Divin Yan
Manifold-Constrained Nucleus-Level Denoising Diffusion Model for Structure-Based Drug Design
Sep 16, 2024Abstract:Artificial intelligence models have shown great potential in structure-based drug design, generating ligands with high binding affinities. However, existing models have often overlooked a crucial physical constraint: atoms must maintain a minimum pairwise distance to avoid separation violation, a phenomenon governed by the balance of attractive and repulsive forces. To mitigate such separation violations, we propose NucleusDiff. It models the interactions between atomic nuclei and their surrounding electron clouds by enforcing the distance constraint between the nuclei and manifolds. We quantitatively evaluate NucleusDiff using the CrossDocked2020 dataset and a COVID-19 therapeutic target, demonstrating that NucleusDiff reduces violation rate by up to 100.00% and enhances binding affinity by up to 22.16%, surpassing state-of-the-art models for structure-based drug design. We also provide qualitative analysis through manifold sampling, visually confirming the effectiveness of NucleusDiff in reducing separation violations and improving binding affinities.
Training Class-Imbalanced Diffusion Model Via Overlap Optimization
Feb 16, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models have made significant advances recently in high-quality image synthesis and related tasks. However, diffusion models trained on real-world datasets, which often follow long-tailed distributions, yield inferior fidelity for tail classes. Deep generative models, including diffusion models, are biased towards classes with abundant training images. To address the observed appearance overlap between synthesized images of rare classes and tail classes, we propose a method based on contrastive learning to minimize the overlap between distributions of synthetic images for different classes. We show variants of our probabilistic contrastive learning method can be applied to any class conditional diffusion model. We show significant improvement in image synthesis using our loss for multiple datasets with long-tailed distribution. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively handle imbalanced data for diffusion-based generation and classification models. Our code and datasets will be publicly available at https://github.com/yanliang3612/DiffROP.
Understanding Community Bias Amplification in Graph Representation Learning
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:In this work, we discover a phenomenon of community bias amplification in graph representation learning, which refers to the exacerbation of performance bias between different classes by graph representation learning. We conduct an in-depth theoretical study of this phenomenon from a novel spectral perspective. Our analysis suggests that structural bias between communities results in varying local convergence speeds for node embeddings. This phenomenon leads to bias amplification in the classification results of downstream tasks. Based on the theoretical insights, we propose random graph coarsening, which is proved to be effective in dealing with the above issue. Finally, we propose a novel graph contrastive learning model called Random Graph Coarsening Contrastive Learning (RGCCL), which utilizes random coarsening as data augmentation and mitigates community bias by contrasting the coarsened graph with the original graph. Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate the advantage of our method when dealing with community bias amplification.
Rethinking Semi-Supervised Imbalanced Node Classification from Bias-Variance Decomposition
Oct 28, 2023


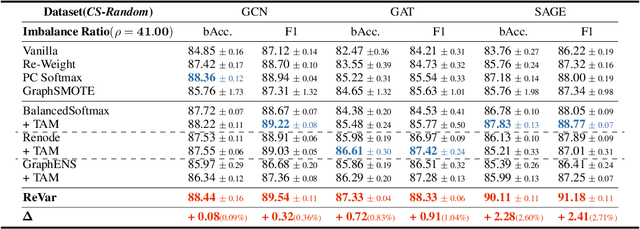
Abstract:This paper introduces a new approach to address the issue of class imbalance in graph neural networks (GNNs) for learning on graph-structured data. Our approach integrates imbalanced node classification and Bias-Variance Decomposition, establishing a theoretical framework that closely relates data imbalance to model variance. We also leverage graph augmentation technique to estimate the variance, and design a regularization term to alleviate the impact of imbalance. Exhaustive tests are conducted on multiple benchmarks, including naturally imbalanced datasets and public-split class-imbalanced datasets, demonstrating that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods in various imbalanced scenarios. This work provides a novel theoretical perspective for addressing the problem of imbalanced node classification in GNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge