Chenxi Yang
A Practical Cross-Layer Approach for ML-Driven Storage Placement in Warehouse-Scale Computers
Jan 10, 2025Abstract:Storage systems account for a major portion of the total cost of ownership (TCO) of warehouse-scale computers, and thus have a major impact on the overall system's efficiency. Machine learning (ML)-based methods for solving key problems in storage system efficiency, such as data placement, have shown significant promise. However, there are few known practical deployments of such methods. Studying this problem in the context of real-world hyperscale data center deployments at Google, we identify a number of challenges that we believe cause this lack of practical adoption. Specifically, prior work assumes a monolithic model that resides entirely within the storage layer, an unrealistic assumption in real-world data center deployments. We propose a cross-layer approach that moves ML out of the storage system and performs it in the application running on top of it, co-designed with a scheduling algorithm at the storage layer that consumes predictions from these application-level models. This approach combines small, interpretable models with a co-designed heuristic that adapts to different online environments. We build a proof-of-concept of this approach in a production distributed computation framework at Google. Evaluations in a test deployment and large-scale simulation studies using production traces show improvements of as much as 3.47x in TCO savings compared to state of the art baselines. We believe this work represents a significant step towards more practical ML-driven storage placement in warehouse-scale computers.
C3: Learning Congestion Controllers with Formal Certificates
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Learning-based congestion controllers offer better adaptability compared to traditional heuristic algorithms. However, the inherent unreliability of learning techniques can cause learning-based controllers to behave poorly, creating a need for formal guarantees. While methods for formally verifying learned congestion controllers exist, these methods offer binary feedback that cannot optimize the controller toward better behavior. We improve this state-of-the-art via C3, a new learning framework for congestion control that integrates the concept of formal certification in the learning loop. C3 uses an abstract interpreter that can produce robustness and performance certificates to guide the training process, rewarding models that are robust and performant even on worst-case inputs. Our evaluation demonstrates that unlike state-of-the-art learned controllers, C3-trained controllers provide both adaptability and worst-case reliability across a range of network conditions.
Beyond Score Changes: Adversarial Attack on No-Reference Image Quality Assessment from Two Perspectives
Apr 24, 2024



Abstract:Deep neural networks have demonstrated impressive success in No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA). However, recent researches highlight the vulnerability of NR-IQA models to subtle adversarial perturbations, leading to inconsistencies between model predictions and subjective ratings. Current adversarial attacks, however, focus on perturbing predicted scores of individual images, neglecting the crucial aspect of inter-score correlation relationships within an entire image set. Meanwhile, it is important to note that the correlation, like ranking correlation, plays a significant role in NR-IQA tasks. To comprehensively explore the robustness of NR-IQA models, we introduce a new framework of correlation-error-based attacks that perturb both the correlation within an image set and score changes on individual images. Our research primarily focuses on ranking-related correlation metrics like Spearman's Rank-Order Correlation Coefficient (SROCC) and prediction error-related metrics like Mean Squared Error (MSE). As an instantiation, we propose a practical two-stage SROCC-MSE-Attack (SMA) that initially optimizes target attack scores for the entire image set and then generates adversarial examples guided by these scores. Experimental results demonstrate that our SMA method not only significantly disrupts the SROCC to negative values but also maintains a considerable change in the scores of individual images. Meanwhile, it exhibits state-of-the-art performance across metrics with different categories. Our method provides a new perspective on the robustness of NR-IQA models.
Deep Policy Optimization with Temporal Logic Constraints
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Temporal logics, such as linear temporal logic (LTL), offer a precise means of specifying tasks for (deep) reinforcement learning (RL) agents. In our work, we consider the setting where the task is specified by an LTL objective and there is an additional scalar reward that we need to optimize. Previous works focus either on learning a LTL task-satisfying policy alone or are restricted to finite state spaces. We make two contributions: First, we introduce an RL-friendly approach to this setting by formulating this problem as a single optimization objective. Our formulation guarantees that an optimal policy will be reward-maximal from the set of policies that maximize the likelihood of satisfying the LTL specification. Second, we address a sparsity issue that often arises for LTL-guided Deep RL policies by introducing Cycle Experience Replay (CyclER), a technique that automatically guides RL agents towards the satisfaction of an LTL specification. Our experiments demonstrate the efficacy of CyclER in finding performant deep RL policies in both continuous and discrete experimental domains.
Defense Against Adversarial Attacks on No-Reference Image Quality Models with Gradient Norm Regularization
Mar 18, 2024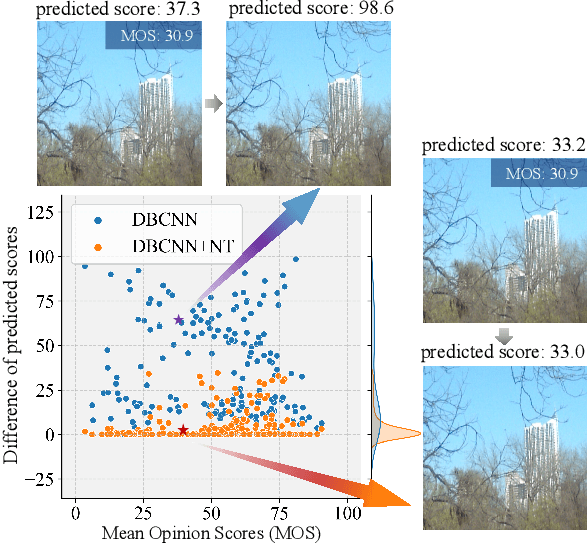
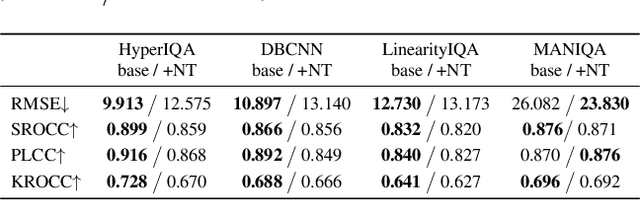
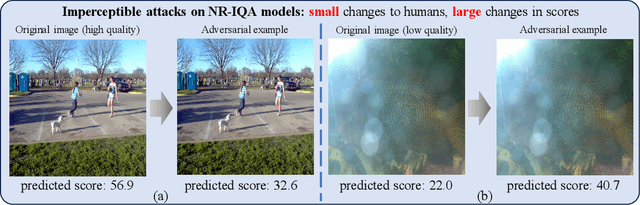
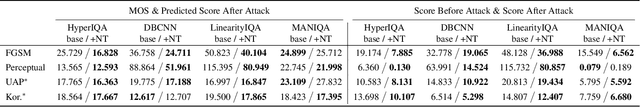
Abstract:The task of No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) is to estimate the quality score of an input image without additional information. NR-IQA models play a crucial role in the media industry, aiding in performance evaluation and optimization guidance. However, these models are found to be vulnerable to adversarial attacks, which introduce imperceptible perturbations to input images, resulting in significant changes in predicted scores. In this paper, we propose a defense method to improve the stability in predicted scores when attacked by small perturbations, thus enhancing the adversarial robustness of NR-IQA models. To be specific, we present theoretical evidence showing that the magnitude of score changes is related to the $\ell_1$ norm of the model's gradient with respect to the input image. Building upon this theoretical foundation, we propose a norm regularization training strategy aimed at reducing the $\ell_1$ norm of the gradient, thereby boosting the robustness of NR-IQA models. Experiments conducted on four NR-IQA baseline models demonstrate the effectiveness of our strategy in reducing score changes in the presence of adversarial attacks. To the best of our knowledge, this work marks the first attempt to defend against adversarial attacks on NR-IQA models. Our study offers valuable insights into the adversarial robustness of NR-IQA models and provides a foundation for future research in this area.
Exploring Vulnerabilities of No-Reference Image Quality Assessment Models: A Query-Based Black-Box Method
Jan 17, 2024



Abstract:No-Reference Image Quality Assessment (NR-IQA) aims to predict image quality scores consistent with human perception without relying on pristine reference images, serving as a crucial component in various visual tasks. Ensuring the robustness of NR-IQA methods is vital for reliable comparisons of different image processing techniques and consistent user experiences in recommendations. The attack methods for NR-IQA provide a powerful instrument to test the robustness of NR-IQA. However, current attack methods of NR-IQA heavily rely on the gradient of the NR-IQA model, leading to limitations when the gradient information is unavailable. In this paper, we present a pioneering query-based black box attack against NR-IQA methods. We propose the concept of score boundary and leverage an adaptive iterative approach with multiple score boundaries. Meanwhile, the initial attack directions are also designed to leverage the characteristics of the Human Visual System (HVS). Experiments show our method outperforms all compared state-of-the-art attack methods and is far ahead of previous black-box methods. The effective NR-IQA model DBCNN suffers a Spearman's rank-order correlation coefficient (SROCC) decline of 0.6381 attacked by our method, revealing the vulnerability of NR-IQA models to black-box attacks. The proposed attack method also provides a potent tool for further exploration into NR-IQA robustness.
On a Foundation Model for Operating Systems
Dec 13, 2023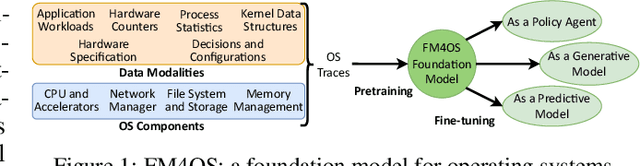
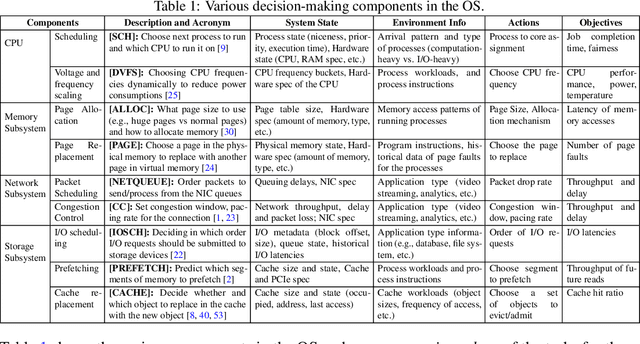
Abstract:This paper lays down the research agenda for a domain-specific foundation model for operating systems (OSes). Our case for a foundation model revolves around the observations that several OS components such as CPU, memory, and network subsystems are interrelated and that OS traces offer the ideal dataset for a foundation model to grasp the intricacies of diverse OS components and their behavior in varying environments and workloads. We discuss a wide range of possibilities that then arise, from employing foundation models as policy agents to utilizing them as generators and predictors to assist traditional OS control algorithms. Our hope is that this paper spurs further research into OS foundation models and creating the next generation of operating systems for the evolving computing landscape.
Adaptive Scheduling for Edge-Assisted DNN Serving
May 02, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have been widely used in various video analytic tasks. These tasks demand real-time responses. Due to the limited processing power on mobile devices, a common way to support such real-time analytics is to offload the processing to an edge server. This paper examines how to speed up the edge server DNN processing for multiple clients. In particular, we observe batching multiple DNN requests significantly speeds up the processing time. Based on this observation, we first design a novel scheduling algorithm to exploit the batching benefits of all requests that run the same DNN. This is compelling since there are only a handful of DNNs and many requests tend to use the same DNN. Our algorithms are general and can support different objectives, such as minimizing the completion time or maximizing the on-time ratio. We then extend our algorithm to handle requests that use different DNNs with or without shared layers. Finally, we develop a collaborative approach to further improve performance by adaptively processing some of the requests or portions of the requests locally at the clients. This is especially useful when the network and/or server is congested. Our implementation shows the effectiveness of our approach under different request distributions (e.g., Poisson, Pareto, and Constant inter-arrivals).
Policy Optimization with Robustness Certificates
Jan 26, 2023Abstract:We present a policy optimization framework in which the learned policy comes with a machine-checkable certificate of adversarial robustness. Our approach, called CAROL, learns a model of the environment. In each learning iteration, it uses the current version of this model and an external abstract interpreter to construct a differentiable signal for provable robustness. This signal is used to guide policy learning, and the abstract interpretation used to construct it directly leads to the robustness certificate returned at convergence. We give a theoretical analysis that bounds the worst-case accumulative reward of CAROL. We also experimentally evaluate CAROL on four MuJoCo environments. On these tasks, which involve continuous state and action spaces, CAROL learns certified policies that have performance comparable to the (non-certified) policies learned using state-of-the-art robust RL methods.
Safe Neurosymbolic Learning with Differentiable Symbolic Execution
Mar 15, 2022



Abstract:We study the problem of learning worst-case-safe parameters for programs that use neural networks as well as symbolic, human-written code. Such neurosymbolic programs arise in many safety-critical domains. However, because they can use nondifferentiable operations, it is hard to learn their parameters using existing gradient-based approaches to safe learning. Our approach to this problem, Differentiable Symbolic Execution (DSE), samples control flow paths in a program, symbolically constructs worst-case "safety losses" along these paths, and backpropagates the gradients of these losses through program operations using a generalization of the REINFORCE estimator. We evaluate the method on a mix of synthetic tasks and real-world benchmarks. Our experiments show that DSE significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art DiffAI method on these tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge