Claudio Pomo
A Reproducible and Fair Evaluation of Partition-aware Collaborative Filtering
Dec 18, 2025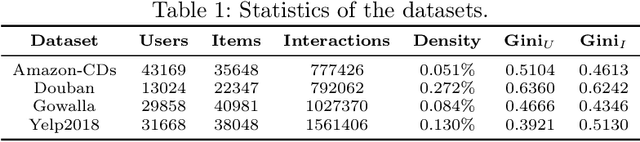
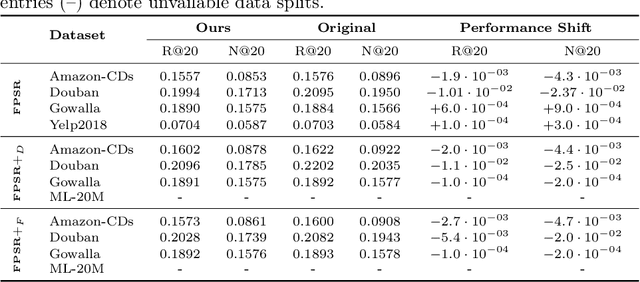
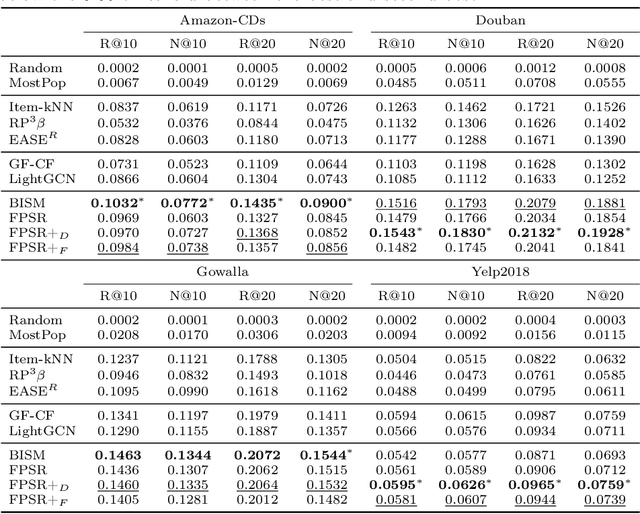
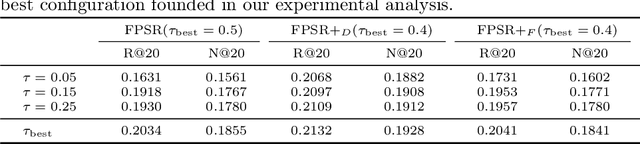
Abstract:Similarity-based collaborative filtering (CF) models have long demonstrated strong offline performance and conceptual simplicity. However, their scalability is limited by the quadratic cost of maintaining dense item-item similarity matrices. Partitioning-based paradigms have recently emerged as an effective strategy for balancing effectiveness and efficiency, enabling models to learn local similarities within coherent subgraphs while maintaining a limited global context. In this work, we focus on the Fine-tuning Partition-aware Similarity Refinement (FPSR) framework, a prominent representative of this family, as well as its extension, FPSR+. Reproducible evaluation of partition-aware collaborative filtering remains challenging, as prior FPSR/FPSR+ reports often rely on splits of unclear provenance and omit some similarity-based baselines, thereby complicating fair comparison. We present a transparent, fully reproducible benchmark of FPSR and FPSR+. Based on our results, the family of FPSR models does not consistently perform at the highest level. Overall, it remains competitive, validates its design choices, and shows significant advantages in long-tail scenarios. This highlights the accuracy-coverage trade-offs resulting from partitioning, global components, and hub design. Our investigation clarifies when partition-aware similarity modeling is most beneficial and offers actionable guidance for scalable recommender system design under reproducible protocols.
On the Impact of Graph Neural Networks in Recommender Systems: A Topological Perspective
Dec 08, 2025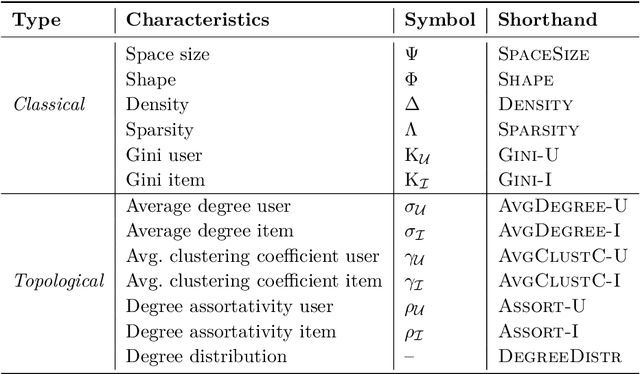
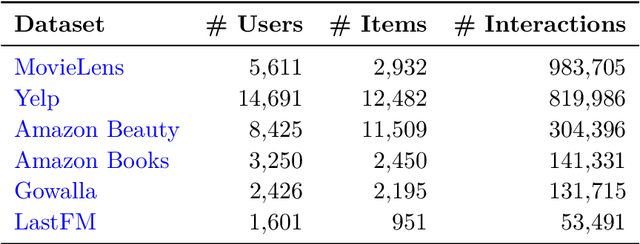
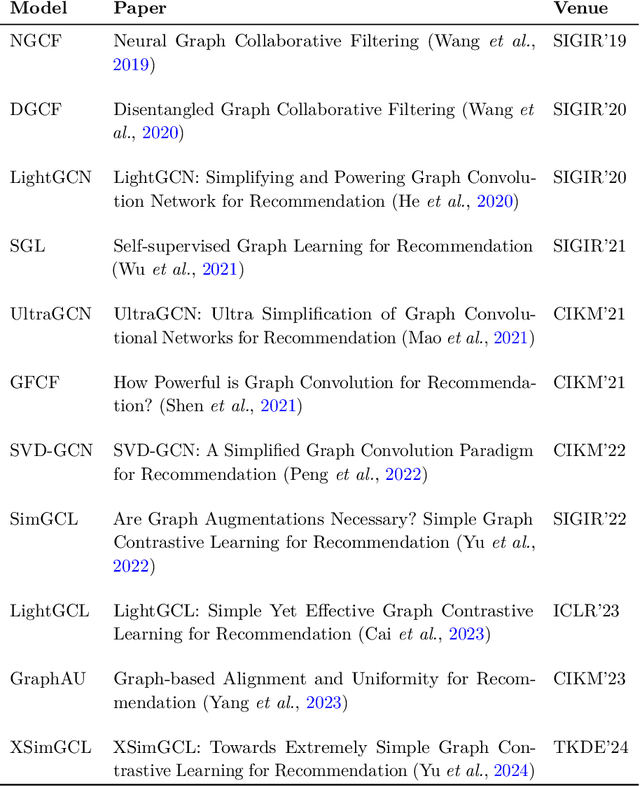
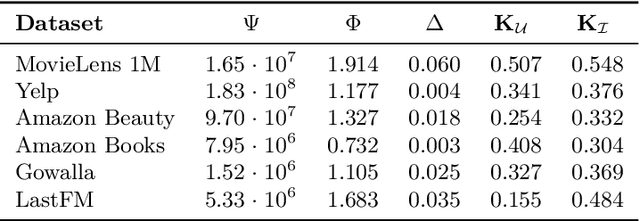
Abstract:In recommender systems, user-item interactions can be modeled as a bipartite graph, where user and item nodes are connected by undirected edges. This graph-based view has motivated the rapid adoption of graph neural networks (GNNs), which often outperform collaborative filtering (CF) methods such as latent factor models, deep neural networks, and generative strategies. Yet, despite their empirical success, the reasons why GNNs offer systematic advantages over other CF approaches remain only partially understood. This monograph advances a topology-centered perspective on GNN-based recommendation. We argue that a comprehensive understanding of these models' performance should consider the structural properties of user-item graphs and their interaction with GNN architectural design. To support this view, we introduce a formal taxonomy that distills common modeling patterns across eleven representative GNN-based recommendation approaches and consolidates them into a unified conceptual pipeline. We further formalize thirteen classical and topological characteristics of recommendation datasets and reinterpret them through the lens of graph machine learning. Using these definitions, we analyze the considered GNN-based recommender architectures to assess how and to what extent they encode such properties. Building on this analysis, we derive an explanatory framework that links measurable dataset characteristics to model behavior and performance. Taken together, this monograph re-frames GNN-based recommendation through its topological underpinnings and outlines open theoretical, data-centric, and evaluation challenges for the next generation of topology-aware recommender systems.
Do Recommender Systems Really Leverage Multimodal Content? A Comprehensive Analysis on Multimodal Representations for Recommendation
Aug 06, 2025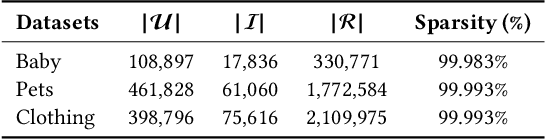
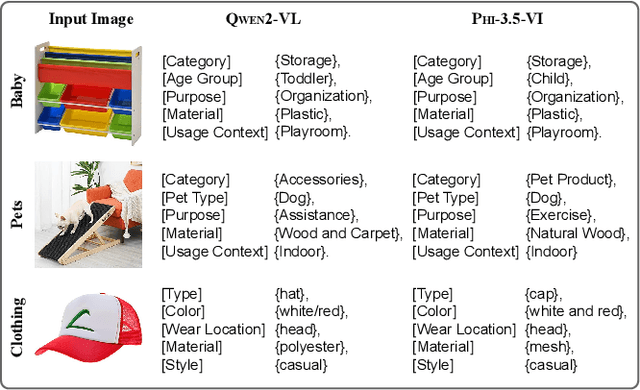
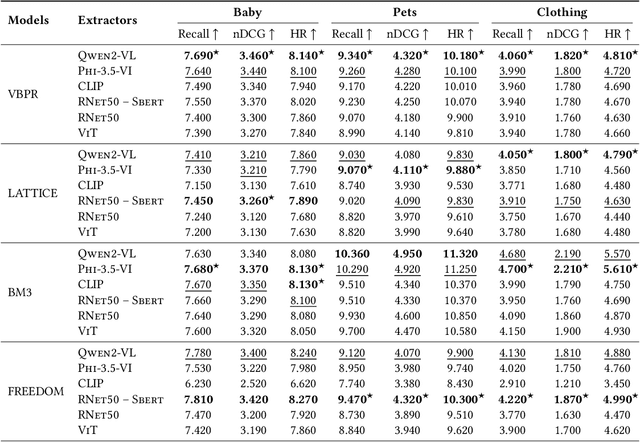
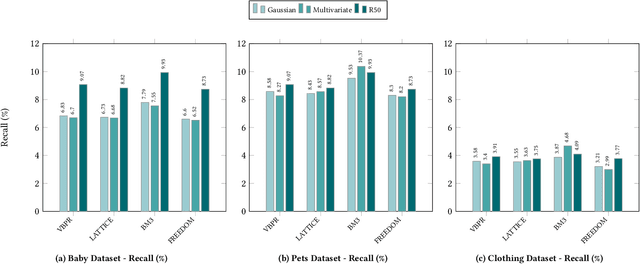
Abstract:Multimodal Recommender Systems aim to improve recommendation accuracy by integrating heterogeneous content, such as images and textual metadata. While effective, it remains unclear whether their gains stem from true multimodal understanding or increased model complexity. This work investigates the role of multimodal item embeddings, emphasizing the semantic informativeness of the representations. Initial experiments reveal that embeddings from standard extractors (e.g., ResNet50, Sentence-Bert) enhance performance, but rely on modality-specific encoders and ad hoc fusion strategies that lack control over cross-modal alignment. To overcome these limitations, we leverage Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to generate multimodal-by-design embeddings via structured prompts. This approach yields semantically aligned representations without requiring any fusion. Experiments across multiple settings show notable performance improvements. Furthermore, LVLMs embeddings offer a distinctive advantage: they can be decoded into structured textual descriptions, enabling direct assessment of their multimodal comprehension. When such descriptions are incorporated as side content into recommender systems, they improve recommendation performance, empirically validating the semantic depth and alignment encoded within LVLMs outputs. Our study highlights the importance of semantically rich representations and positions LVLMs as a compelling foundation for building robust and meaningful multimodal representations in recommendation tasks.
DataRec: A Framework for Standardizing Recommendation Data Processing and Analysis
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:Thanks to the great interest posed by researchers and companies, recommendation systems became a cornerstone of machine learning applications. However, concerns have arisen recently about the need for reproducibility, making it challenging to identify suitable pipelines. Several frameworks have been proposed to improve reproducibility, covering the entire process from data reading to performance evaluation. Despite this effort, these solutions often overlook the role of data management, do not promote interoperability, and neglect data analysis despite its well-known impact on recommender performance. To address these gaps, we propose DataRec, which facilitates using and manipulating recommendation datasets. DataRec supports reading and writing in various formats, offers filtering and splitting techniques, and enables data distribution analysis using well-known metrics. It encourages a unified approach to data manipulation by allowing data export in formats compatible with several recommendation frameworks.
EB-NeRD: A Large-Scale Dataset for News Recommendation
Oct 04, 2024
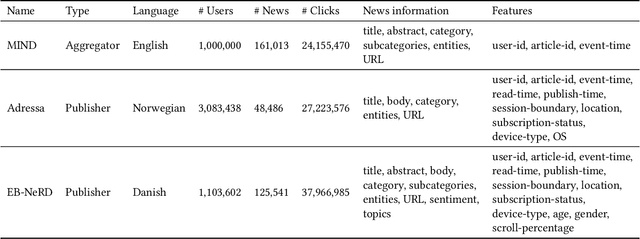

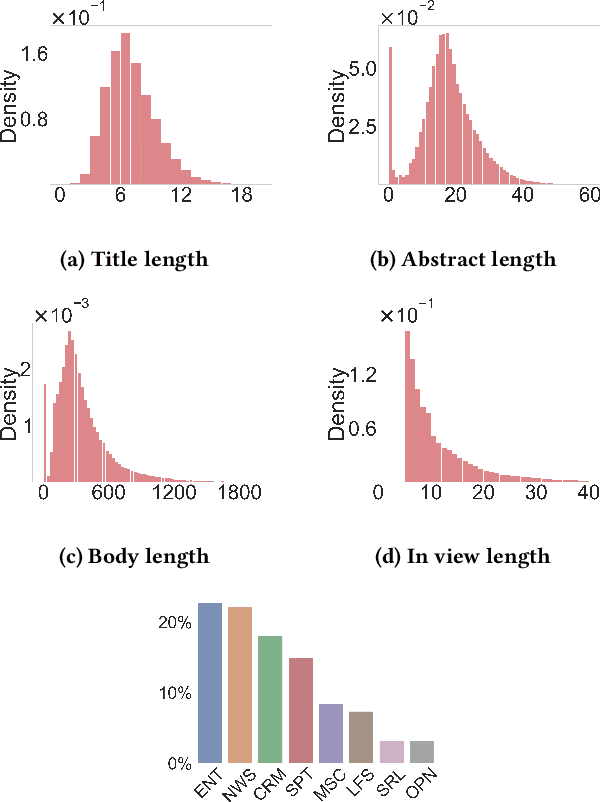
Abstract:Personalized content recommendations have been pivotal to the content experience in digital media from video streaming to social networks. However, several domain specific challenges have held back adoption of recommender systems in news publishing. To address these challenges, we introduce the Ekstra Bladet News Recommendation Dataset (EB-NeRD). The dataset encompasses data from over a million unique users and more than 37 million impression logs from Ekstra Bladet. It also includes a collection of over 125,000 Danish news articles, complete with titles, abstracts, bodies, and metadata, such as categories. EB-NeRD served as the benchmark dataset for the RecSys '24 Challenge, where it was demonstrated how the dataset can be used to address both technical and normative challenges in designing effective and responsible recommender systems for news publishing. The dataset is available at: https://recsys.eb.dk.
RecSys Challenge 2024: Balancing Accuracy and Editorial Values in News Recommendations
Sep 30, 2024
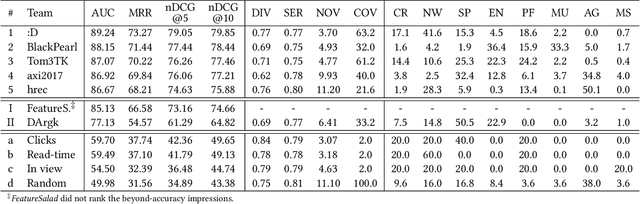
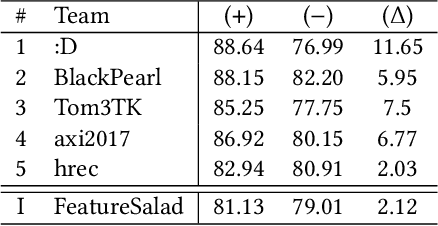
Abstract:The RecSys Challenge 2024 aims to advance news recommendation by addressing both the technical and normative challenges inherent in designing effective and responsible recommender systems for news publishing. This paper describes the challenge, including its objectives, problem setting, and the dataset provided by the Danish news publishers Ekstra Bladet and JP/Politikens Media Group ("Ekstra Bladet"). The challenge explores the unique aspects of news recommendation, such as modeling user preferences based on behavior, accounting for the influence of the news agenda on user interests, and managing the rapid decay of news items. Additionally, the challenge embraces normative complexities, investigating the effects of recommender systems on news flow and their alignment with editorial values. We summarize the challenge setup, dataset characteristics, and evaluation metrics. Finally, we announce the winners and highlight their contributions. The dataset is available at: https://recsys.eb.dk.
Ducho meets Elliot: Large-scale Benchmarks for Multimodal Recommendation
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:In specific domains like fashion, music, and movie recommendation, the multi-faceted features characterizing products and services may influence each customer on online selling platforms differently, paving the way to novel multimodal recommendation models that can learn from such multimodal content. According to the literature, the common multimodal recommendation pipeline involves (i) extracting multimodal features, (ii) refining their high-level representations to suit the recommendation task, (iii) optionally fusing all multimodal features, and (iv) predicting the user-item score. While great effort has been put into designing optimal solutions for (ii-iv), to the best of our knowledge, very little attention has been devoted to exploring procedures for (i). In this respect, the existing literature outlines the large availability of multimodal datasets and the ever-growing number of large models accounting for multimodal-aware tasks, but (at the same time) an unjustified adoption of limited standardized solutions. This motivates us to explore more extensive techniques for the (i) stage of the pipeline. To this end, this paper settles as the first attempt to offer a large-scale benchmarking for multimodal recommender systems, with a specific focus on multimodal extractors. Specifically, we take advantage of two popular and recent frameworks for multimodal feature extraction and reproducibility in recommendation, Ducho and Elliot, to offer a unified and ready-to-use experimental environment able to run extensive benchmarking analyses leveraging novel multimodal feature extractors. Results, largely validated under different hyper-parameter settings for the chosen extractors, provide important insights on how to train and tune the next generation of multimodal recommendation algorithms.
Do We Really Need to Drop Items with Missing Modalities in Multimodal Recommendation?
Aug 21, 2024
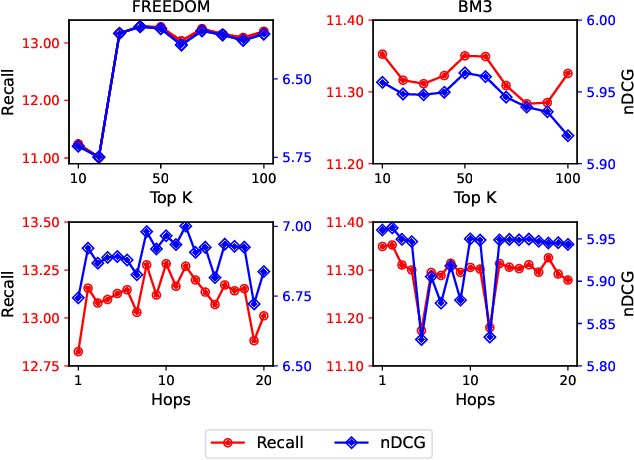
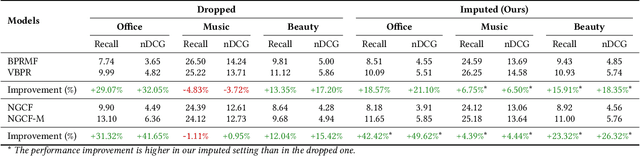
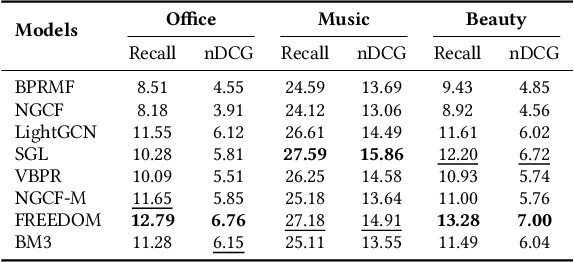
Abstract:Generally, items with missing modalities are dropped in multimodal recommendation. However, with this work, we question this procedure, highlighting that it would further damage the pipeline of any multimodal recommender system. First, we show that the lack of (some) modalities is, in fact, a widely-diffused phenomenon in multimodal recommendation. Second, we propose a pipeline that imputes missing multimodal features in recommendation by leveraging traditional imputation strategies in machine learning. Then, given the graph structure of the recommendation data, we also propose three more effective imputation solutions that leverage the item-item co-purchase graph and the multimodal similarities of co-interacted items. Our method can be plugged into any multimodal RSs in the literature working as an untrained pre-processing phase, showing (through extensive experiments) that any data pre-filtering is not only unnecessary but also harmful to the performance.
A Novel Evaluation Perspective on GNNs-based Recommender Systems through the Topology of the User-Item Graph
Aug 21, 2024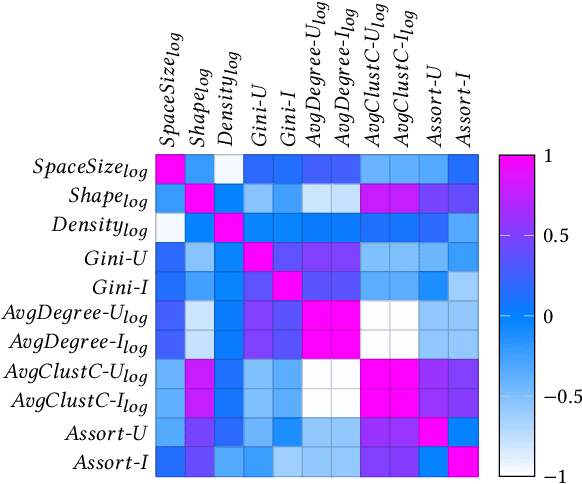
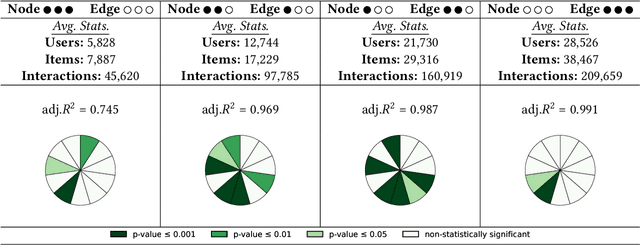
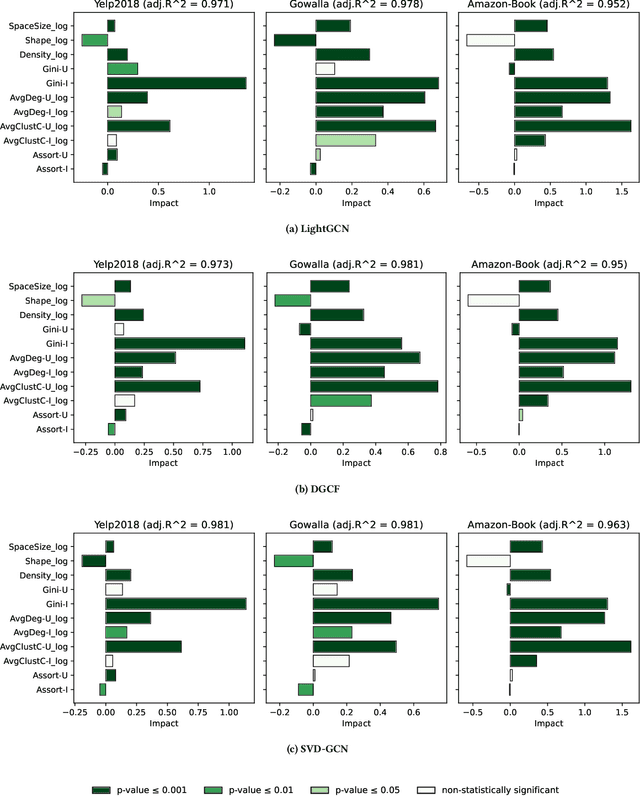
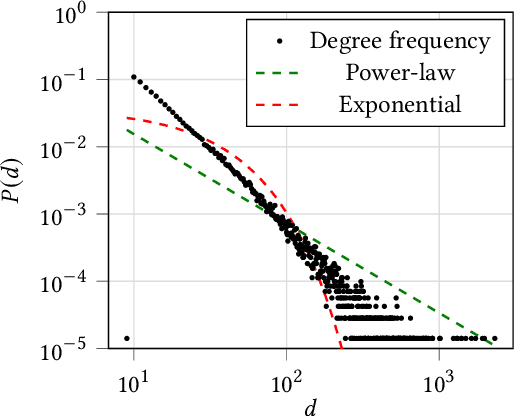
Abstract:Recently, graph neural networks (GNNs)-based recommender systems have encountered great success in recommendation. As the number of GNNs approaches rises, some works have started questioning the theoretical and empirical reasons behind their superior performance. Nevertheless, this investigation still disregards that GNNs treat the recommendation data as a topological graph structure. Building on this assumption, in this work, we provide a novel evaluation perspective on GNNs-based recommendation, which investigates the impact of the graph topology on the recommendation performance. To this end, we select some (topological) properties of the recommendation data and three GNNs-based recommender systems (i.e., LightGCN, DGCF, and SVD-GCN). Then, starting from three popular recommendation datasets (i.e., Yelp2018, Gowalla, and Amazon-Book) we sample them to obtain 1,800 size-reduced datasets that still resemble the original ones but can encompass a wider range of topological structures. We use this procedure to build a large pool of samples for which data characteristics and recommendation performance of the selected GNNs models are measured. Through an explanatory framework, we find strong correspondences between graph topology and GNNs performance, offering a novel evaluation perspective on these models.
Fashion Image-to-Image Translation for Complementary Item Retrieval
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:The increasing demand for online fashion retail has boosted research in fashion compatibility modeling and item retrieval, focusing on matching user queries (textual descriptions or reference images) with compatible fashion items. A key challenge is top-bottom retrieval, where precise compatibility modeling is essential. Traditional methods, often based on Bayesian Personalized Ranking (BPR), have shown limited performance. Recent efforts have explored using generative models in compatibility modeling and item retrieval, where generated images serve as additional inputs. However, these approaches often overlook the quality of generated images, which could be crucial for model performance. Additionally, generative models typically require large datasets, posing challenges when such data is scarce. To address these issues, we introduce the Generative Compatibility Model (GeCo), a two-stage approach that improves fashion image retrieval through paired image-to-image translation. First, the Complementary Item Generation Model (CIGM), built on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), generates target item images (e.g., bottoms) from seed items (e.g., tops), offering conditioning signals for retrieval. These generated samples are then integrated into GeCo, enhancing compatibility modeling and retrieval accuracy. Evaluations on three datasets show that GeCo outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Key contributions include: (i) the GeCo model utilizing paired image-to-image translation within the Composed Image Retrieval framework, (ii) comprehensive evaluations on benchmark datasets, and (iii) the release of a new Fashion Taobao dataset designed for top-bottom retrieval, promoting further research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge