Bingbing Wang
Robust Outlier Detection and Low-Latency Concept Drift Adaptation for Data Stream Regression: A Dual-Channel Architecture
Dec 13, 2025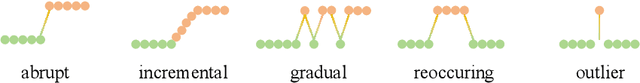

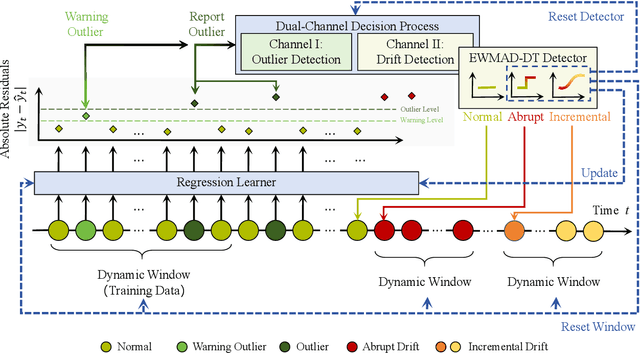
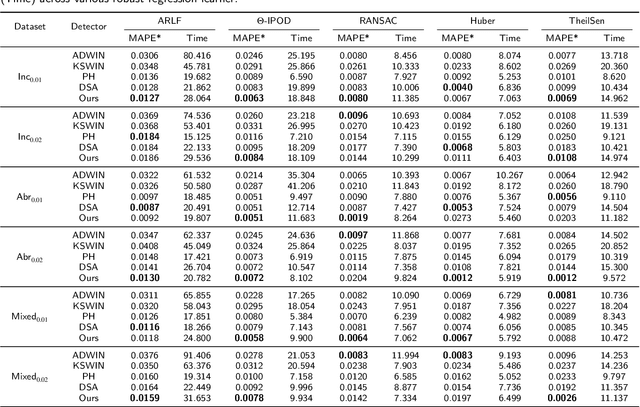
Abstract:Outlier detection and concept drift detection represent two challenges in data analysis. Most studies address these issues separately. However, joint detection mechanisms in regression remain underexplored, where the continuous nature of output spaces makes distinguishing drifts from outliers inherently challenging. To address this, we propose a novel robust regression framework for joint outlier and concept drift detection. Specifically, we introduce a dual-channel decision process that orchestrates prediction residuals into two coupled logic flows: a rapid response channel for filtering point outliers and a deep analysis channel for diagnosing drifts. We further develop the Exponentially Weighted Moving Absolute Deviation with Distinguishable Types (EWMAD-DT) detector to autonomously differentiate between abrupt and incremental drifts via dynamic thresholding. Comprehensive experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our unified framework, enhanced by EWMAD-DT, exhibits superior detection performance even when point outliers and concept drifts coexist.
PRISM of Opinions: A Persona-Reasoned Multimodal Framework for User-centric Conversational Stance Detection
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:The rapid proliferation of multimodal social media content has driven research in Multimodal Conversational Stance Detection (MCSD), which aims to interpret users' attitudes toward specific targets within complex discussions. However, existing studies remain limited by: **1) pseudo-multimodality**, where visual cues appear only in source posts while comments are treated as text-only, misaligning with real-world multimodal interactions; and **2) user homogeneity**, where diverse users are treated uniformly, neglecting personal traits that shape stance expression. To address these issues, we introduce **U-MStance**, the first user-centric MCSD dataset, containing over 40k annotated comments across six real-world targets. We further propose **PRISM**, a **P**ersona-**R**easoned mult**I**modal **S**tance **M**odel for MCSD. PRISM first derives longitudinal user personas from historical posts and comments to capture individual traits, then aligns textual and visual cues within conversational context via Chain-of-Thought to bridge semantic and pragmatic gaps across modalities. Finally, a mutual task reinforcement mechanism is employed to jointly optimize stance detection and stance-aware response generation for bidirectional knowledge transfer. Experiments on U-MStance demonstrate that PRISM yields significant gains over strong baselines, underscoring the effectiveness of user-centric and context-grounded multimodal reasoning for realistic stance understanding.
ReMoD: Rethinking Modality Contribution in Multimodal Stance Detection via Dual Reasoning
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Stance Detection (MSD) is a crucial task for understanding public opinion on social media. Existing work simply fuses information from various modalities to learn stance representations, overlooking the varying contributions of stance expression from different modalities. Therefore, stance misunderstanding noises may be drawn into the stance learning process due to the risk of learning errors by rough modality combination. To address this, we get inspiration from the dual-process theory of human cognition and propose **ReMoD**, a framework that **Re**thinks **Mo**dality contribution of stance expression through a **D**ual-reasoning paradigm. ReMoD integrates *experience-driven intuitive reasoning* to capture initial stance cues with *deliberate reflective reasoning* to adjust for modality biases, refine stance judgments, and thereby dynamically weight modality contributions based on their actual expressive power for the target stance. Specifically, the intuitive stage queries the Modality Experience Pool (MEP) and Semantic Experience Pool (SEP) to form an initial stance hypothesis, prioritizing historically impactful modalities. This hypothesis is then refined in the reflective stage via two reasoning chains: Modality-CoT updates MEP with adaptive fusion strategies to amplify relevant modalities, while Semantic-CoT refines SEP with deeper contextual insights of stance semantics. These dual experience structures are continuously refined during training and recalled at inference to guide robust and context-aware stance decisions. Extensive experiments on the public MMSD benchmark demonstrate that our ReMoD significantly outperforms most baseline models and exhibits strong generalization capabilities.
Bridging the Long-Term Gap: A Memory-Active Policy for Multi-Session Task-Oriented Dialogue
May 26, 2025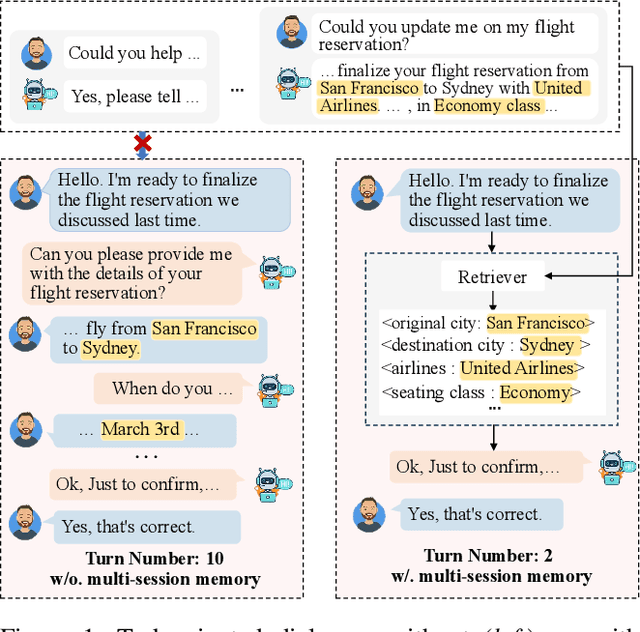
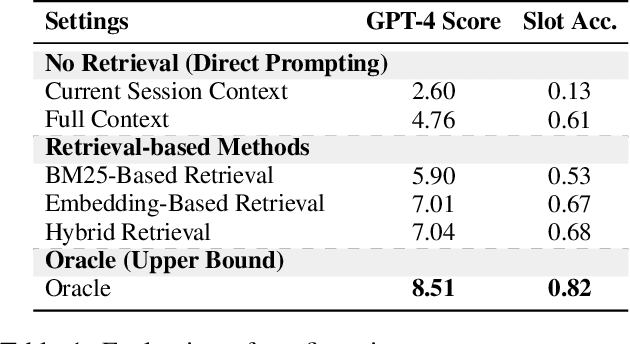
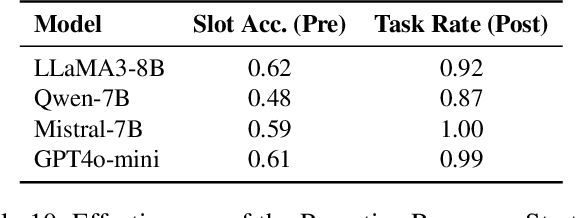
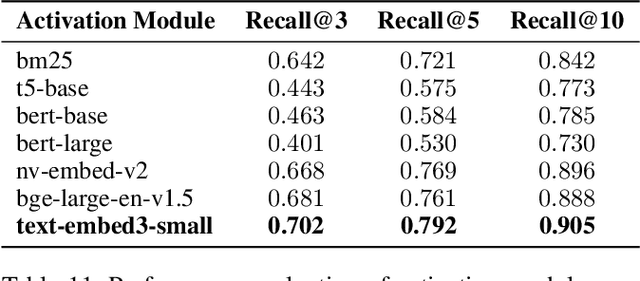
Abstract:Existing Task-Oriented Dialogue (TOD) systems primarily focus on single-session dialogues, limiting their effectiveness in long-term memory augmentation. To address this challenge, we introduce a MS-TOD dataset, the first multi-session TOD dataset designed to retain long-term memory across sessions, enabling fewer turns and more efficient task completion. This defines a new benchmark task for evaluating long-term memory in multi-session TOD. Based on this new dataset, we propose a Memory-Active Policy (MAP) that improves multi-session dialogue efficiency through a two-stage approach. 1) Memory-Guided Dialogue Planning retrieves intent-aligned history, identifies key QA units via a memory judger, refines them by removing redundant questions, and generates responses based on the reconstructed memory. 2) Proactive Response Strategy detects and correct errors or omissions, ensuring efficient and accurate task completion. We evaluate MAP on MS-TOD dataset, focusing on response quality and effectiveness of the proactive strategy. Experiments on MS-TOD demonstrate that MAP significantly improves task success and turn efficiency in multi-session scenarios, while maintaining competitive performance on conventional single-session tasks.
Exploring Context Window of Large Language Models via Decomposed Positional Vectors
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) typically have a limited context window, resulting in significant performance degradation when processing text beyond the length of the context window. Extensive studies have been proposed to extend the context window and achieve length extrapolation of LLMs, but there is still a lack of in-depth interpretation of these approaches. In this study, we explore the positional information within and beyond the context window for deciphering the underlying mechanism of LLMs. By using a mean-based decomposition method, we disentangle positional vectors from hidden states of LLMs and analyze their formation and effect on attention. Furthermore, when texts exceed the context window, we analyze the change of positional vectors in two settings, i.e., direct extrapolation and context window extension. Based on our findings, we design two training-free context window extension methods, positional vector replacement and attention window extension. Experimental results show that our methods can effectively extend the context window length.
MFA-Net: Multi-Scale feature fusion attention network for liver tumor segmentation
May 07, 2024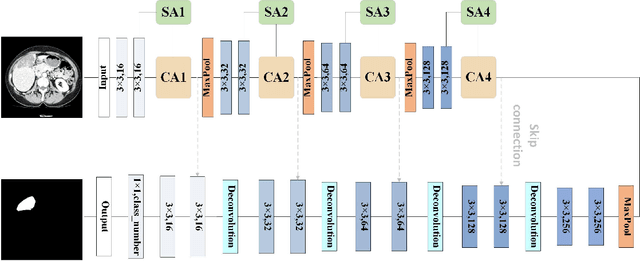

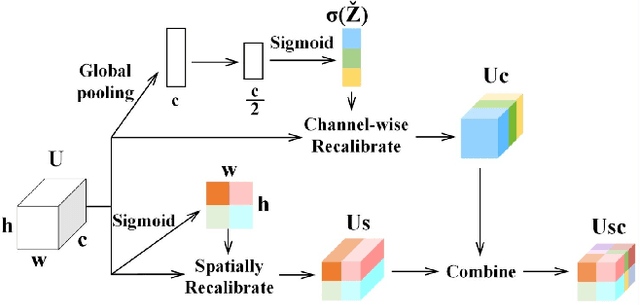
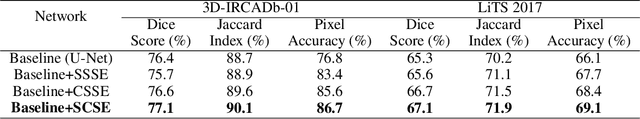
Abstract:Segmentation of organs of interest in medical CT images is beneficial for diagnosis of diseases. Though recent methods based on Fully Convolutional Neural Networks (F-CNNs) have shown success in many segmentation tasks, fusing features from images with different scales is still a challenge: (1) Due to the lack of spatial awareness, F-CNNs share the same weights at different spatial locations. (2) F-CNNs can only obtain surrounding information through local receptive fields. To address the above challenge, we propose a new segmentation framework based on attention mechanisms, named MFA-Net (Multi-Scale Feature Fusion Attention Network). The proposed framework can learn more meaningful feature maps among multiple scales and result in more accurate automatic segmentation. We compare our proposed MFA-Net with SOTA methods on two 2D liver CT datasets. The experimental results show that our MFA-Net produces more precise segmentation on images with different scales.
SDIF-DA: A Shallow-to-Deep Interaction Framework with Data Augmentation for Multi-modal Intent Detection
Dec 31, 2023Abstract:Multi-modal intent detection aims to utilize various modalities to understand the user's intentions, which is essential for the deployment of dialogue systems in real-world scenarios. The two core challenges for multi-modal intent detection are (1) how to effectively align and fuse different features of modalities and (2) the limited labeled multi-modal intent training data. In this work, we introduce a shallow-to-deep interaction framework with data augmentation (SDIF-DA) to address the above challenges. Firstly, SDIF-DA leverages a shallow-to-deep interaction module to progressively and effectively align and fuse features across text, video, and audio modalities. Secondly, we propose a ChatGPT-based data augmentation approach to automatically augment sufficient training data. Experimental results demonstrate that SDIF-DA can effectively align and fuse multi-modal features by achieving state-of-the-art performance. In addition, extensive analyses show that the introduced data augmentation approach can successfully distill knowledge from the large language model.
Improving Few-shot and Zero-shot Entity Linking with Coarse-to-Fine Lexicon-based Retriever
Aug 13, 2023Abstract:Few-shot and zero-shot entity linking focus on the tail and emerging entities, which are more challenging but closer to real-world scenarios. The mainstream method is the ''retrieve and rerank'' two-stage framework. In this paper, we propose a coarse-to-fine lexicon-based retriever to retrieve entity candidates in an effective manner, which operates in two layers. The first layer retrieves coarse-grained candidates by leveraging entity names, while the second layer narrows down the search to fine-grained candidates within the coarse-grained ones. In addition, this second layer utilizes entity descriptions to effectively disambiguate tail or new entities that share names with existing popular entities. Experimental results indicate that our approach can obtain superior performance without requiring extensive finetuning in the retrieval stage. Notably, our approach ranks the 1st in NLPCC 2023 Shared Task 6 on Chinese Few-shot and Zero-shot Entity Linking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge