Matteo Attimonelli
FlowLet: Conditional 3D Brain MRI Synthesis using Wavelet Flow Matching
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) plays a central role in studying neurological development, aging, and diseases. One key application is Brain Age Prediction (BAP), which estimates an individual's biological brain age from MRI data. Effective BAP models require large, diverse, and age-balanced datasets, whereas existing 3D MRI datasets are demographically skewed, limiting fairness and generalizability. Acquiring new data is costly and ethically constrained, motivating generative data augmentation. Current generative methods are often based on latent diffusion models, which operate in learned low dimensional latent spaces to address the memory demands of volumetric MRI data. However, these methods are typically slow at inference, may introduce artifacts due to latent compression, and are rarely conditioned on age, thereby affecting the BAP performance. In this work, we propose FlowLet, a conditional generative framework that synthesizes age-conditioned 3D MRIs by leveraging flow matching within an invertible 3D wavelet domain, helping to avoid reconstruction artifacts and reducing computational demands. Experiments show that FlowLet generates high-fidelity volumes with few sampling steps. Training BAP models with data generated by FlowLet improves performance for underrepresented age groups, and region-based analysis confirms preservation of anatomical structures.
Do Recommender Systems Really Leverage Multimodal Content? A Comprehensive Analysis on Multimodal Representations for Recommendation
Aug 06, 2025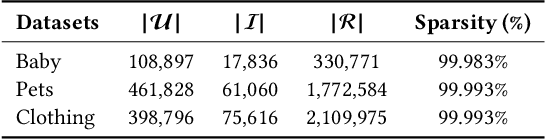
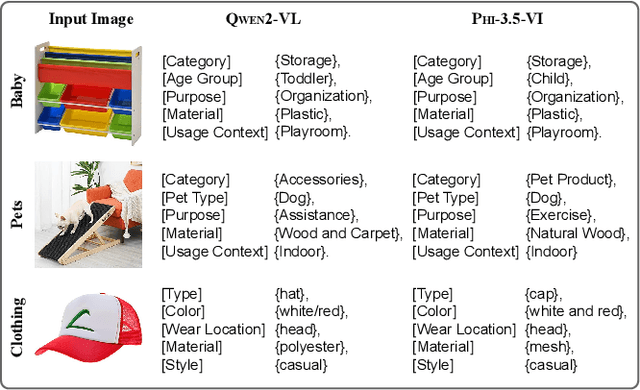
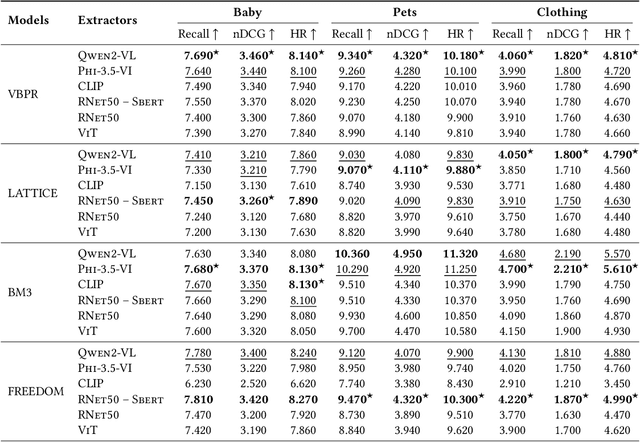
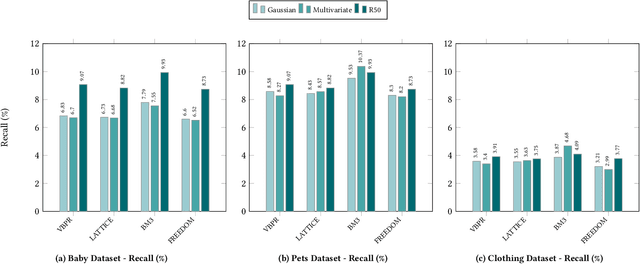
Abstract:Multimodal Recommender Systems aim to improve recommendation accuracy by integrating heterogeneous content, such as images and textual metadata. While effective, it remains unclear whether their gains stem from true multimodal understanding or increased model complexity. This work investigates the role of multimodal item embeddings, emphasizing the semantic informativeness of the representations. Initial experiments reveal that embeddings from standard extractors (e.g., ResNet50, Sentence-Bert) enhance performance, but rely on modality-specific encoders and ad hoc fusion strategies that lack control over cross-modal alignment. To overcome these limitations, we leverage Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to generate multimodal-by-design embeddings via structured prompts. This approach yields semantically aligned representations without requiring any fusion. Experiments across multiple settings show notable performance improvements. Furthermore, LVLMs embeddings offer a distinctive advantage: they can be decoded into structured textual descriptions, enabling direct assessment of their multimodal comprehension. When such descriptions are incorporated as side content into recommender systems, they improve recommendation performance, empirically validating the semantic depth and alignment encoded within LVLMs outputs. Our study highlights the importance of semantically rich representations and positions LVLMs as a compelling foundation for building robust and meaningful multimodal representations in recommendation tasks.
Ducho meets Elliot: Large-scale Benchmarks for Multimodal Recommendation
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:In specific domains like fashion, music, and movie recommendation, the multi-faceted features characterizing products and services may influence each customer on online selling platforms differently, paving the way to novel multimodal recommendation models that can learn from such multimodal content. According to the literature, the common multimodal recommendation pipeline involves (i) extracting multimodal features, (ii) refining their high-level representations to suit the recommendation task, (iii) optionally fusing all multimodal features, and (iv) predicting the user-item score. While great effort has been put into designing optimal solutions for (ii-iv), to the best of our knowledge, very little attention has been devoted to exploring procedures for (i). In this respect, the existing literature outlines the large availability of multimodal datasets and the ever-growing number of large models accounting for multimodal-aware tasks, but (at the same time) an unjustified adoption of limited standardized solutions. This motivates us to explore more extensive techniques for the (i) stage of the pipeline. To this end, this paper settles as the first attempt to offer a large-scale benchmarking for multimodal recommender systems, with a specific focus on multimodal extractors. Specifically, we take advantage of two popular and recent frameworks for multimodal feature extraction and reproducibility in recommendation, Ducho and Elliot, to offer a unified and ready-to-use experimental environment able to run extensive benchmarking analyses leveraging novel multimodal feature extractors. Results, largely validated under different hyper-parameter settings for the chosen extractors, provide important insights on how to train and tune the next generation of multimodal recommendation algorithms.
Fashion Image-to-Image Translation for Complementary Item Retrieval
Aug 19, 2024



Abstract:The increasing demand for online fashion retail has boosted research in fashion compatibility modeling and item retrieval, focusing on matching user queries (textual descriptions or reference images) with compatible fashion items. A key challenge is top-bottom retrieval, where precise compatibility modeling is essential. Traditional methods, often based on Bayesian Personalized Ranking (BPR), have shown limited performance. Recent efforts have explored using generative models in compatibility modeling and item retrieval, where generated images serve as additional inputs. However, these approaches often overlook the quality of generated images, which could be crucial for model performance. Additionally, generative models typically require large datasets, posing challenges when such data is scarce. To address these issues, we introduce the Generative Compatibility Model (GeCo), a two-stage approach that improves fashion image retrieval through paired image-to-image translation. First, the Complementary Item Generation Model (CIGM), built on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), generates target item images (e.g., bottoms) from seed items (e.g., tops), offering conditioning signals for retrieval. These generated samples are then integrated into GeCo, enhancing compatibility modeling and retrieval accuracy. Evaluations on three datasets show that GeCo outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Key contributions include: (i) the GeCo model utilizing paired image-to-image translation within the Composed Image Retrieval framework, (ii) comprehensive evaluations on benchmark datasets, and (iii) the release of a new Fashion Taobao dataset designed for top-bottom retrieval, promoting further research.
Ducho 2.0: Towards a More Up-to-Date Feature Extraction and Processing Framework for Multimodal Recommendation
Mar 07, 2024
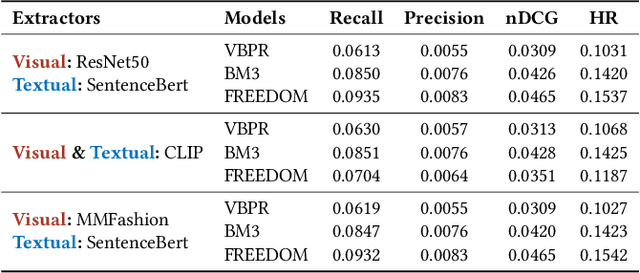
Abstract:In this work, we introduce Ducho 2.0, the latest stable version of our framework. Differently from Ducho, Ducho 2.0 offers a more personalized user experience with the definition and import of custom extraction models fine-tuned on specific tasks and datasets. Moreover, the new version is capable of extracting and processing features through multimodal-by-design large models. Notably, all these new features are supported by optimized data loading and storing to the local memory. To showcase the capabilities of Ducho 2.0, we demonstrate a complete multimodal recommendation pipeline, from the extraction/processing to the final recommendation. The idea is to provide practitioners and experienced scholars with a ready-to-use tool that, put on top of any multimodal recommendation framework, may permit them to run extensive benchmarking analyses. All materials are accessible at: \url{https://github.com/sisinflab/Ducho}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge