expression (ME) actions. Most existing methods depend on hand-crafted features, key frames like onset, apex, and offset frames, or deep networks limited by small-scale and low-diversity datasets. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end micro-action-aware deep learning framework with advantages from transformer, graph convolution, and vanilla convolution. In particular, we propose a novel F5C block composed of fully-connected convolution and channel correspondence convolution to directly extract local-global features from a sequence of raw frames, without the prior knowledge of key frames. The transformer-style fully-connected convolution is proposed to extract local features while maintaining global receptive fields, and the graph-style channel correspondence convolution is introduced to model the correlations among feature patterns. Moreover, MER, optical flow estimation, and facial landmark detection are jointly trained by sharing the local-global features. The two latter tasks contribute to capturing facial subtle action information for MER, which can alleviate the impact of insufficient training data. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework (i) outperforms the state-of-the-art MER methods on CASME II, SAMM, and SMIC benchmarks, (ii) works well for optical flow estimation and facial landmark detection, and (iii) can capture facial subtle muscle actions in local regions associated with MEs. The code is available at https://github.com/CYF-cuber/MOL.
One Image is Worth a Thousand Words: A Usability Preservable Text-Image Collaborative Erasing Framework
May 16, 2025Abstract:Concept erasing has recently emerged as an effective paradigm to prevent text-to-image diffusion models from generating visually undesirable or even harmful content. However, current removal methods heavily rely on manually crafted text prompts, making it challenging to achieve a high erasure (efficacy) while minimizing the impact on other benign concepts (usability). In this paper, we attribute the limitations to the inherent gap between the text and image modalities, which makes it hard to transfer the intricately entangled concept knowledge from text prompts to the image generation process. To address this, we propose a novel solution by directly integrating visual supervision into the erasure process, introducing the first text-image Collaborative Concept Erasing (Co-Erasing) framework. Specifically, Co-Erasing describes the concept jointly by text prompts and the corresponding undesirable images induced by the prompts, and then reduces the generating probability of the target concept through negative guidance. This approach effectively bypasses the knowledge gap between text and image, significantly enhancing erasure efficacy. Additionally, we design a text-guided image concept refinement strategy that directs the model to focus on visual features most relevant to the specified text concept, minimizing disruption to other benign concepts. Finally, comprehensive experiments suggest that Co-Erasing outperforms state-of-the-art erasure approaches significantly with a better trade-off between efficacy and usability. Codes are available at https://github.com/Ferry-Li/Co-Erasing.
Noise Modeling in One Hour: Minimizing Preparation Efforts for Self-supervised Low-Light RAW Image Denoising
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Noise synthesis is a promising solution for addressing the data shortage problem in data-driven low-light RAW image denoising. However, accurate noise synthesis methods often necessitate labor-intensive calibration and profiling procedures during preparation, preventing them from landing to practice at scale. This work introduces a practically simple noise synthesis pipeline based on detailed analyses of noise properties and extensive justification of widespread techniques. Compared to other approaches, our proposed pipeline eliminates the cumbersome system gain calibration and signal-independent noise profiling steps, reducing the preparation time for noise synthesis from days to hours. Meanwhile, our method exhibits strong denoising performance, showing an up to 0.54dB PSNR improvement over the current state-of-the-art noise synthesis technique. Code is released at https://github.com/SonyResearch/raw_image_denoising
Beyond RGB: Adaptive Parallel Processing for RAW Object Detection
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Object detection models are typically applied to standard RGB images processed through Image Signal Processing (ISP) pipelines, which are designed to enhance sensor-captured RAW images for human vision. However, these ISP functions can lead to a loss of critical information that may be essential in optimizing for computer vision tasks, such as object detection. In this work, we introduce Raw Adaptation Module (RAM), a module designed to replace the traditional ISP, with parameters optimized specifically for RAW object detection. Inspired by the parallel processing mechanisms of the human visual system, RAM departs from existing learned ISP methods by applying multiple ISP functions in parallel rather than sequentially, allowing for a more comprehensive capture of image features. These processed representations are then fused in a specialized module, which dynamically integrates and optimizes the information for the target task. This novel approach not only leverages the full potential of RAW sensor data but also enables task-specific pre-processing, resulting in superior object detection performance. Our approach outperforms RGB-based methods and achieves state-of-the-art results across diverse RAW image datasets under varying lighting conditions and dynamic ranges.
Size-invariance Matters: Rethinking Metrics and Losses for Imbalanced Multi-object Salient Object Detection
May 16, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores the size-invariance of evaluation metrics in Salient Object Detection (SOD), especially when multiple targets of diverse sizes co-exist in the same image. We observe that current metrics are size-sensitive, where larger objects are focused, and smaller ones tend to be ignored. We argue that the evaluation should be size-invariant because bias based on size is unjustified without additional semantic information. In pursuit of this, we propose a generic approach that evaluates each salient object separately and then combines the results, effectively alleviating the imbalance. We further develop an optimization framework tailored to this goal, achieving considerable improvements in detecting objects of different sizes. Theoretically, we provide evidence supporting the validity of our new metrics and present the generalization analysis of SOD. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/Ferry-Li/SI-SOD.
Using panoramic videos for multi-person localization and tracking in a 3D panoramic coordinate
Dec 05, 2019
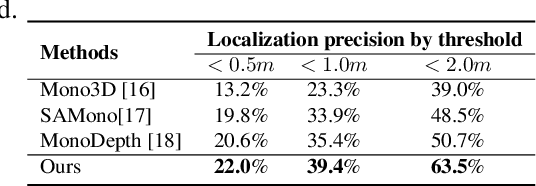

Abstract:This work proposes a new human-related video processing task named 3D panoramic multi-person localization and tracking. With a benchmark dataset and a simple yet effective solution, it establishes a new paradigm for multi-person tracking systems and related applications. Unlike existing methods that can only work on a 2D coordinate or a narrow-angle-view 3D coordinate, our proposal can maximally explore the 3D trajectory information of tracking targets. This is approached by applying camera geometry to transform human locations from 2D panoramic image coordinates to a 3D panoramic camera coordinate, and then by applying a tracking algorithm that associates human appearance and 3D trajectory together.
Multi-View Inpainting for RGB-D Sequence
Nov 22, 2018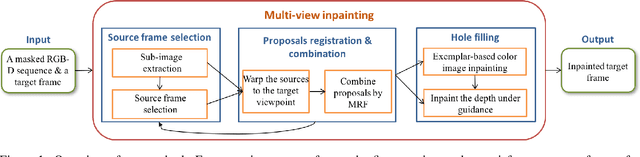
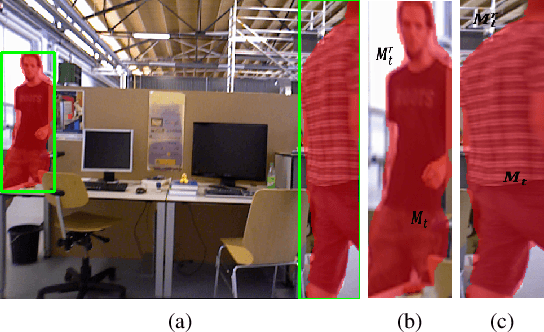
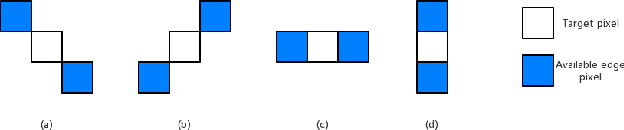

Abstract:In this work we propose a novel approach to remove undesired objects from RGB-D sequences captured with freely moving cameras, which enables static 3D reconstruction. Our method jointly uses existing information from multiple frames as well as generates new one via inpainting techniques. We use balanced rules to select source frames; local homography based image warping method for alignment and Markov random field (MRF) based approach for combining existing information. For the left holes, we employ exemplar based multi-view inpainting method to deal with the color image and coherently use it as guidance to complete the depth correspondence. Experiments show that our approach is qualified for removing the undesired objects and inpainting the holes.
* 10 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge