Bin Tian
AIR-VLA: Vision-Language-Action Systems for Aerial Manipulation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:While Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have achieved remarkable success in ground-based embodied intelligence, their application to Aerial Manipulation Systems (AMS) remains a largely unexplored frontier. The inherent characteristics of AMS, including floating-base dynamics, strong coupling between the UAV and the manipulator, and the multi-step, long-horizon nature of operational tasks, pose severe challenges to existing VLA paradigms designed for static or 2D mobile bases. To bridge this gap, we propose AIR-VLA, the first VLA benchmark specifically tailored for aerial manipulation. We construct a physics-based simulation environment and release a high-quality multimodal dataset comprising 3000 manually teleoperated demonstrations, covering base manipulation, object & spatial understanding, semantic reasoning, and long-horizon planning. Leveraging this platform, we systematically evaluate mainstream VLA models and state-of-the-art VLM models. Our experiments not only validate the feasibility of transferring VLA paradigms to aerial systems but also, through multi-dimensional metrics tailored to aerial tasks, reveal the capabilities and boundaries of current models regarding UAV mobility, manipulator control, and high-level planning. AIR-VLA establishes a standardized testbed and data foundation for future research in general-purpose aerial robotics. The resource of AIR-VLA will be available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/AIR-VLA-dataset-B5CC/.
Reinforcement Learning with Curriculum-inspired Adaptive Direct Policy Guidance for Truck Dispatching
Feb 28, 2025



Abstract:Efficient truck dispatching via Reinforcement Learning (RL) in open-pit mining is often hindered by reliance on complex reward engineering and value-based methods. This paper introduces Curriculum-inspired Adaptive Direct Policy Guidance, a novel curriculum learning strategy for policy-based RL to address these issues. We adapt Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) for mine dispatching's uneven decision intervals using time deltas in Temporal Difference and Generalized Advantage Estimation, and employ a Shortest Processing Time teacher policy for guided exploration via policy regularization and adaptive guidance. Evaluations in OpenMines demonstrate our approach yields a 10% performance gain and faster convergence over standard PPO across sparse and dense reward settings, showcasing improved robustness to reward design. This direct policy guidance method provides a general and effective curriculum learning technique for RL-based truck dispatching, enabling future work on advanced architectures.
3D Unsupervised Learning by Distilling 2D Open-Vocabulary Segmentation Models for Autonomous Driving
May 24, 2024



Abstract:Point cloud data labeling is considered a time-consuming and expensive task in autonomous driving, whereas unsupervised learning can avoid it by learning point cloud representations from unannotated data. In this paper, we propose UOV, a novel 3D Unsupervised framework assisted by 2D Open-Vocabulary segmentation models. It consists of two stages: In the first stage, we innovatively integrate high-quality textual and image features of 2D open-vocabulary models and propose the Tri-Modal contrastive Pre-training (TMP). In the second stage, spatial mapping between point clouds and images is utilized to generate pseudo-labels, enabling cross-modal knowledge distillation. Besides, we introduce the Approximate Flat Interaction (AFI) to address the noise during alignment and label confusion. To validate the superiority of UOV, extensive experiments are conducted on multiple related datasets. We achieved a record-breaking 47.73% mIoU on the annotation-free point cloud segmentation task in nuScenes, surpassing the previous best model by 10.70% mIoU. Meanwhile, the performance of fine-tuning with 1% data on nuScenes and SemanticKITTI reached a remarkable 51.75% mIoU and 48.14% mIoU, outperforming all previous pre-trained models.
Point Cloud Classification Using Content-based Transformer via Clustering in Feature Space
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:Recently, there have been some attempts of Transformer in 3D point cloud classification. In order to reduce computations, most existing methods focus on local spatial attention, but ignore their content and fail to establish relationships between distant but relevant points. To overcome the limitation of local spatial attention, we propose a point content-based Transformer architecture, called PointConT for short. It exploits the locality of points in the feature space (content-based), which clusters the sampled points with similar features into the same class and computes the self-attention within each class, thus enabling an effective trade-off between capturing long-range dependencies and computational complexity. We further introduce an Inception feature aggregator for point cloud classification, which uses parallel structures to aggregate high-frequency and low-frequency information in each branch separately. Extensive experiments show that our PointConT model achieves a remarkable performance on point cloud shape classification. Especially, our method exhibits 90.3% Top-1 accuracy on the hardest setting of ScanObjectNN. Source code of this paper is available at https://github.com/yahuiliu99/PointConT.
InTEn-LOAM: Intensity and Temporal Enhanced LiDAR Odometry and Mapping
Sep 13, 2022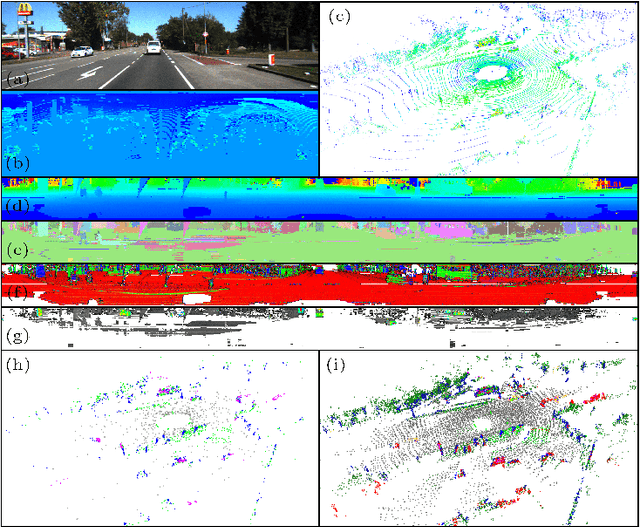
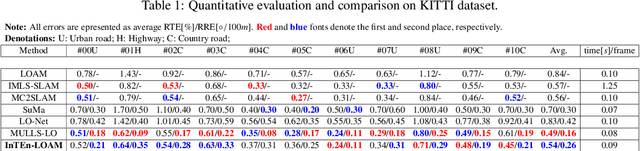
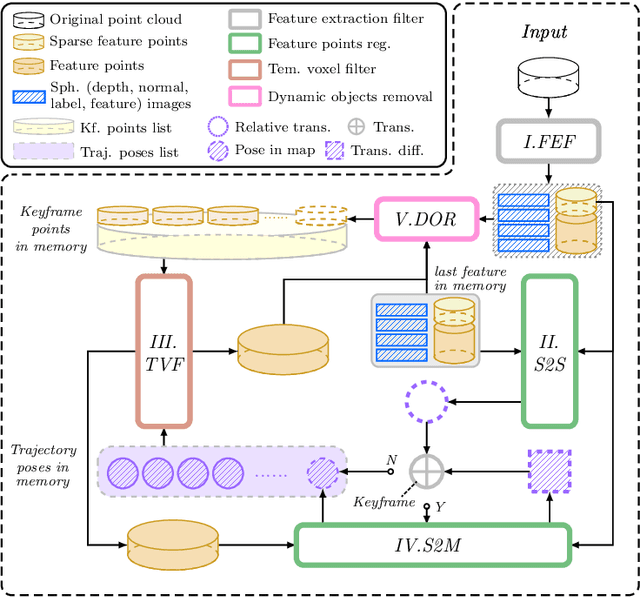

Abstract:Traditional LiDAR odometry (LO) systems mainly leverage geometric information obtained from the traversed surroundings to register laser scans and estimate LiDAR ego-motion, while it may be unreliable in dynamic or unstructured environments. This paper proposes InTEn-LOAM, a low-drift and robust LiDAR odometry and mapping method that fully exploits implicit information of laser sweeps (i.e., geometric, intensity, and temporal characteristics). Scanned points are projected to cylindrical images, which facilitate the efficient and adaptive extraction of various types of features, i.e., ground, beam, facade, and reflector. We propose a novel intensity-based points registration algorithm and incorporate it into the LiDAR odometry, enabling the LO system to jointly estimate the LiDAR ego-motion using both geometric and intensity feature points. To eliminate the interference of dynamic objects, we propose a temporal-based dynamic object removal approach to filter them out before map update. Moreover, the local map is organized and downsampled using a temporal-related voxel grid filter to maintain the similarity between the current scan and the static local map. Extensive experiments are conducted on both simulated and real-world datasets. The results show that the proposed method achieves similar or better accuracy w.r.t the state-of-the-arts in normal driving scenarios and outperforms geometric-based LO in unstructured environments.
Multi-View Adaptive Fusion Network for 3D Object Detection
Nov 02, 2020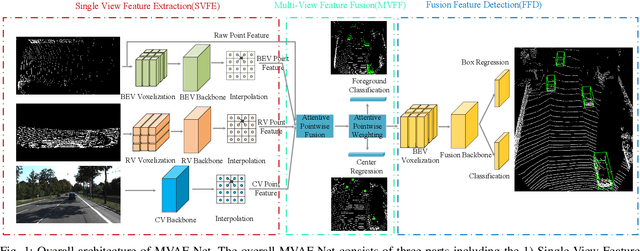

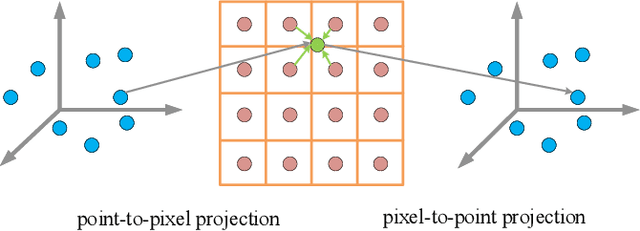
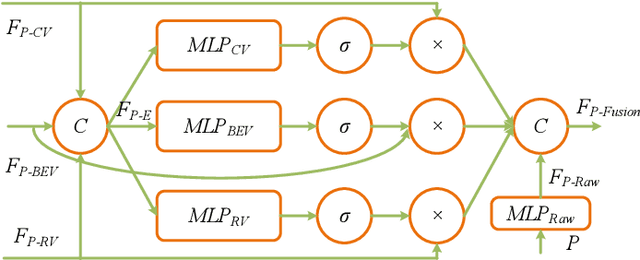
Abstract:3D object detection based on LiDAR-camera fusion is becoming an emerging research theme for autonomous driving. However, it has been surprisingly difficult to effectively fuse both modalities without information loss and interference. To solve this issue, we propose a single-stage multi-view fusion framework that takes LiDAR Birds-Eye View, LiDAR Range View and Camera View images as inputs for 3D object detection. To effectively fuse multi-view features, we propose an Attentive Pointwise Fusion (APF) module to estimate the importance of the three sources with attention mechanisms which can achieve adaptive fusion of multi-view features in a pointwise manner. Besides, an Attentive Pointwise Weighting (APW) module is designed to help the network learn structure information and point feature importance with two extra tasks: foreground classification and center regression, and the predicted foreground probability will be used to reweight the point features. We design an end-to-end learnable network named MVAF-Net to integrate these two components. Our evaluations conducted on the KITTI 3D object detection datasets demonstrate that the proposed APF and APW module offer significant performance gain and that the proposed MVAF-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance in the KITTI benchmark.
Comparison of Different Methods for Time Sequence Prediction in Autonomous Vehicles
Jul 16, 2020



Abstract:As a combination of various kinds of technologies, autonomous vehicles could complete a series of driving tasks by itself, such as perception, decision-making, planning, and control. Since there is no human driver to handle the emergency situation, future transportation information is significant for automated vehicles. This paper proposes different methods to forecast the time series for autonomous vehicles, which are the nearest neighborhood (NN), fuzzy coding (FC), and long short term memory (LSTM). First, the formulation and operational process for these three approaches are introduced. Then, the vehicle velocity is regarded as a case study and the real-world dataset is utilized to predict future information via these techniques. Finally, the performance, merits, and drawbacks of the presented methods are analyzed and discussed.
CenterNet3D:An Anchor free Object Detector for Autonomous Driving
Jul 16, 2020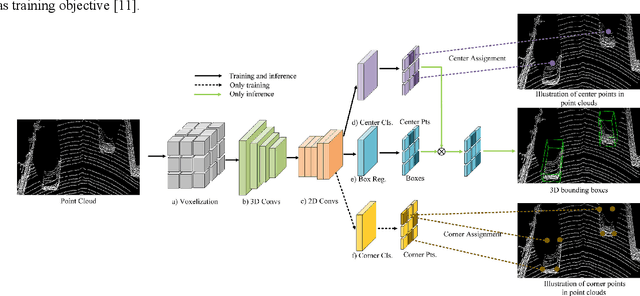
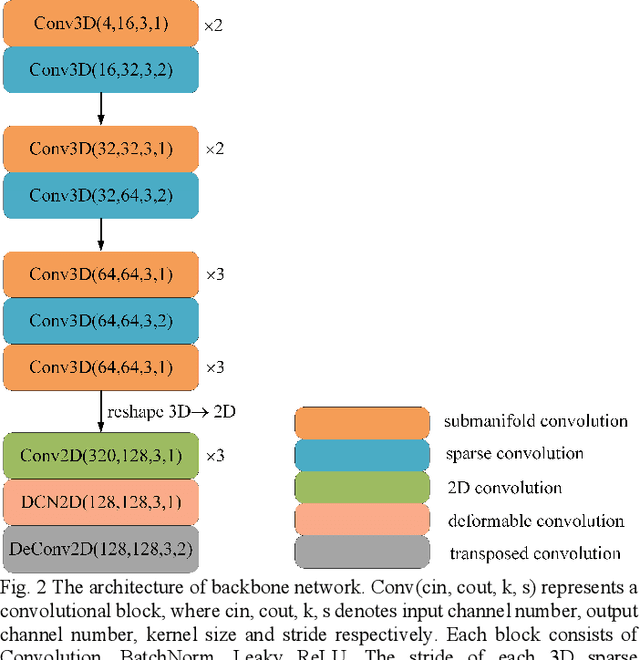

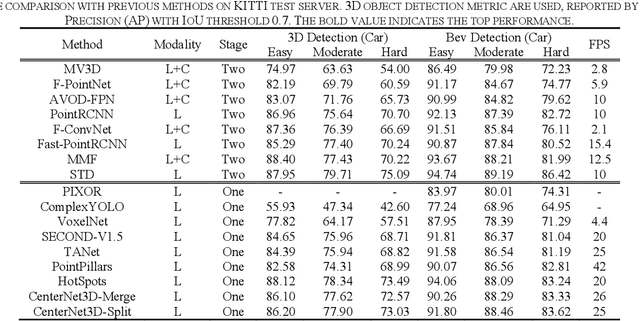
Abstract:Accurate and fast 3D object detection from point clouds is a key task in autonomous driving. Existing one-stage 3D object detection methods can achieve real-time performance, however, they are dominated by anchor-based detectors which are inefficient and require additional post-processing. In this paper, we eliminate anchors and model an object as a single point the center point of its bounding box. Based on the center point, we propose an anchor-free CenterNet3D Network that performs 3D object detection without anchors. Our CenterNet3D uses keypoint estimation to find center points and directly regresses 3D bounding boxes. However, because inherent sparsity of point clouds, 3D object center points are likely to be in empty space which makes it difficult to estimate accurate boundary. To solve this issue, we propose an auxiliary corner attention module to enforce the CNN backbone to pay more attention to object boundaries which is effective to obtain more accurate bounding boxes. Besides, our CenterNet3D is Non-Maximum Suppression free which makes it more efficient and simpler. On the KITTI benchmark, our proposed CenterNet3D achieves competitive performance with other one stage anchor-based methods which show the efficacy of our proposed center point representation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge