Dengji Zhao
Collecting Larg-Scale Robotic Datasets on a High-Speed Mobile Platform
Aug 01, 2024Abstract:Mobile robotics datasets are essential for research on robotics, for example for research on Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). Therefore the ShanghaiTech Mapping Robot was constructed, that features a multitude high-performance sensors and a 16-node cluster to collect all this data. That robot is based on a Clearpath Husky mobile base with a maximum speed of 1 meter per second. This is fine for indoor datasets, but to collect large-scale outdoor datasets a faster platform is needed. This system paper introduces our high-speed mobile platform for data collection. The mapping robot is secured on the rear-steered flatbed car with maximum field of view. Additionally two encoders collect odometry data from two of the car wheels and an external sensor plate houses a downlooking RGB and event camera. With this setup a dataset of more than 10km in the underground parking garage and the outside of our campus was collected and is published with this paper.
Sybil-Proof Diffusion Auction in Social Networks
Nov 03, 2022Abstract:A diffusion auction is a market to sell commodities over a social network, where the challenge is to incentivize existing buyers to invite their neighbors in the network to join the market. Existing mechanisms have been designed to solve the challenge in various settings, aiming at desirable properties such as non-deficiency, incentive compatibility and social welfare maximization. Since the mechanisms are employed in dynamic networks with ever-changing structures, buyers could easily generate fake nodes in the network to manipulate the mechanisms for their own benefits, which is commonly known as the Sybil attack. We observe that strategic agents may gain an unfair advantage in existing mechanisms through such attacks. To resist this potential attack, we propose two diffusion auction mechanisms, the Sybil tax mechanism (STM) and the Sybil cluster mechanism (SCM), to achieve both Sybil-proofness and incentive compatibility in the single-item setting. Our proposal provides the first mechanisms to protect the interests of buyers against Sybil attacks with a mild sacrifice of social welfare and revenue.
Multi-Unit Diffusion Auctions with Intermediaries
Mar 15, 2022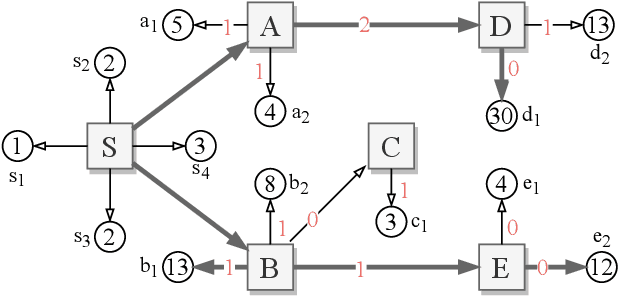
Abstract:This paper studies multi-unit auctions powered by intermediaries, where each intermediary owns a private set of unit-demand buyers and all intermediaries are networked with each other. Our goal is to incentivize the intermediaries to diffuse the auction information to individuals they can reach, including their private buyers and neighboring intermediaries, so that more potential buyers are able to participate in the auction. To this end, we build a diffusion-based auction framework which incorporates the strategic interaction of intermediaries. It is showed that the classic Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) mechanism within the framework can achieve the maximum social welfare, but it may decrease the seller's revenue or even lead to a deficit. To overcome the revenue issue, we propose a novel auction, called critical neighborhood auction, which not only maximizes the social welfare, but also improves the seller's revenue comparing to the VCG mechanism with/without intermediaries.
Coalitional Games with Stochastic Characteristic Functions and Private Types
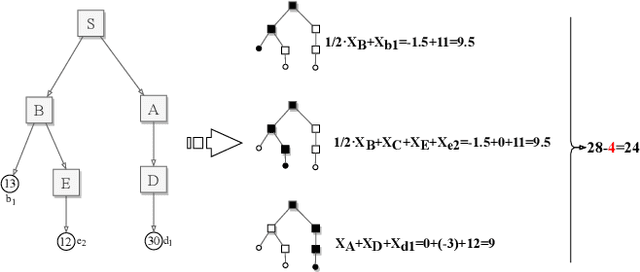
Oct 25, 2019
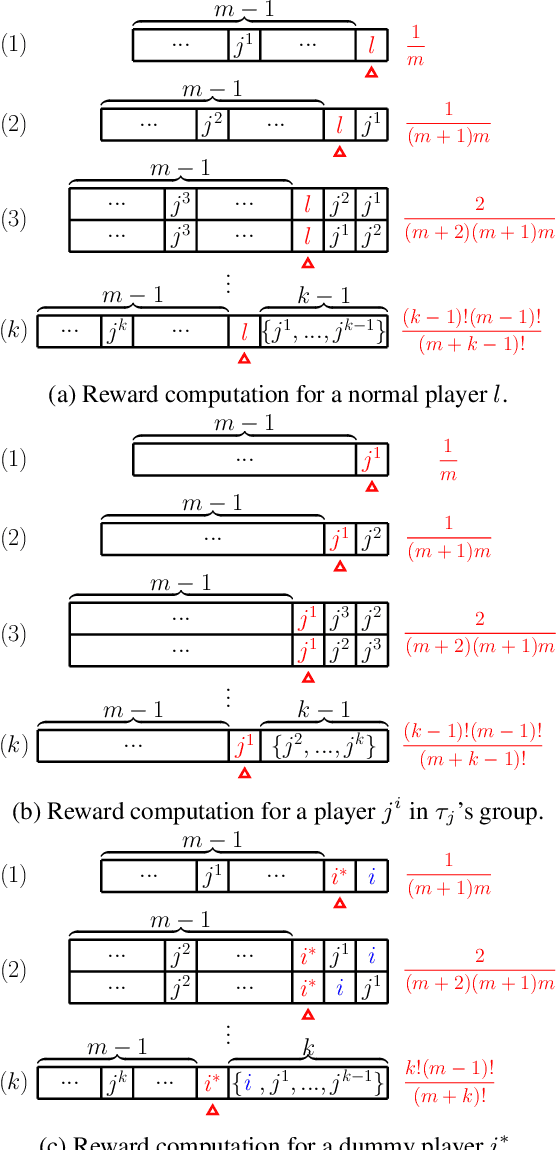
Abstract:The research on coalitional games has focused on how to share the reward among a coalition such that players are incentivised to collaborate together. It assumes that the (deterministic or stochastic) characteristic function is known in advance. This paper studies a new setting (a task allocation problem) where the characteristic function is not known and it is controlled by some private information from the players. Hence, the challenge here is twofold: (i) incentivize players to reveal their private information truthfully, (ii) incentivize them to collaborate together. We show that existing reward distribution mechanisms or auctions cannot solve the challenge. Hence, we propose the very first mechanism for the problem from the perspective of both mechanism design and coalitional games.
Redistribution Mechanism Design on Networks
Oct 21, 2019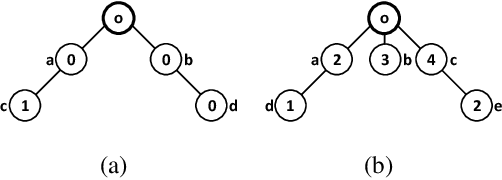
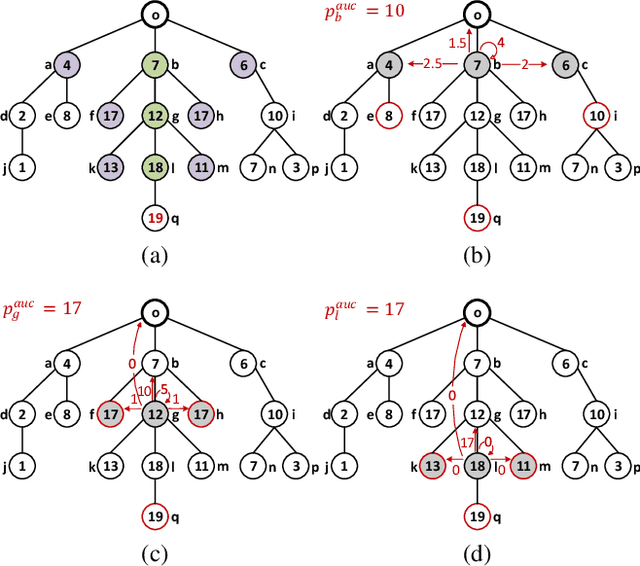
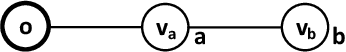
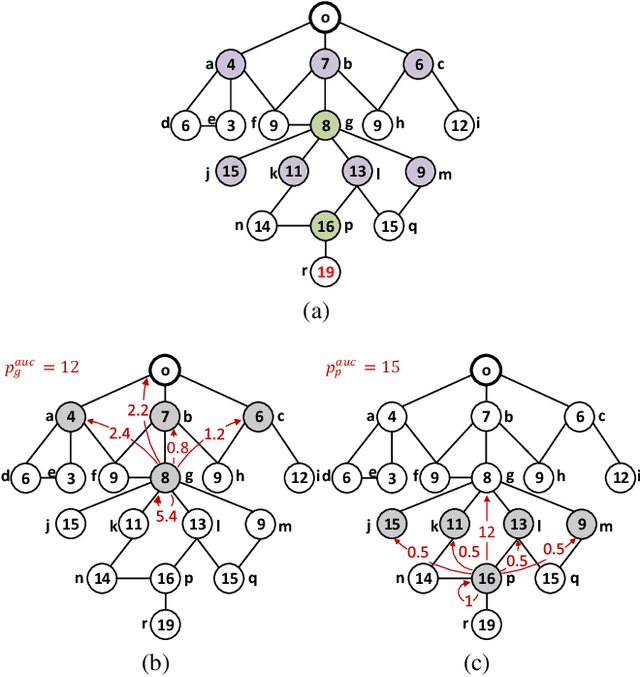
Abstract:Redistribution mechanisms have been proposed for more efficient resource allocation but not for profit. We consider redistribution mechanism design for the first time in a setting where participants are connected and the resource owner is only aware of her neighbours. In this setting, to make the resource allocation more efficient, the resource owner has to inform the others who are not her neighbours, but her neighbours do not want more participants to compete with them. Hence, the goal is to design a redistribution mechanism such that participants are incentivized to invite more participants and the resource owner does not earn or lose much money from the allocation. We first show that existing redistribution mechanisms cannot be directly applied in the network setting to achieve the goal. Then we propose a novel network-based redistribution mechanism such that all participants in the network are invited, the allocation is more efficient and the resource owner has no deficit.
Diffusion and Auction on Graphs
May 24, 2019
Abstract:Auction is the common paradigm for resource allocation which is a fundamental problem in human society. Existing research indicates that the two primary objectives, the seller's revenue and the allocation efficiency, are generally conflicting in auction design. For the first time, we expand the domain of the classic auction to a social graph and formally identify a new class of auction mechanisms on graphs. All mechanisms in this class are incentive-compatible and also promote all buyers to diffuse the auction information to others, whereby both the seller's revenue and the allocation efficiency are significantly improved comparing with the Vickrey auction. It is found that the recently proposed information diffusion mechanism is an extreme case with the lowest revenue in this new class. Our work could potentially inspire a new perspective for the efficient and optimal auction design and could be applied into the prevalent online social and economic networks.
Crowdsourcing Data Acquisition via Social Networks
May 14, 2019
Abstract:We consider a requester who acquires a set of data (e.g. images) that is not owned by one party. In order to collect all the data, crowdsourcing mechanisms have been widely used to seek help from the crowd. However, existing mechanisms rely on third-party platforms, and the workers from these platforms are not necessarily helpful and redundant data are also not properly handled. To combat this problem, we propose a novel crowdsourcing mechanism based on social networks, where the rewards of the workers are calculated by information entropy and a modified Shapley value. This mechanism incentivizes the workers from the network to not only provide all data they have, but also further invite their neighbours to offer more data. Eventually, the mechanism is able to acquire all data from all workers on the network with a constrained reward spending.
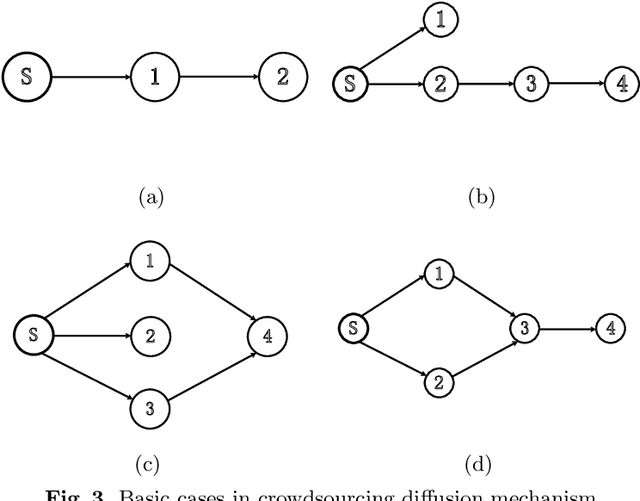
Fixed-price Diffusion Mechanism Design
May 14, 2019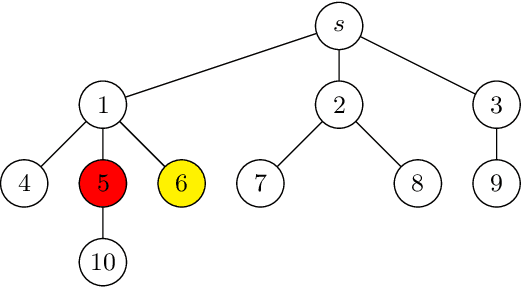
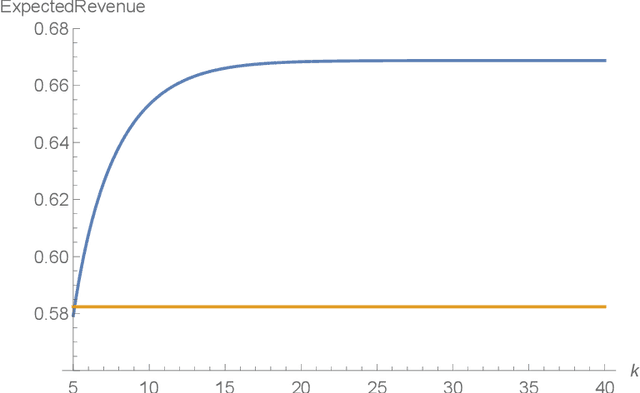
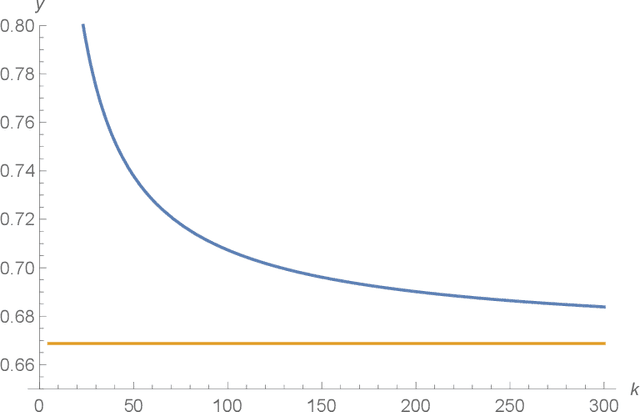
Abstract:We consider a fixed-price mechanism design setting where a seller sells one item via a social network, but the seller can only directly communicate with her neighbours initially. Each other node in the network is a potential buyer with a valuation derived from a common distribution. With a standard fixed-price mechanism, the seller can only sell the item among her neighbours. To improve her revenue, she needs more buyers to join in the sale. To achieve this, we propose the very first fixed-price mechanism to incentivize the seller's neighbours to inform their neighbours about the sale and to eventually inform all buyers in the network to improve seller's revenue. Compared with the existing mechanisms for the same purpose, our mechanism does not require the buyers to reveal their valuations and it is computationally easy. More importantly, it guarantees that the improved revenue is at least 1/2 of the optimal.
Selling Multiple Items via Social Networks
Mar 07, 2019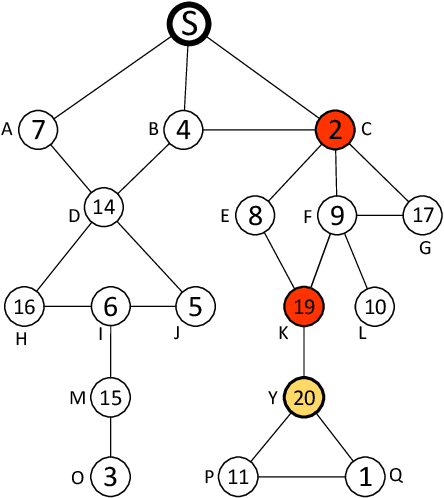
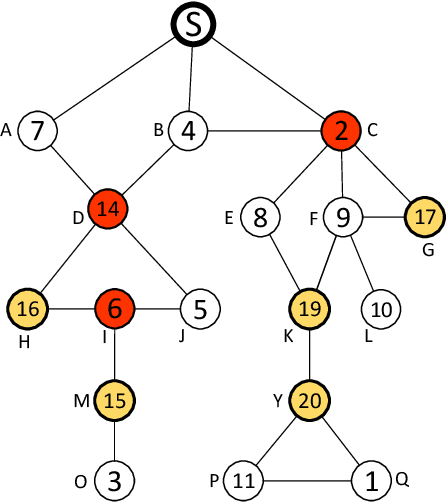
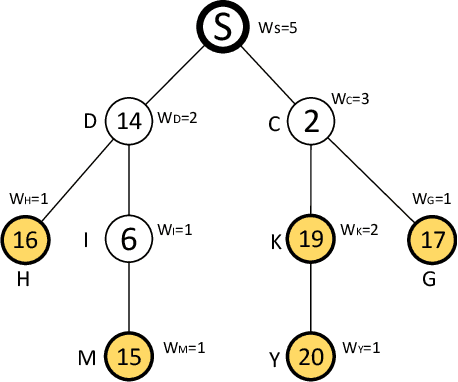
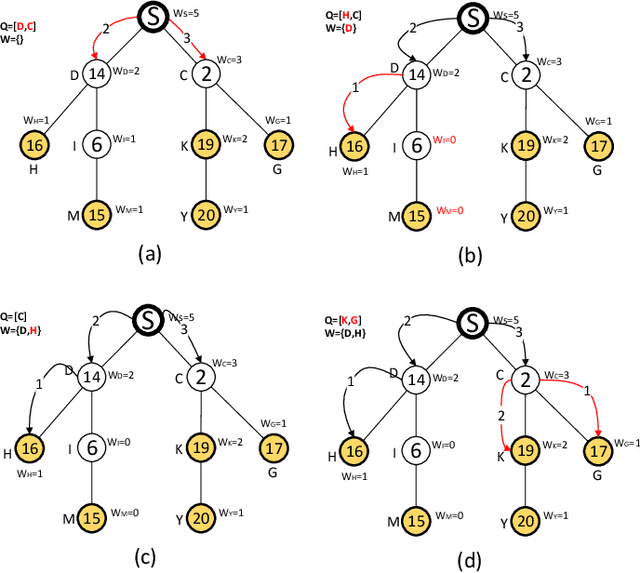
Abstract:We consider a market where a seller sells multiple units of a commodity in a social network. Each node/buyer in the social network can only directly communicate with her neighbours, i.e. the seller can only sell the commodity to her neighbours if she could not find a way to inform other buyers. In this paper, we design a novel promotion mechanism that incentivizes all buyers, who are aware of the sale, to invite all their neighbours to join the sale, even though there is no guarantee that their efforts will be paid. While traditional sale promotions such as sponsored search auctions cannot guarantee a positive return for the advertiser (the seller), our mechanism guarantees that the seller's revenue is better than not using the advertising. More importantly, the seller does not need to pay if the advertising is not beneficial to her.
Customer Sharing in Economic Networks with Costs
Jul 18, 2018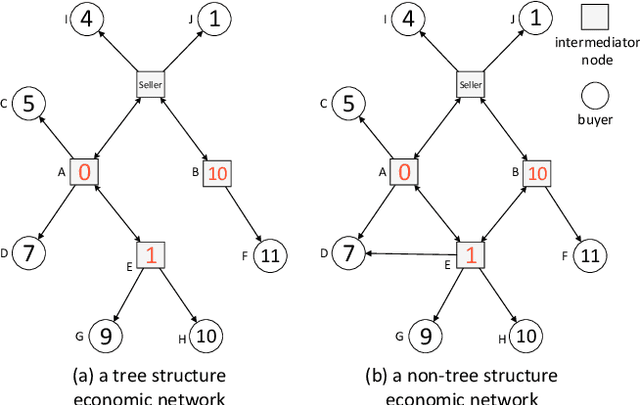
Abstract:In an economic market, sellers, infomediaries and customers constitute an economic network. Each seller has her own customer group and the seller's private customers are unobservable to other sellers. Therefore, a seller can only sell commodities among her own customers unless other sellers or infomediaries share her sale information to their customer groups. However, a seller is not incentivized to share others' sale information by default, which leads to inefficient resource allocation and limited revenue for the sale. To tackle this problem, we develop a novel mechanism called customer sharing mechanism (CSM) which incentivizes all sellers to share each other's sale information to their private customer groups. Furthermore, CSM also incentivizes all customers to truthfully participate in the sale. In the end, CSM not only allocates the commodities efficiently but also optimizes the seller's revenue.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge