Cameron Voloshin
Deep Policy Optimization with Temporal Logic Constraints
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:Temporal logics, such as linear temporal logic (LTL), offer a precise means of specifying tasks for (deep) reinforcement learning (RL) agents. In our work, we consider the setting where the task is specified by an LTL objective and there is an additional scalar reward that we need to optimize. Previous works focus either on learning a LTL task-satisfying policy alone or are restricted to finite state spaces. We make two contributions: First, we introduce an RL-friendly approach to this setting by formulating this problem as a single optimization objective. Our formulation guarantees that an optimal policy will be reward-maximal from the set of policies that maximize the likelihood of satisfying the LTL specification. Second, we address a sparsity issue that often arises for LTL-guided Deep RL policies by introducing Cycle Experience Replay (CyclER), a technique that automatically guides RL agents towards the satisfaction of an LTL specification. Our experiments demonstrate the efficacy of CyclER in finding performant deep RL policies in both continuous and discrete experimental domains.
Eventual Discounting Temporal Logic Counterfactual Experience Replay
Mar 03, 2023Abstract:Linear temporal logic (LTL) offers a simplified way of specifying tasks for policy optimization that may otherwise be difficult to describe with scalar reward functions. However, the standard RL framework can be too myopic to find maximally LTL satisfying policies. This paper makes two contributions. First, we develop a new value-function based proxy, using a technique we call eventual discounting, under which one can find policies that satisfy the LTL specification with highest achievable probability. Second, we develop a new experience replay method for generating off-policy data from on-policy rollouts via counterfactual reasoning on different ways of satisfying the LTL specification. Our experiments, conducted in both discrete and continuous state-action spaces, confirm the effectiveness of our counterfactual experience replay approach.
Policy Optimization with Linear Temporal Logic Constraints
Jun 20, 2022
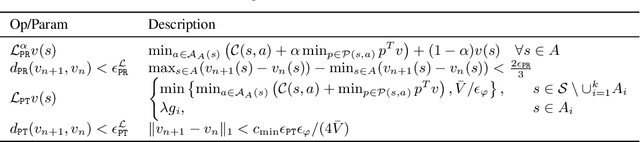
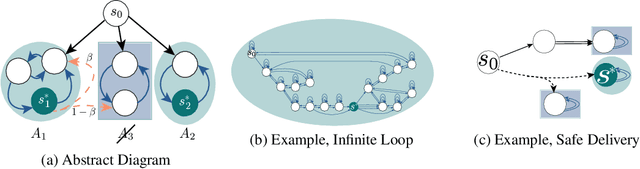
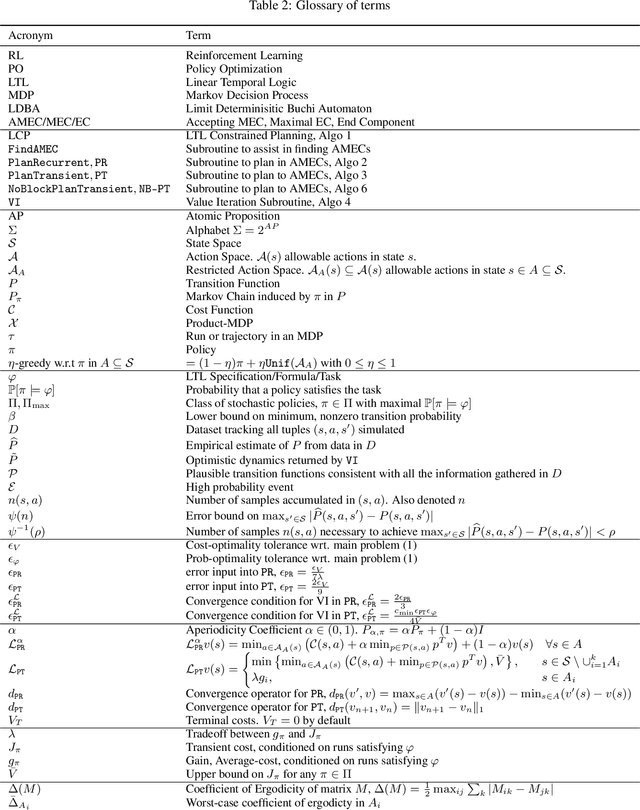
Abstract:We study the problem of policy optimization (PO) with linear temporal logic (LTL) constraints. The language of LTL allows flexible description of tasks that may be unnatural to encode as a scalar cost function. We consider LTL-constrained PO as a systematic framework, decoupling task specification from policy selection, and an alternative to the standard of cost shaping. With access to a generative model, we develop a model-based approach that enjoys a sample complexity analysis for guaranteeing both task satisfaction and cost optimality (through a reduction to a reachability problem). Empirically, our algorithm can achieve strong performance even in low sample regimes.
Minimax Model Learning
Mar 02, 2021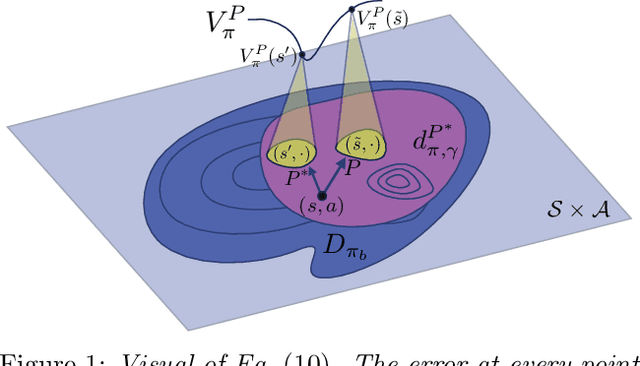

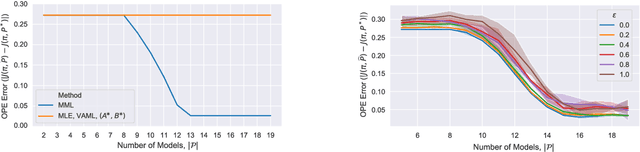
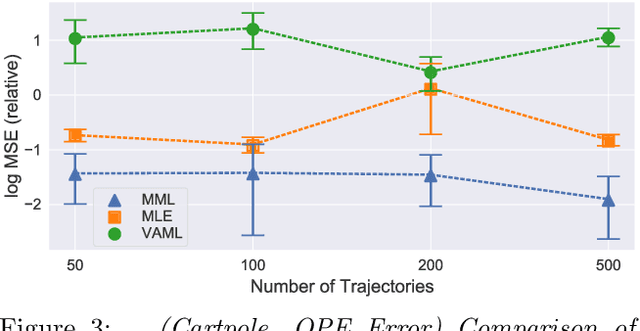
Abstract:We present a novel off-policy loss function for learning a transition model in model-based reinforcement learning. Notably, our loss is derived from the off-policy policy evaluation objective with an emphasis on correcting distribution shift. Compared to previous model-based techniques, our approach allows for greater robustness under model misspecification or distribution shift induced by learning/evaluating policies that are distinct from the data-generating policy. We provide a theoretical analysis and show empirical improvements over existing model-based off-policy evaluation methods. We provide further analysis showing our loss can be used for off-policy optimization (OPO) and demonstrate its integration with more recent improvements in OPO.
Empirical Study of Off-Policy Policy Evaluation for Reinforcement Learning
Nov 15, 2019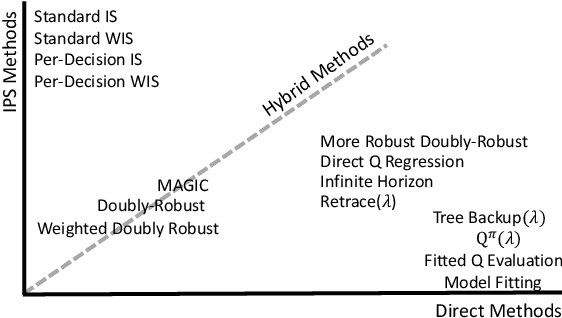
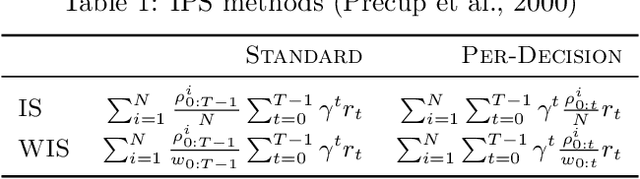
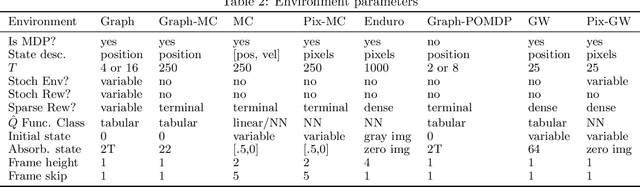
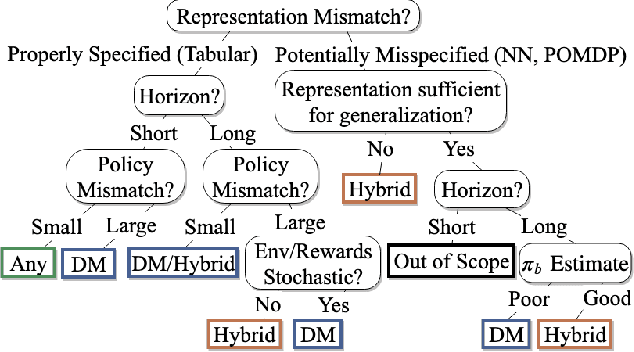
Abstract:Off-policy policy evaluation (OPE) is the problem of estimating the online performance of a policy using only pre-collected historical data generated by another policy. Given the increasing interest in deploying learning-based methods for safety-critical applications, many recent OPE methods have recently been proposed. Due to disparate experimental conditions from recent literature, the relative performance of current OPE methods is not well understood. In this work, we present the first comprehensive empirical analysis of a broad suite of OPE methods. Based on thousands of experiments and detailed empirical analyses, we offer a summarized set of guidelines for effectively using OPE in practice, and suggest directions for future research.
Batch Policy Learning under Constraints
Mar 20, 2019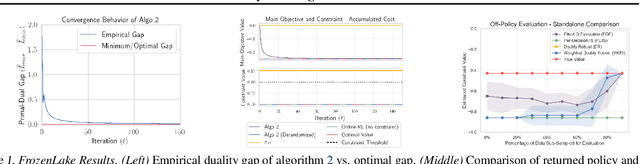
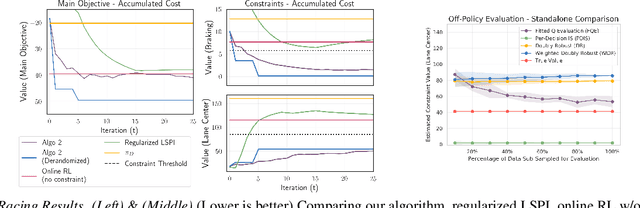
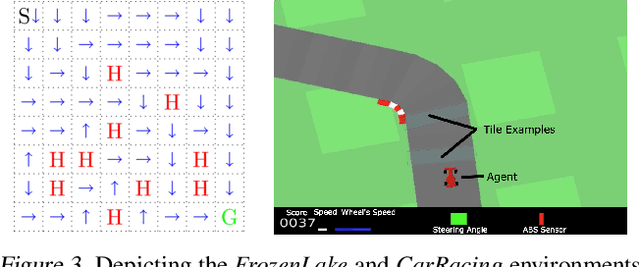
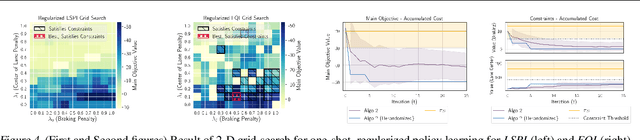
Abstract:When learning policies for real-world domains, two important questions arise: (i) how to efficiently use pre-collected off-policy, non-optimal behavior data; and (ii) how to mediate among different competing objectives and constraints. We thus study the problem of batch policy learning under multiple constraints, and offer a systematic solution. We first propose a flexible meta-algorithm that admits any batch reinforcement learning and online learning procedure as subroutines. We then present a specific algorithmic instantiation and provide performance guarantees for the main objective and all constraints. To certify constraint satisfaction, we propose a new and simple method for off-policy policy evaluation (OPE) and derive PAC-style bounds. Our algorithm achieves strong empirical results in different domains, including in a challenging problem of simulated car driving subject to multiple constraints such as lane keeping and smooth driving. We also show experimentally that our OPE method outperforms other popular OPE techniques on a standalone basis, especially in a high-dimensional setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge