MetMamba: Regional Weather Forecasting with Spatial-Temporal Mamba Model
Paper and Code
Aug 14, 2024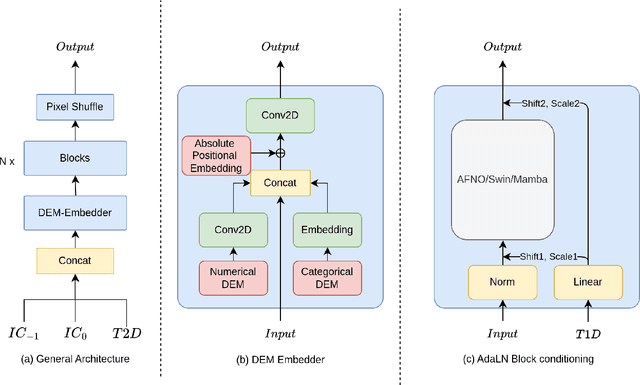
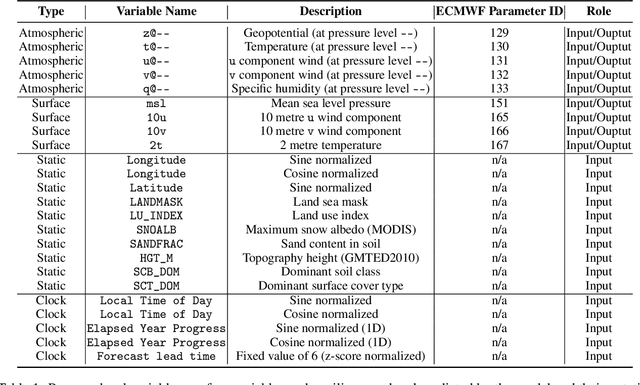
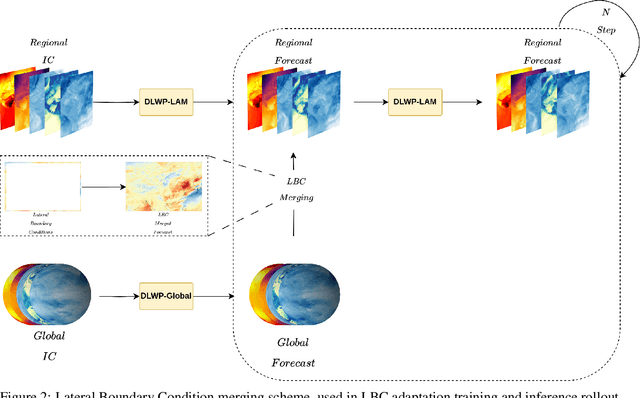
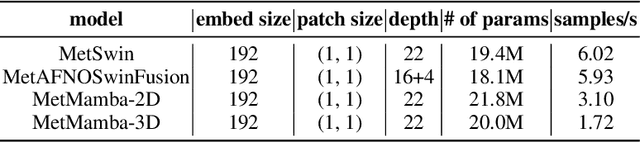
Deep Learning based Weather Prediction (DLWP) models have been improving rapidly over the last few years, surpassing state of the art numerical weather forecasts by significant margins. While much of the optimization effort is focused on training curriculum to extend forecast range in the global context, two aspects remains less explored: limited area modeling and better backbones for weather forecasting. We show in this paper that MetMamba, a DLWP model built on a state-of-the-art state-space model, Mamba, offers notable performance gains and unique advantages over other popular backbones using traditional attention mechanisms and neural operators. We also demonstrate the feasibility of deep learning based limited area modeling via coupled training with a global host model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge