Conggang Hu
STAR: Similarity-guided Teacher-Assisted Refinement for Super-Tiny Function Calling Models
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:The proliferation of Large Language Models (LLMs) in function calling is pivotal for creating advanced AI agents, yet their large scale hinders widespread adoption, necessitating transferring their capabilities into smaller ones. However, existing paradigms are often plagued by overfitting, training instability, ineffective binary rewards for multi-solution tasks, and the difficulty of synergizing techniques. We introduce STAR: Similarity-guided Teacher-Assisted Refinement, a novel holistic framework that effectively transfers LLMs' capabilities to super-tiny models. STAR consists of two core technical innovations: (1) Constrained Knowledge Distillation (CKD), a training objective that augments top-k forward KL divergence to suppress confidently incorrect predictions, ensuring training stability while preserving exploration capacity for downstream RL. STAR holistically synergizes these strategies within a cohesive training curriculum, enabling super-tiny models to achieve exceptional performance on complex function calling tasks; (2) Similarity-guided RL (Sim-RL), a RL mechanism that introduces a fine-grained, similarity-based reward. This provides a robust, continuous, and rich signal for better policy optimization by evaluating the similarity between generated outputs and the ground truth. Extensive experiments on challenging and renowned benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. Our STAR models establish SOTA in their size classes, significantly outperforming baselines. Remarkably, our 0.6B STAR model achieves the best performance among all open models under 1B, surpassing even several well-known open models at a larger scale. STAR demonstrates a training framework that distills capabilities of LLMs into super-tiny models, paving the way for powerful, accessible, and efficient AI agents.
From Large to Super-Tiny: End-to-End Optimization for Cost-Efficient LLMs
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly advanced artificial intelligence by optimizing traditional Natural Language Processing (NLP) pipelines, improving performance and generalization. This has spurred their integration into various systems. Many NLP systems, including ours, employ a "one-stage" pipeline directly incorporating LLMs. While effective, this approach incurs substantial costs and latency due to the need for large model parameters to achieve satisfactory outcomes. This paper introduces a three-stage cost-efficient end-to-end LLM deployment pipeline-including prototyping, knowledge transfer, and model compression-to tackle the cost-performance dilemma in LLM-based frameworks. Our approach yields a super tiny model optimized for cost and performance in online systems, simplifying the system architecture. Initially, by transforming complex tasks into a function call-based LLM-driven pipeline, an optimal performance prototype system is constructed to produce high-quality data as a teacher model. The second stage combine techniques like rejection fine-tuning, reinforcement learning and knowledge distillation to transfer knowledge to a smaller 0.5B student model, delivering effective performance at minimal cost. The final stage applies quantization and pruning to extremely compress model to 0.4B, achieving ultra-low latency and cost. The framework's modular design and cross-domain capabilities suggest potential applicability in other NLP areas.
AI-Empowered RIS-Assisted Networks: CV-Enabled RIS Selection and DNN-Enabled Transmission
Apr 18, 2024Abstract:This paper investigates artificial intelligence (AI) empowered schemes for reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) assisted networks from the perspective of fast implementation. We formulate a weighted sum-rate maximization problem for a multi-RIS-assisted network. To avoid huge channel estimation overhead due to activate all RISs, we propose a computer vision (CV) enabled RIS selection scheme based on a single shot multi-box detector. To realize real-time resource allocation, a deep neural network (DNN) enabled transmit design is developed to learn the optimal mapping from channel information to transmit beamformers and phase shift matrix. Numerical results illustrate that the CV module is able to select of RIS with the best propagation condition. The well-trained DNN achieves similar sum-rate performance to the existing alternative optimization method but with much smaller inference time.
Network Pruning Spaces
Apr 19, 2023Abstract:Network pruning techniques, including weight pruning and filter pruning, reveal that most state-of-the-art neural networks can be accelerated without a significant performance drop. This work focuses on filter pruning which enables accelerated inference with any off-the-shelf deep learning library and hardware. We propose the concept of \emph{network pruning spaces} that parametrize populations of subnetwork architectures. Based on this concept, we explore the structure aspect of subnetworks that result in minimal loss of accuracy in different pruning regimes and arrive at a series of observations by comparing subnetwork distributions. We conjecture through empirical studies that there exists an optimal FLOPs-to-parameter-bucket ratio related to the design of original network in a pruning regime. Statistically, the structure of a winning subnetwork guarantees an approximately optimal ratio in this regime. Upon our conjectures, we further refine the initial pruning space to reduce the cost of searching a good subnetwork architecture. Our experimental results on ImageNet show that the subnetwork we found is superior to those from the state-of-the-art pruning methods under comparable FLOPs.
Accelerating Neural Network Inference by Overflow Aware Quantization
May 27, 2020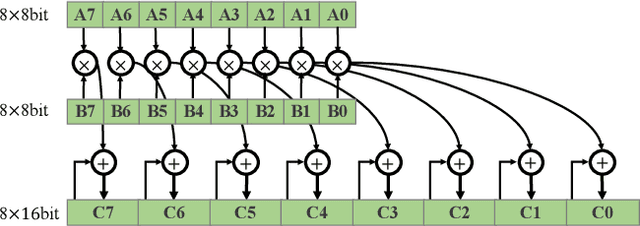
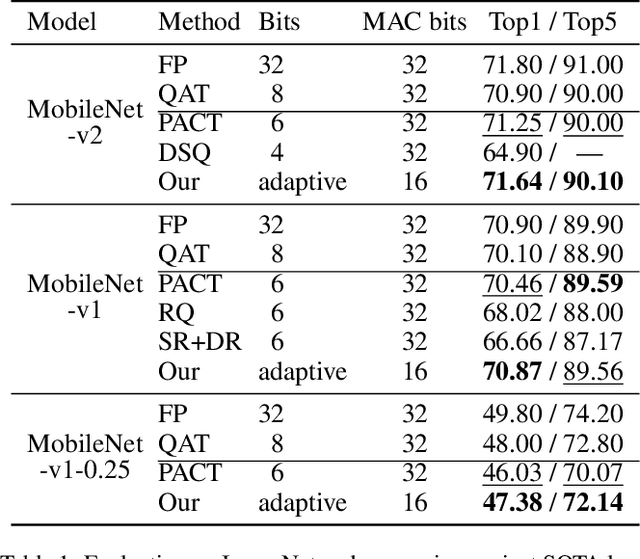
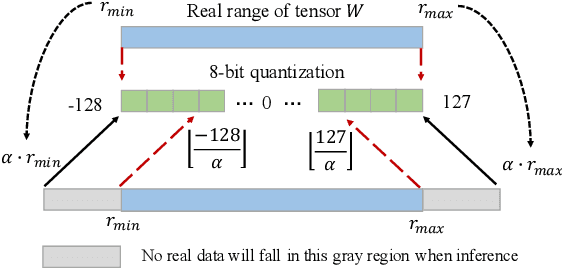
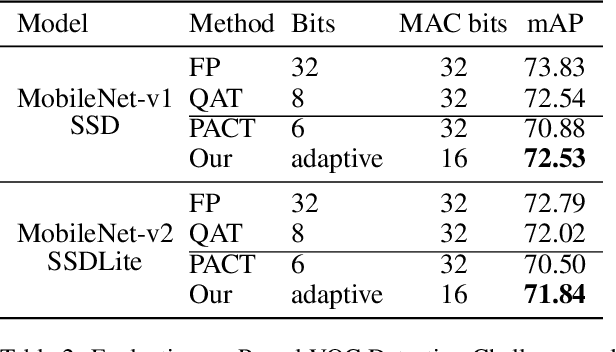
Abstract:The inherent heavy computation of deep neural networks prevents their widespread applications. A widely used method for accelerating model inference is quantization, by replacing the input operands of a network using fixed-point values. Then the majority of computation costs focus on the integer matrix multiplication accumulation. In fact, high-bit accumulator leads to partially wasted computation and low-bit one typically suffers from numerical overflow. To address this problem, we propose an overflow aware quantization method by designing trainable adaptive fixed-point representation, to optimize the number of bits for each input tensor while prohibiting numeric overflow during the computation. With the proposed method, we are able to fully utilize the computing power to minimize the quantization loss and obtain optimized inference performance. To verify the effectiveness of our method, we conduct image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation tasks on ImageNet, Pascal VOC, and COCO datasets, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve comparable performance with state-of-the-art quantization methods while accelerating the inference process by about 2 times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge