Eva Mohedano
Dublin City University
QMRNet: Quality Metric Regression for EO Image Quality Assessment and Super-Resolution
Oct 14, 2022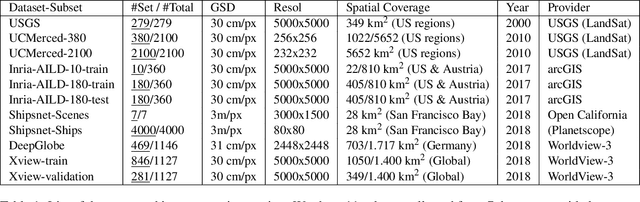
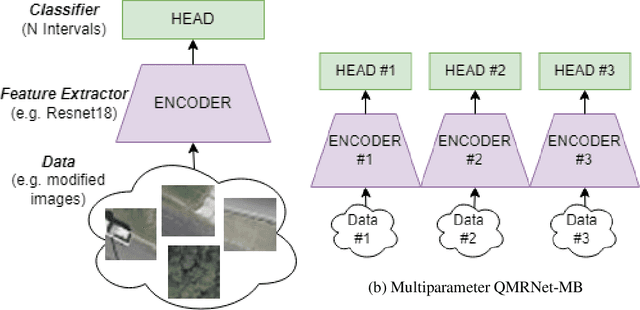
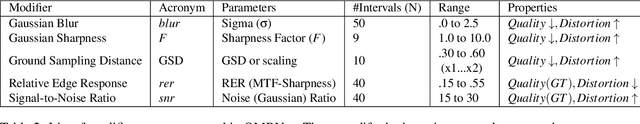
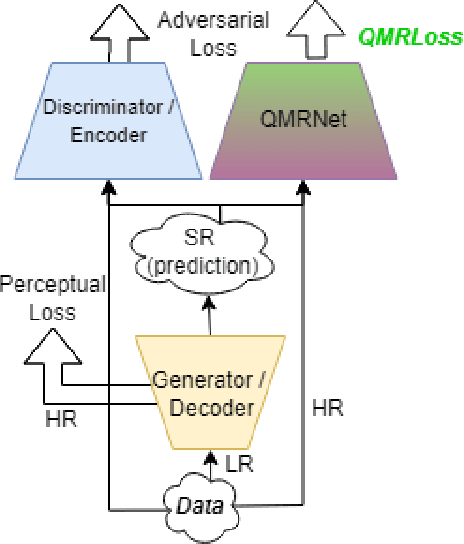
Abstract:Latest advances in Super-Resolution (SR) have been tested with general purpose images such as faces, landscapes and objects, mainly unused for the task of super-resolving Earth Observation (EO) images. In this research paper, we benchmark state-of-the-art SR algorithms for distinct EO datasets using both Full-Reference and No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (IQA) metrics. We also propose a novel Quality Metric Regression Network (QMRNet) that is able to predict quality (as a No-Reference metric) by training on any property of the image (i.e. its resolution, its distortions...) and also able to optimize SR algorithms for a specific metric objective. This work is part of the implementation of the framework IQUAFLOW which has been developed for evaluating image quality, detection and classification of objects as well as image compression in EO use cases. We integrated our experimentation and tested our QMRNet algorithm on predicting features like blur, sharpness, snr, rer and ground sampling distance (GSD) and obtain validation medRs below 1.0 (out of N=50) and recall rates above 95\%. Overall benchmark shows promising results for LIIF, CAR and MSRN and also the potential use of QMRNet as Loss for optimizing SR predictions. Due to its simplicity, QMRNet could also be used for other use cases and image domains, as its architecture and data processing is fully scalable.
Temporal Bilinear Encoding Network of Audio-Visual Features at Low Sampling Rates
Dec 18, 2020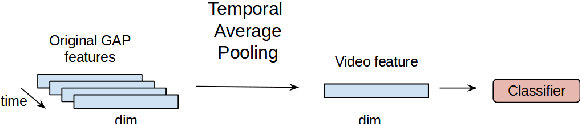
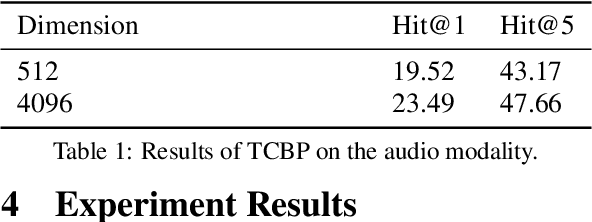
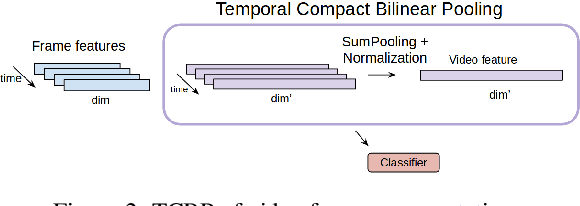
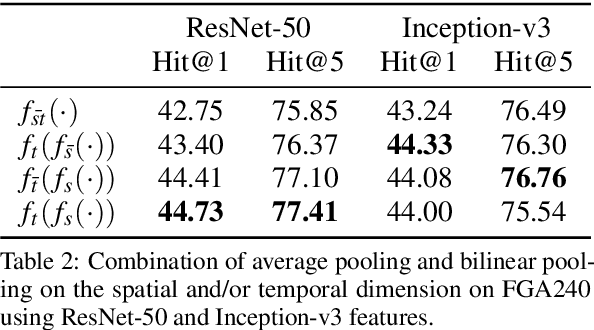
Abstract:Current deep learning based video classification architectures are typically trained end-to-end on large volumes of data and require extensive computational resources. This paper aims to exploit audio-visual information in video classification with a 1 frame per second sampling rate. We propose Temporal Bilinear Encoding Networks (TBEN) for encoding both audio and visual long range temporal information using bilinear pooling and demonstrate bilinear pooling is better than average pooling on the temporal dimension for videos with low sampling rate. We also embed the label hierarchy in TBEN to further improve the robustness of the classifier. Experiments on the FGA240 fine-grained classification dataset using TBEN achieve a new state-of-the-art (hit@1=47.95%). We also exploit the possibility of incorporating TBEN with multiple decoupled modalities like visual semantic and motion features: experiments on UCF101 sampled at 1 FPS achieve close to state-of-the-art accuracy (hit@1=91.03%) while requiring significantly less computational resources than competing approaches for both training and prediction.
Simple vs complex temporal recurrences for video saliency prediction
Jul 16, 2019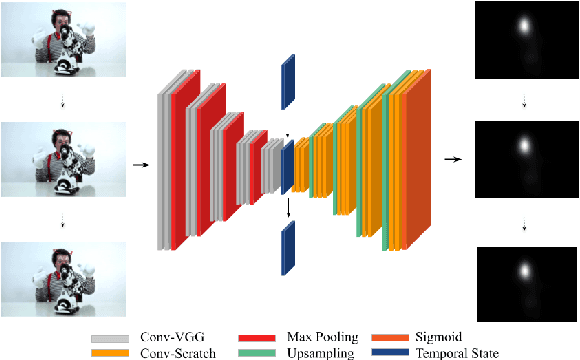
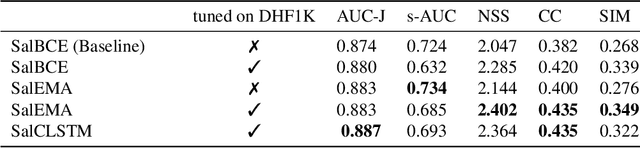
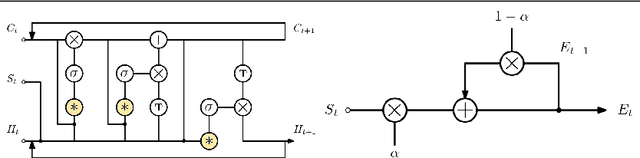
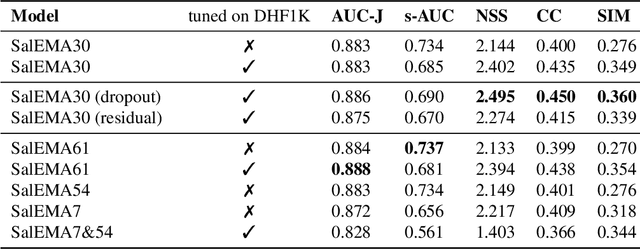
Abstract:This paper investigates modifying an existing neural network architecture for static saliency prediction using two types of recurrences that integrate information from the temporal domain. The first modification is the addition of a ConvLSTM within the architecture, while the second is a conceptually simple exponential moving average of an internal convolutional state. We use weights pre-trained on the SALICON dataset and fine-tune our model on DHF1K. Our results show that both modifications achieve state-of-the-art results and produce similar saliency maps. Source code is available at https://git.io/fjPiB.
An Efficient Approximate kNN Graph Method for Diffusion on Image Retrieval
Apr 18, 2019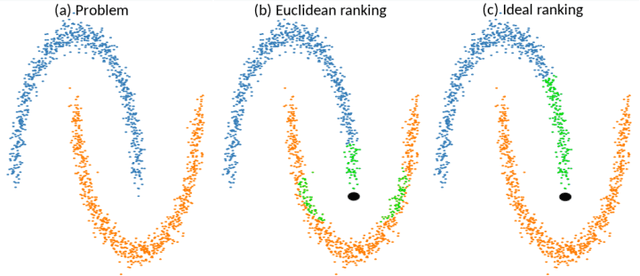
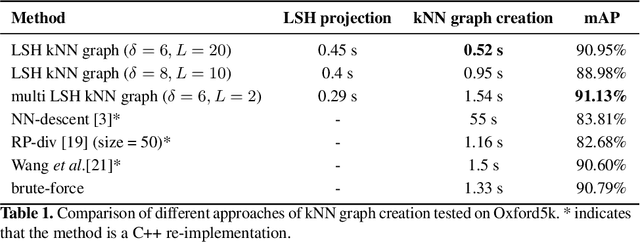
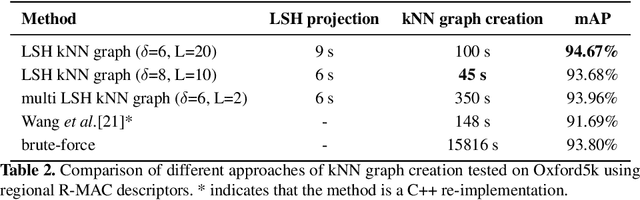
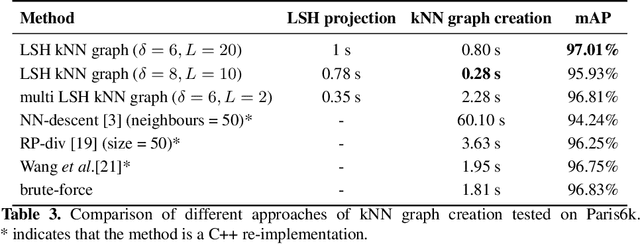
Abstract:The application of the diffusion in many computer vision and artificial intelligence projects has been shown to give excellent improvements in performance. One of the main bottlenecks of this technique is the quadratic growth of the kNN graph size due to the high-quantity of new connections between nodes in the graph, resulting in long computation times. Several strategies have been proposed to address this, but none are effective and efficient. Our novel technique, based on LSH projections, obtains the same performance as the exact kNN graph after diffusion, but in less time (approximately 18 times faster on a dataset of a hundred thousand images). The proposed method was validated and compared with other state-of-the-art on several public image datasets, including Oxford5k, Paris6k, and Oxford105k.
Wav2Pix: Speech-conditioned Face Generation using Generative Adversarial Networks
Mar 25, 2019



Abstract:Speech is a rich biometric signal that contains information about the identity, gender and emotional state of the speaker. In this work, we explore its potential to generate face images of a speaker by conditioning a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) with raw speech input. We propose a deep neural network that is trained from scratch in an end-to-end fashion, generating a face directly from the raw speech waveform without any additional identity information (e.g reference image or one-hot encoding). Our model is trained in a self-supervised approach by exploiting the audio and visual signals naturally aligned in videos. With the purpose of training from video data, we present a novel dataset collected for this work, with high-quality videos of youtubers with notable expressiveness in both the speech and visual signals.
Temporal Saliency Adaptation in Egocentric Videos
Sep 04, 2018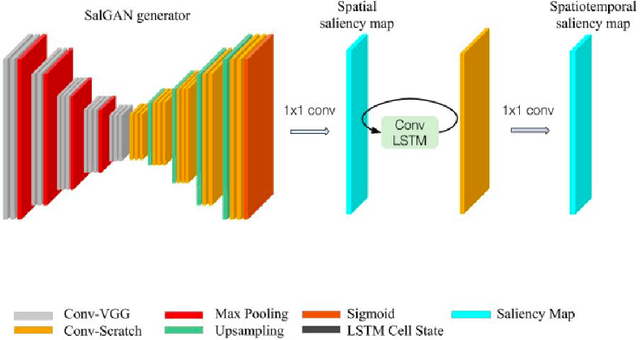
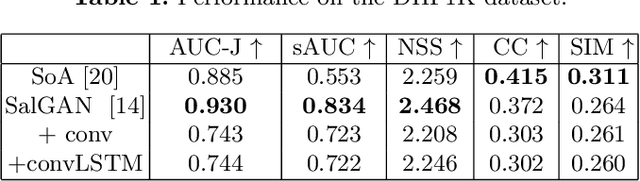
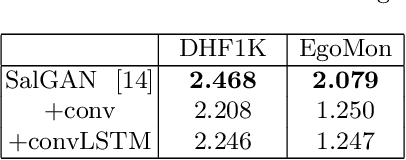
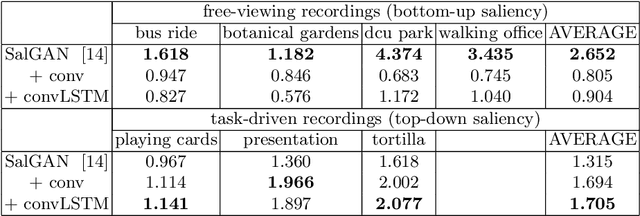
Abstract:This work adapts a deep neural model for image saliency prediction to the temporal domain of egocentric video. We compute the saliency map for each video frame, firstly with an off-the-shelf model trained from static images, secondly by adding a a convolutional or conv-LSTM layers trained with a dataset for video saliency prediction. We study each configuration on EgoMon, a new dataset made of seven egocentric videos recorded by three subjects in both free-viewing and task-driven set ups. Our results indicate that the temporal adaptation is beneficial when the viewer is not moving and observing the scene from a narrow field of view. Encouraged by this observation, we compute and publish the saliency maps for the EPIC Kitchens dataset, in which viewers are cooking. Source code and models available at https://imatge-upc.github.io/saliency-2018-videosalgan/
Saliency Weighted Convolutional Features for Instance Search
Nov 29, 2017



Abstract:This work explores attention models to weight the contribution of local convolutional representations for the instance search task. We present a retrieval framework based on bags of local convolutional features (BLCF) that benefits from saliency weighting to build an efficient image representation. The use of human visual attention models (saliency) allows significant improvements in retrieval performance without the need to conduct region analysis or spatial verification, and without requiring any feature fine tuning. We investigate the impact of different saliency models, finding that higher performance on saliency benchmarks does not necessarily equate to improved performance when used in instance search tasks. The proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art on the challenging INSTRE benchmark by a large margin, and provides similar performance on the Oxford and Paris benchmarks compared to more complex methods that use off-the-shelf representations. The source code used in this project is available at https://imatge-upc.github.io/salbow/
Where is my Phone ? Personal Object Retrieval from Egocentric Images
Mar 02, 2017



Abstract:This work presents a retrieval pipeline and evaluation scheme for the problem of finding the last appearance of personal objects in a large dataset of images captured from a wearable camera. Each personal object is modelled by a small set of images that define a query for a visual search engine.The retrieved results are reranked considering the temporal timestamps of the images to increase the relevance of the later detections. Finally, a temporal interleaving of the results is introduced for robustness against false detections. The Mean Reciprocal Rank is proposed as a metric to evaluate this problem. This application could help into developing personal assistants capable of helping users when they do not remember where they left their personal belongings.
Bags of Local Convolutional Features for Scalable Instance Search
Apr 15, 2016



Abstract:This work proposes a simple instance retrieval pipeline based on encoding the convolutional features of CNN using the bag of words aggregation scheme (BoW). Assigning each local array of activations in a convolutional layer to a visual word produces an \textit{assignment map}, a compact representation that relates regions of an image with a visual word. We use the assignment map for fast spatial reranking, obtaining object localizations that are used for query expansion. We demonstrate the suitability of the BoW representation based on local CNN features for instance retrieval, achieving competitive performance on the Oxford and Paris buildings benchmarks. We show that our proposed system for CNN feature aggregation with BoW outperforms state-of-the-art techniques using sum pooling at a subset of the challenging TRECVid INS benchmark.
Exploring EEG for Object Detection and Retrieval
Apr 09, 2015



Abstract:This paper explores the potential for using Brain Computer Interfaces (BCI) as a relevance feedback mechanism in content-based image retrieval. We investigate if it is possible to capture useful EEG signals to detect if relevant objects are present in a dataset of realistic and complex images. We perform several experiments using a rapid serial visual presentation (RSVP) of images at different rates (5Hz and 10Hz) on 8 users with different degrees of familiarization with BCI and the dataset. We then use the feedback from the BCI and mouse-based interfaces to retrieve localized objects in a subset of TRECVid images. We show that it is indeed possible to detect such objects in complex images and, also, that users with previous knowledge on the dataset or experience with the RSVP outperform others. When the users have limited time to annotate the images (100 seconds in our experiments) both interfaces are comparable in performance. Comparing our best users in a retrieval task, we found that EEG-based relevance feedback outperforms mouse-based feedback. The realistic and complex image dataset differentiates our work from previous studies on EEG for image retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge