Chao Lin
Towards Understanding and Enhancing Security of Proof-of-Training for DNN Model Ownership Verification
Oct 06, 2024



Abstract:The great economic values of deep neural networks (DNNs) urge AI enterprises to protect their intellectual property (IP) for these models. Recently, proof-of-training (PoT) has been proposed as a promising solution to DNN IP protection, through which AI enterprises can utilize the record of DNN training process as their ownership proof. To prevent attackers from forging ownership proof, a secure PoT scheme should be able to distinguish honest training records from those forged by attackers. Although existing PoT schemes provide various distinction criteria, these criteria are based on intuitions or observations. The effectiveness of these criteria lacks clear and comprehensive analysis, resulting in existing schemes initially deemed secure being swiftly compromised by simple ideas. In this paper, we make the first move to identify distinction criteria in the style of formal methods, so that their effectiveness can be explicitly demonstrated. Specifically, we conduct systematic modeling to cover a wide range of attacks and then theoretically analyze the distinctions between honest and forged training records. The analysis results not only induce a universal distinction criterion, but also provide detailed reasoning to demonstrate its effectiveness in defending against attacks covered by our model. Guided by the criterion, we propose a generic PoT construction that can be instantiated into concrete schemes. This construction sheds light on the realization that trajectory matching algorithms, previously employed in data distillation, possess significant advantages in PoT construction. Experimental results demonstrate that our scheme can resist attacks that have compromised existing PoT schemes, which corroborates its superiority in security.
MetMamba: Regional Weather Forecasting with Spatial-Temporal Mamba Model
Aug 14, 2024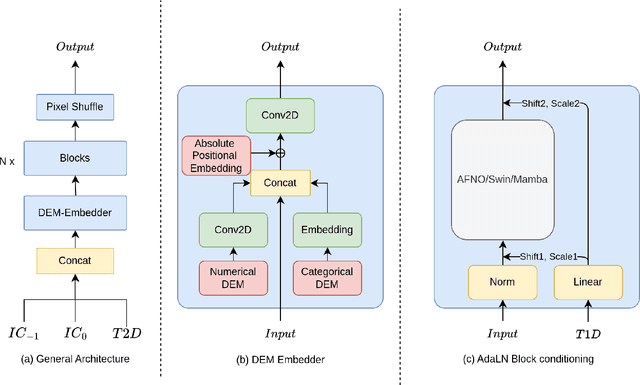
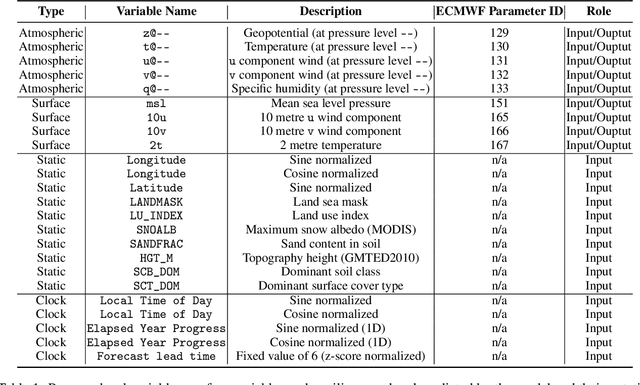
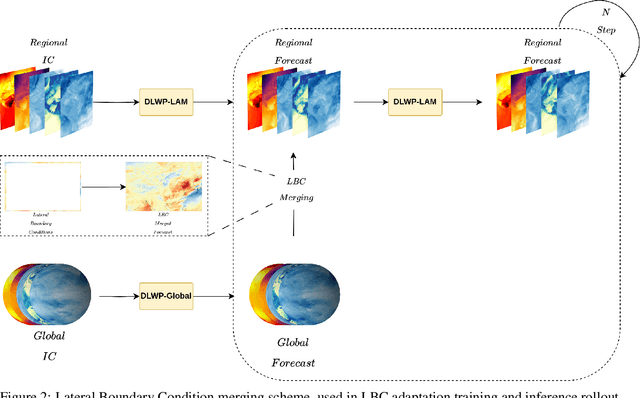
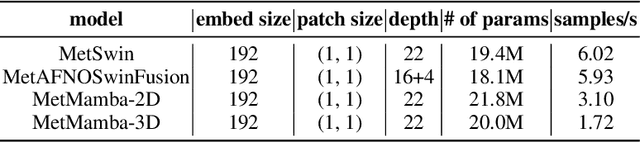
Abstract:Deep Learning based Weather Prediction (DLWP) models have been improving rapidly over the last few years, surpassing state of the art numerical weather forecasts by significant margins. While much of the optimization effort is focused on training curriculum to extend forecast range in the global context, two aspects remains less explored: limited area modeling and better backbones for weather forecasting. We show in this paper that MetMamba, a DLWP model built on a state-of-the-art state-space model, Mamba, offers notable performance gains and unique advantages over other popular backbones using traditional attention mechanisms and neural operators. We also demonstrate the feasibility of deep learning based limited area modeling via coupled training with a global host model.
RMGN: A Regional Mask Guided Network for Parser-free Virtual Try-on
Apr 24, 2022



Abstract:Virtual try-on(VTON) aims at fitting target clothes to reference person images, which is widely adopted in e-commerce.Existing VTON approaches can be narrowly categorized into Parser-Based(PB) and Parser-Free(PF) by whether relying on the parser information to mask the persons' clothes and synthesize try-on images. Although abandoning parser information has improved the applicability of PF methods, the ability of detail synthesizing has also been sacrificed. As a result, the distraction from original cloth may persistin synthesized images, especially in complicated postures and high resolution applications. To address the aforementioned issue, we propose a novel PF method named Regional Mask Guided Network(RMGN). More specifically, a regional mask is proposed to explicitly fuse the features of target clothes and reference persons so that the persisted distraction can be eliminated. A posture awareness loss and a multi-level feature extractor are further proposed to handle the complicated postures and synthesize high resolution images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed RMGN outperforms both state-of-the-art PB and PF methods.Ablation studies further verify the effectiveness ofmodules in RMGN.
iQIYI-VID: A Large Dataset for Multi-modal Person Identification
Nov 19, 2018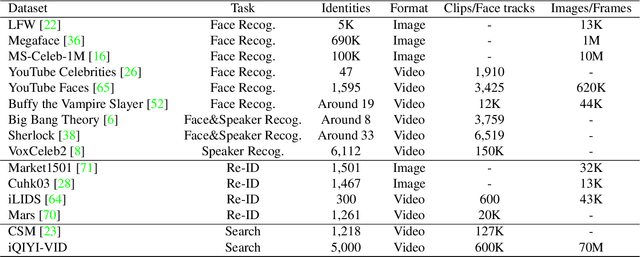
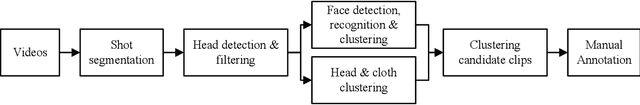
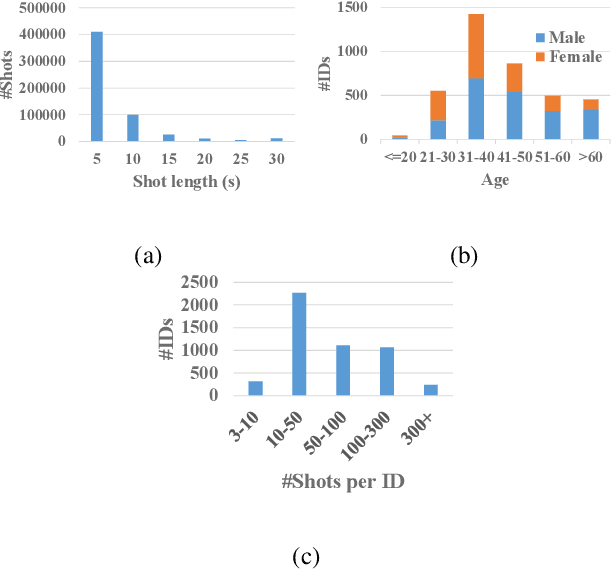
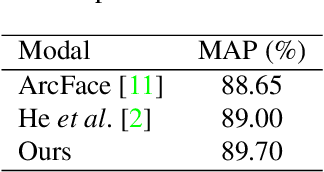
Abstract:Person identification in the wild is very challenging due to great variation in poses, face quality, clothes, makeup and so on. Traditional research, such as face recognition, person re-identification, and speaker recognition, often focuses on a single modal of information, which is inadequate to handle all the situations in practice. Multi-modal person identification is a more promising way that we can jointly utilize face, head, body, audio features, and so on. In this paper, we introduce iQIYI-VID, the largest video dataset for multi-modal person identification. It is composed of 600K video clips of 5,000 celebrities. These video clips are extracted from 400K hours of online videos of various types, ranging from movies, variety shows, TV series, to news broadcasting. All video clips pass through a careful human annotation process, and the error rate of labels is lower than 0.2%. We evaluated the state-of-art models of face recognition, person re-identification, and speaker recognition on the iQIYI-VID dataset. Experimental results show that these models are still far from being perfect for task of person identification in the wild. We further demonstrate that a simple fusion of multi-modal features can improve person identification considerably. We have released the dataset online to promote multi-modal person identification research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge