Martin Maas
A Practical Cross-Layer Approach for ML-Driven Storage Placement in Warehouse-Scale Computers
Jan 10, 2025Abstract:Storage systems account for a major portion of the total cost of ownership (TCO) of warehouse-scale computers, and thus have a major impact on the overall system's efficiency. Machine learning (ML)-based methods for solving key problems in storage system efficiency, such as data placement, have shown significant promise. However, there are few known practical deployments of such methods. Studying this problem in the context of real-world hyperscale data center deployments at Google, we identify a number of challenges that we believe cause this lack of practical adoption. Specifically, prior work assumes a monolithic model that resides entirely within the storage layer, an unrealistic assumption in real-world data center deployments. We propose a cross-layer approach that moves ML out of the storage system and performs it in the application running on top of it, co-designed with a scheduling algorithm at the storage layer that consumes predictions from these application-level models. This approach combines small, interpretable models with a co-designed heuristic that adapts to different online environments. We build a proof-of-concept of this approach in a production distributed computation framework at Google. Evaluations in a test deployment and large-scale simulation studies using production traces show improvements of as much as 3.47x in TCO savings compared to state of the art baselines. We believe this work represents a significant step towards more practical ML-driven storage placement in warehouse-scale computers.
Learning to Improve Code Efficiency
Aug 09, 2022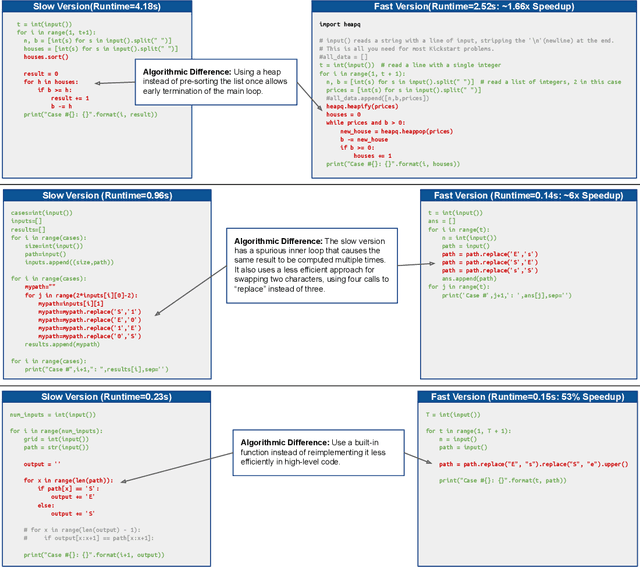
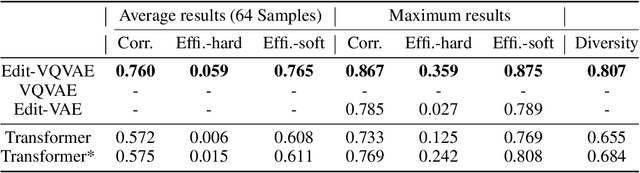
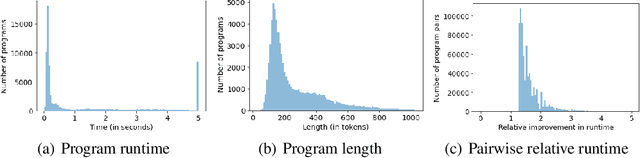
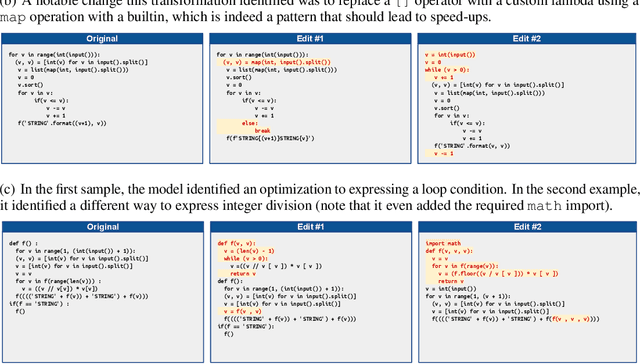
Abstract:Improvements in the performance of computing systems, driven by Moore's Law, have transformed society. As such hardware-driven gains slow down, it becomes even more important for software developers to focus on performance and efficiency during development. While several studies have demonstrated the potential from such improved code efficiency (e.g., 2x better generational improvements compared to hardware), unlocking these gains in practice has been challenging. Reasoning about algorithmic complexity and the interaction of coding patterns on hardware can be challenging for the average programmer, especially when combined with pragmatic constraints around development velocity and multi-person development. This paper seeks to address this problem. We analyze a large competitive programming dataset from the Google Code Jam competition and find that efficient code is indeed rare, with a 2x runtime difference between the median and the 90th percentile of solutions. We propose using machine learning to automatically provide prescriptive feedback in the form of hints, to guide programmers towards writing high-performance code. To automatically learn these hints from the dataset, we propose a novel discrete variational auto-encoder, where each discrete latent variable represents a different learned category of code-edit that increases performance. We show that this method represents the multi-modal space of code efficiency edits better than a sequence-to-sequence baseline and generates a distribution of more efficient solutions.
Analyzing a Caching Model
Dec 13, 2021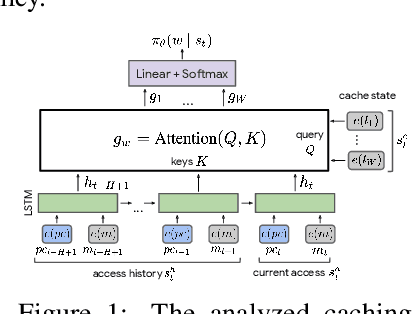
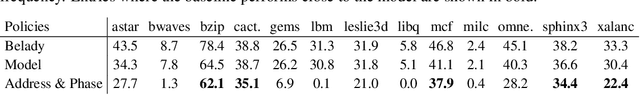
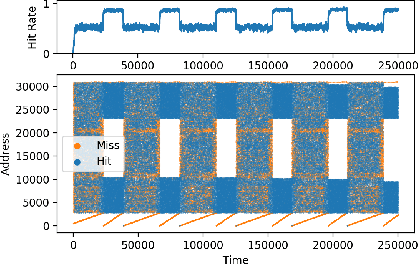
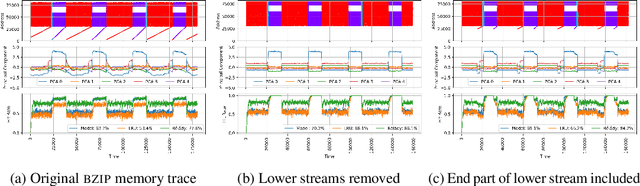
Abstract:Machine Learning has been successfully applied in systems applications such as memory prefetching and caching, where learned models have been shown to outperform heuristics. However, the lack of understanding the inner workings of these models -- interpretability -- remains a major obstacle for adoption in real-world deployments. Understanding a model's behavior can help system administrators and developers gain confidence in the model, understand risks, and debug unexpected behavior in production. Interpretability for models used in computer systems poses a particular challenge: Unlike ML models trained on images or text, the input domain (e.g., memory access patterns, program counters) is not immediately interpretable. A major challenge is therefore to explain the model in terms of concepts that are approachable to a human practitioner. By analyzing a state-of-the-art caching model, we provide evidence that the model has learned concepts beyond simple statistics that can be leveraged for explanations. Our work provides a first step towards explanability of system ML models and highlights both promises and challenges of this emerging research area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge