Bingyi Xia
Robust Docking Maneuvers for Autonomous Trolley Collection: An Optimization-Based Visual Servoing Scheme
Sep 09, 2025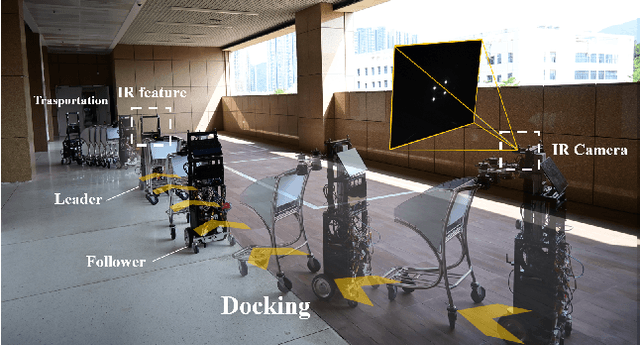
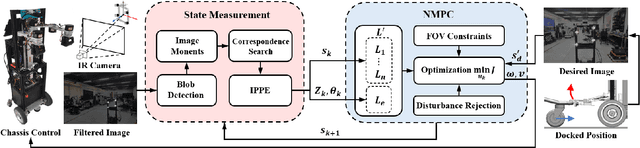
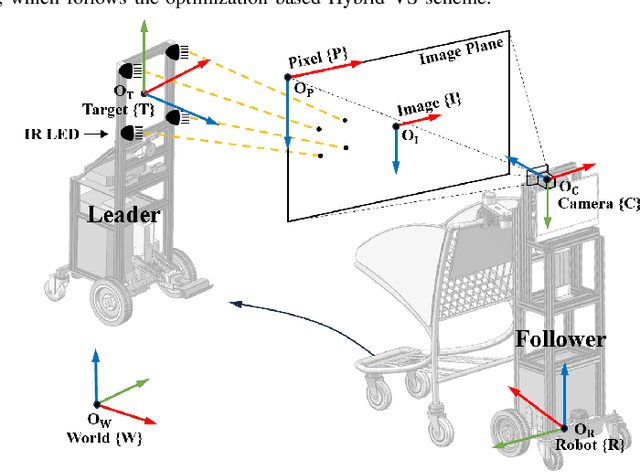
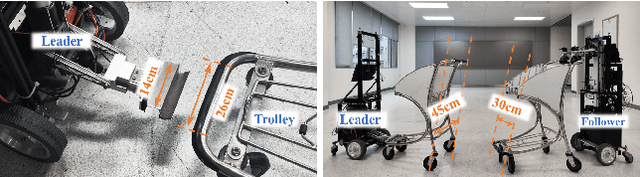
Abstract:Service robots have demonstrated significant potential for autonomous trolley collection and redistribution in public spaces like airports or warehouses to improve efficiency and reduce cost. Usually, a fully autonomous system for the collection and transportation of multiple trolleys is based on a Leader-Follower formation of mobile manipulators, where reliable docking maneuvers of the mobile base are essential to align trolleys into organized queues. However, developing a vision-based robotic docking system faces significant challenges: high precision requirements, environmental disturbances, and inherent robot constraints. To address these challenges, we propose an optimization-based Visual Servoing scheme that incorporates active infrared markers for robust feature extraction across diverse lighting conditions. This framework explicitly models nonholonomic kinematics and visibility constraints within the Hybrid Visual Servoing problem, augmented with an observer for disturbance rejection to ensure precise and stable docking. Experimental results across diverse environments demonstrate the robustness of this system, with quantitative evaluations confirming high docking accuracy.
RPF-Search: Field-based Search for Robot Person Following in Unknown Dynamic Environments
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Autonomous robot person-following (RPF) systems are crucial for personal assistance and security but suffer from target loss due to occlusions in dynamic, unknown environments. Current methods rely on pre-built maps and assume static environments, limiting their effectiveness in real-world settings. There is a critical gap in re-finding targets under topographic (e.g., walls, corners) and dynamic (e.g., moving pedestrians) occlusions. In this paper, we propose a novel heuristic-guided search framework that dynamically builds environmental maps while following the target and resolves various occlusions by prioritizing high-probability areas for locating the target. For topographic occlusions, a belief-guided search field is constructed and used to evaluate the likelihood of the target's presence, while for dynamic occlusions, a fluid-field approach allows the robot to adaptively follow or overtake moving occluders. Past motion cues and environmental observations refine the search decision over time. Our results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches in terms of search efficiency and success rates, both in simulations and real-world tests. Our target search method enhances the adaptability and reliability of RPF systems in unknown and dynamic environments to support their use in real-world applications. Our code, video, experimental results and appendix are available at https://medlartea.github.io/rpf-search/.
NAMR-RRT: Neural Adaptive Motion Planning for Mobile Robots in Dynamic Environments
Nov 01, 2024Abstract:Robots are increasingly deployed in dynamic and crowded environments, such as urban areas and shopping malls, where efficient and robust navigation is crucial. Traditional risk-based motion planning algorithms face challenges in such scenarios due to the lack of a well-defined search region, leading to inefficient exploration in irrelevant areas. While bi-directional and multi-directional search strategies can improve efficiency, they still result in significant unnecessary exploration. This article introduces the Neural Adaptive Multi-directional Risk-based Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (NAMR-RRT) to address these limitations. NAMR-RRT integrates neural network-generated heuristic regions to dynamically guide the exploration process, continuously refining the heuristic region and sampling rates during the planning process. This adaptive feature significantly enhances performance compared to neural-based methods with fixed heuristic regions and sampling rates. NAMR-RRT improves planning efficiency, reduces trajectory length, and ensures higher success by focusing the search on promising areas and continuously adjusting to environments. The experiment results from both simulations and real-world applications demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of our proposed method in navigating dynamic environments. A website about this work is available at https://sites.google.com/view/namr-rrt.
Autonomous Multiple-Trolley Collection System with Nonholonomic Robots: Design, Control, and Implementation
Jan 16, 2024



Abstract:The intricate and multi-stage task in dynamic public spaces like luggage trolley collection in airports presents both a promising opportunity and an ongoing challenge for automated service robots. Previous research has primarily focused on handling a single trolley or individual functional components, creating a gap in providing cost-effective and efficient solutions for practical scenarios. In this paper, we propose a mobile manipulation robot incorporated with an autonomy framework for the collection and transportation of multiple trolleys that can significantly enhance operational efficiency. We address the key challenges in the trolley collection problem through the novel design of the mechanical system and the vision-based control strategy. We design a lightweight manipulator and docking mechanism, optimized for the sequential stacking and transportation of multiple trolleys. Additionally, based on the Control Lyapunov Function and Control Barrier Function, we propose a novel vision-based control with the online Quadratic Programming which significantly improves the accuracy and efficiency of the collection process. The practical application of our system is demonstrated in real world scenarios, where it successfully executes multiple-trolley collection tasks.
Disturbance Rejection Control for Autonomous Trolley Collection Robots with Prescribed Performance
Sep 22, 2023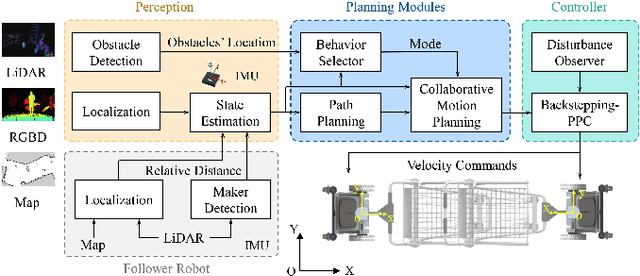
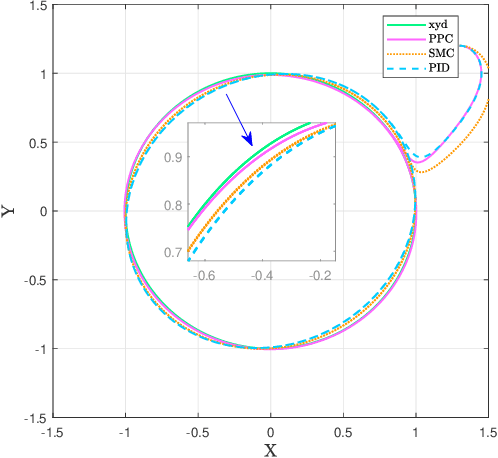
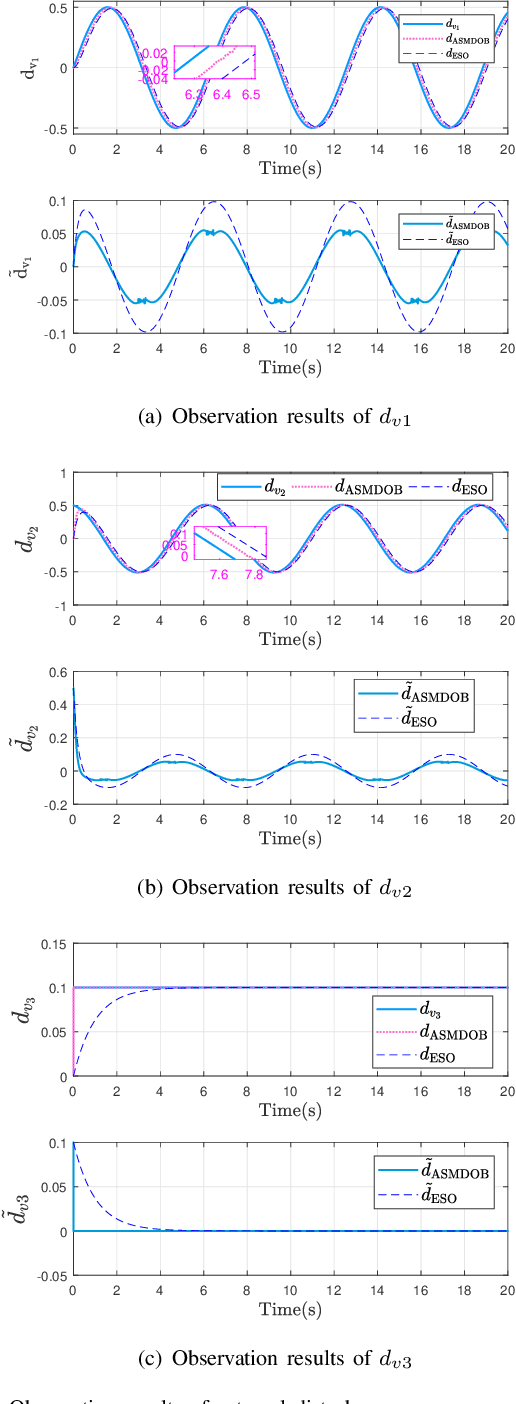
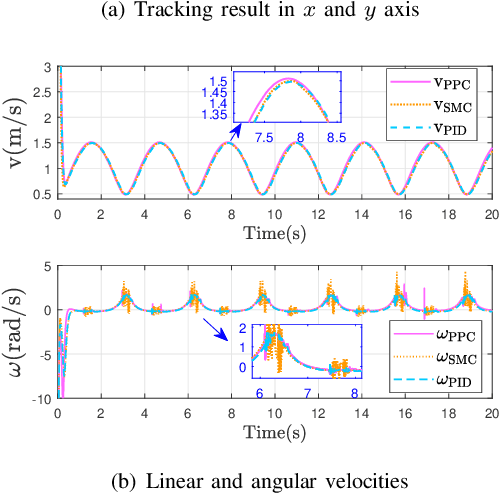
Abstract:Trajectory tracking control of autonomous trolley collection robots (ATCR) is an ambitious work due to the complex environment, serious noise and external disturbances. This work investigates a control scheme for ATCR subjecting to severe environmental interference. A kinematics model based adaptive sliding mode disturbance observer with fast convergence is first proposed to estimate the lumped disturbances. On this basis, a robust controller with prescribed performance is proposed using a backstepping technique, which improves the transient performance and guarantees fast convergence. Simulation outcomes have been provided to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed control scheme.
Collaborative Trolley Transportation System with Autonomous Nonholonomic Robots
Apr 03, 2023
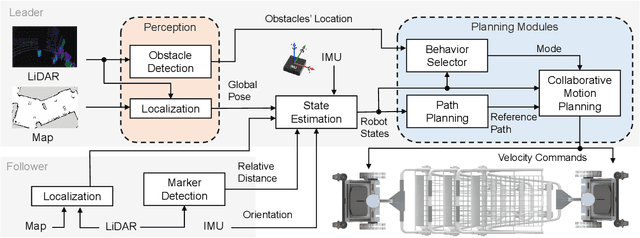
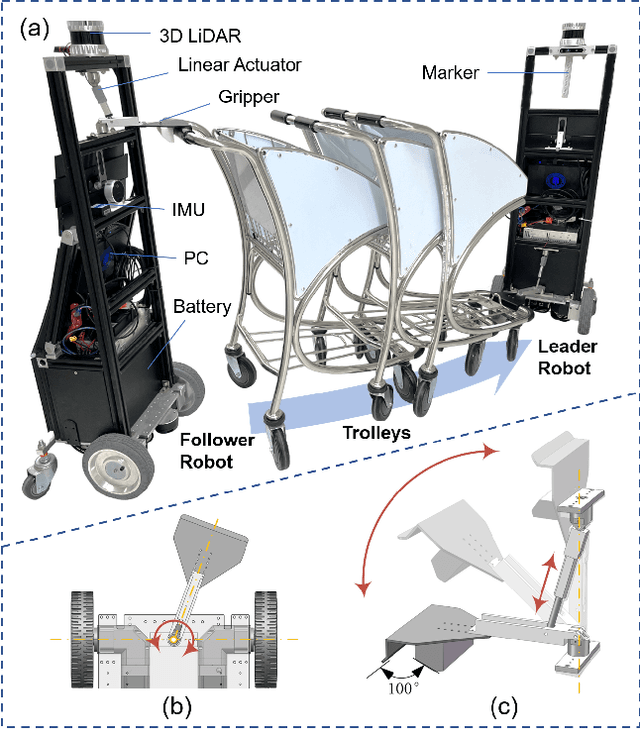
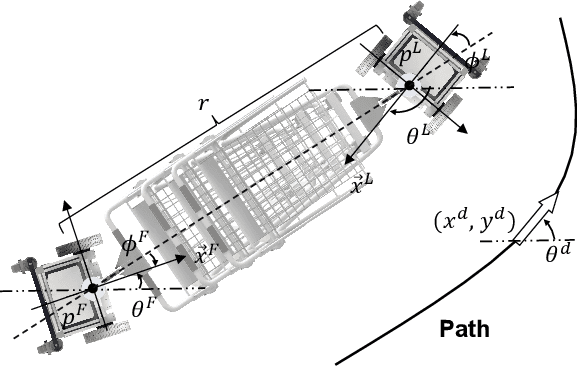
Abstract:Cooperative object transportation using multiple robots has been intensively studied in the control and robotics literature, but most approaches are either only applicable to omnidirectional robots or lack a complete navigation and decision-making framework that operates in real time. This paper presents an autonomous nonholonomic multi-robot system and an end-to-end hierarchical autonomy framework for collaborative luggage trolley transportation. This framework finds kinematic-feasible paths, computes online motion plans, and provides feedback that enables the multi-robot system to handle long lines of luggage trolleys and navigate obstacles and pedestrians while dealing with multiple inherently complex and coupled constraints. We demonstrate the designed collaborative trolley transportation system through practical transportation tasks, and the experiment results reveal their effectiveness and reliability in complex and dynamic environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge