Baitao Shao
Accelerating Neural Network Inference by Overflow Aware Quantization
May 27, 2020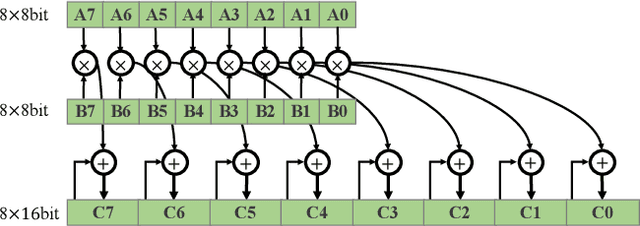
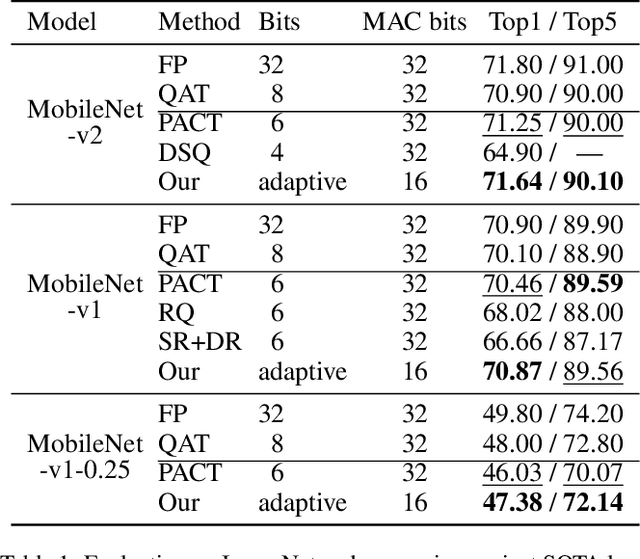
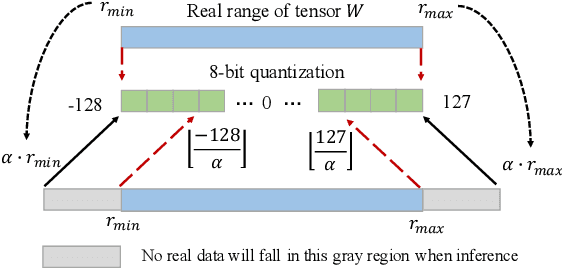
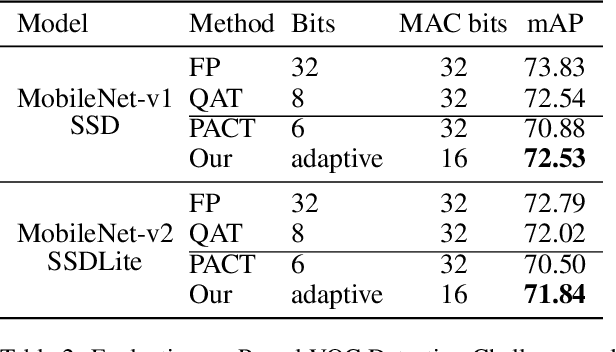
Abstract:The inherent heavy computation of deep neural networks prevents their widespread applications. A widely used method for accelerating model inference is quantization, by replacing the input operands of a network using fixed-point values. Then the majority of computation costs focus on the integer matrix multiplication accumulation. In fact, high-bit accumulator leads to partially wasted computation and low-bit one typically suffers from numerical overflow. To address this problem, we propose an overflow aware quantization method by designing trainable adaptive fixed-point representation, to optimize the number of bits for each input tensor while prohibiting numeric overflow during the computation. With the proposed method, we are able to fully utilize the computing power to minimize the quantization loss and obtain optimized inference performance. To verify the effectiveness of our method, we conduct image classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation tasks on ImageNet, Pascal VOC, and COCO datasets, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve comparable performance with state-of-the-art quantization methods while accelerating the inference process by about 2 times.
LE-HGR: A Lightweight and Efficient RGB-based Online Gesture Recognition Network for Embedded AR Devices
Jan 16, 2020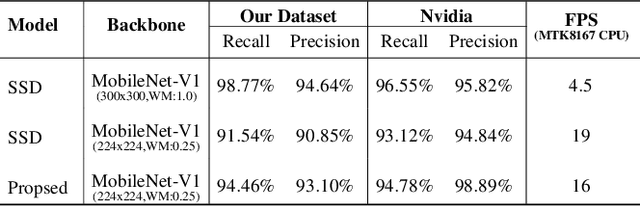
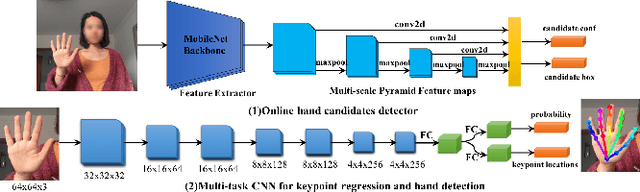
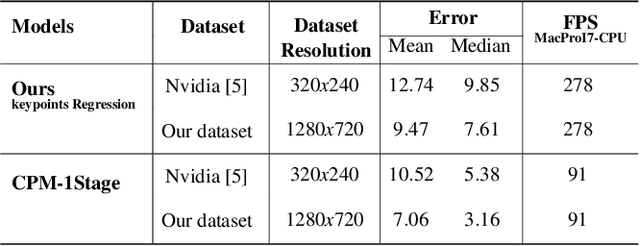

Abstract:Online hand gesture recognition (HGR) techniques are essential in augmented reality (AR) applications for enabling natural human-to-computer interaction and communication. In recent years, the consumer market for low-cost AR devices has been rapidly growing, while the technology maturity in this domain is still limited. Those devices are typical of low prices, limited memory, and resource-constrained computational units, which makes online HGR a challenging problem. To tackle this problem, we propose a lightweight and computationally efficient HGR framework, namely LE-HGR, to enable real-time gesture recognition on embedded devices with low computing power. We also show that the proposed method is of high accuracy and robustness, which is able to reach high-end performance in a variety of complicated interaction environments. To achieve our goal, we first propose a cascaded multi-task convolutional neural network (CNN) to simultaneously predict probabilities of hand detection and regress hand keypoint locations online. We show that, with the proposed cascaded architecture design, false-positive estimates can be largely eliminated. Additionally, an associated mapping approach is introduced to track the hand trace via the predicted locations, which addresses the interference of multi-handedness. Subsequently, we propose a trace sequence neural network (TraceSeqNN) to recognize the hand gesture by exploiting the motion features of the tracked trace. Finally, we provide a variety of experimental results to show that the proposed framework is able to achieve state-of-the-art accuracy with significantly reduced computational cost, which are the key properties for enabling real-time applications in low-cost commercial devices such as mobile devices and AR/VR headsets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge