Atmadeep Banerjee
Learning label-label correlations in Extreme Multi-label Classification via Label Features
May 03, 2024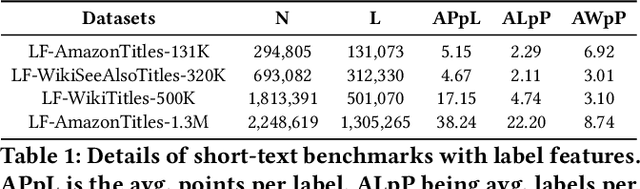
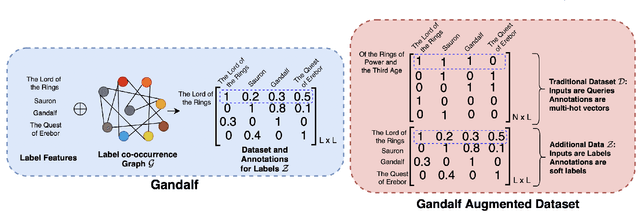
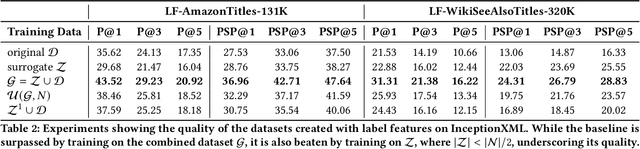
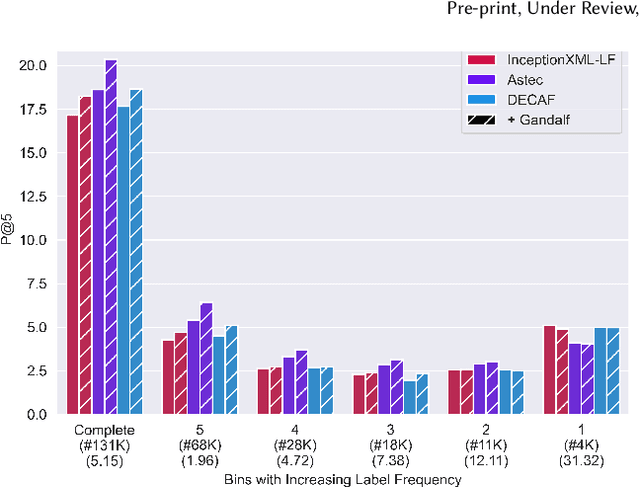
Abstract:Extreme Multi-label Text Classification (XMC) involves learning a classifier that can assign an input with a subset of most relevant labels from millions of label choices. Recent works in this domain have increasingly focused on a symmetric problem setting where both input instances and label features are short-text in nature. Short-text XMC with label features has found numerous applications in areas such as query-to-ad-phrase matching in search ads, title-based product recommendation, prediction of related searches. In this paper, we propose Gandalf, a novel approach which makes use of a label co-occurrence graph to leverage label features as additional data points to supplement the training distribution. By exploiting the characteristics of the short-text XMC problem, it leverages the label features to construct valid training instances, and uses the label graph for generating the corresponding soft-label targets, hence effectively capturing the label-label correlations. Surprisingly, models trained on these new training instances, although being less than half of the original dataset, can outperform models trained on the original dataset, particularly on the PSP@k metric for tail labels. With this insight, we aim to train existing XMC algorithms on both, the original and new training instances, leading to an average 5% relative improvements for 6 state-of-the-art algorithms across 4 benchmark datasets consisting of up to 1.3M labels. Gandalf can be applied in a plug-and-play manner to various methods and thus forwards the state-of-the-art in the domain, without incurring any additional computational overheads.
TriSAM: Tri-Plane SAM for zero-shot cortical blood vessel segmentation in VEM images
Jan 25, 2024
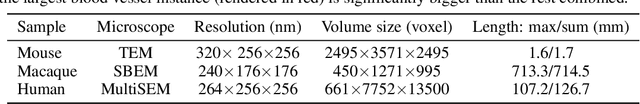

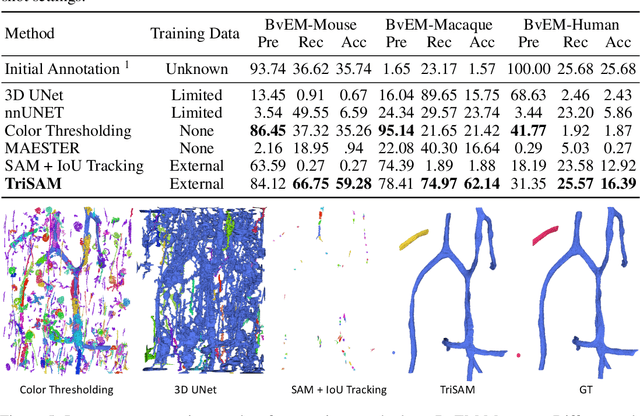
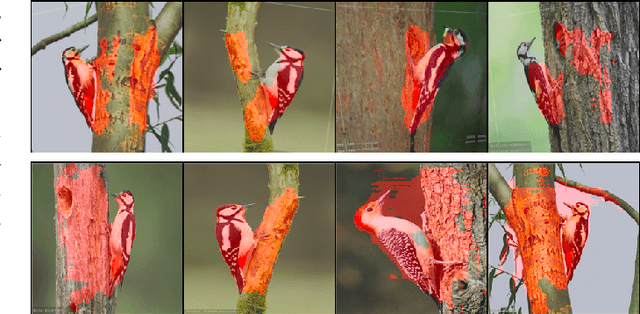
Abstract:In this paper, we address a significant gap in the field of neuroimaging by introducing the largest-to-date public benchmark, BvEM, designed specifically for cortical blood vessel segmentation in Volume Electron Microscopy (VEM) images. The intricate relationship between cerebral blood vessels and neural function underscores the vital role of vascular analysis in understanding brain health. While imaging techniques at macro and mesoscales have garnered substantial attention and resources, the microscale VEM imaging, capable of revealing intricate vascular details, has lacked the necessary benchmarking infrastructure. As researchers delve deeper into the microscale intricacies of cerebral vasculature, our BvEM benchmark represents a critical step toward unraveling the mysteries of neurovascular coupling and its impact on brain function and pathology. The BvEM dataset is based on VEM image volumes from three mammal species: adult mouse, macaque, and human. We standardized the resolution, addressed imaging variations, and meticulously annotated blood vessels through semi-automatic, manual, and quality control processes, ensuring high-quality 3D segmentation. Furthermore, we developed a zero-shot cortical blood vessel segmentation method named TriSAM, which leverages the powerful segmentation model SAM for 3D segmentation. To lift SAM from 2D segmentation to 3D volume segmentation, TriSAM employs a multi-seed tracking framework, leveraging the reliability of certain image planes for tracking while using others to identify potential turning points. This approach, consisting of Tri-Plane selection, SAM-based tracking, and recursive redirection, effectively achieves long-term 3D blood vessel segmentation without model training or fine-tuning. Experimental results show that TriSAM achieved superior performances on the BvEM benchmark across three species.
Reconstructing the Mind's Eye: fMRI-to-Image with Contrastive Learning and Diffusion Priors
May 29, 2023
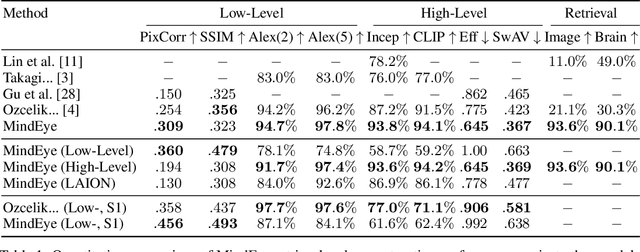
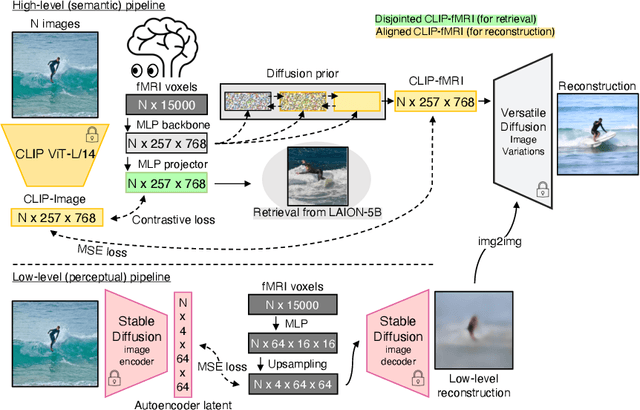
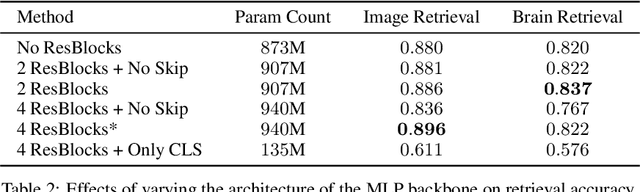
Abstract:We present MindEye, a novel fMRI-to-image approach to retrieve and reconstruct viewed images from brain activity. Our model comprises two parallel submodules that are specialized for retrieval (using contrastive learning) and reconstruction (using a diffusion prior). MindEye can map fMRI brain activity to any high dimensional multimodal latent space, like CLIP image space, enabling image reconstruction using generative models that accept embeddings from this latent space. We comprehensively compare our approach with other existing methods, using both qualitative side-by-side comparisons and quantitative evaluations, and show that MindEye achieves state-of-the-art performance in both reconstruction and retrieval tasks. In particular, MindEye can retrieve the exact original image even among highly similar candidates indicating that its brain embeddings retain fine-grained image-specific information. This allows us to accurately retrieve images even from large-scale databases like LAION-5B. We demonstrate through ablations that MindEye's performance improvements over previous methods result from specialized submodules for retrieval and reconstruction, improved training techniques, and training models with orders of magnitude more parameters. Furthermore, we show that MindEye can better preserve low-level image features in the reconstructions by using img2img, with outputs from a separate autoencoder. All code is available on GitHub.
CascadeXML: Rethinking Transformers for End-to-end Multi-resolution Training in Extreme Multi-label Classification
Oct 29, 2022Abstract:Extreme Multi-label Text Classification (XMC) involves learning a classifier that can assign an input with a subset of most relevant labels from millions of label choices. Recent approaches, such as XR-Transformer and LightXML, leverage a transformer instance to achieve state-of-the-art performance. However, in this process, these approaches need to make various trade-offs between performance and computational requirements. A major shortcoming, as compared to the Bi-LSTM based AttentionXML, is that they fail to keep separate feature representations for each resolution in a label tree. We thus propose CascadeXML, an end-to-end multi-resolution learning pipeline, which can harness the multi-layered architecture of a transformer model for attending to different label resolutions with separate feature representations. CascadeXML significantly outperforms all existing approaches with non-trivial gains obtained on benchmark datasets consisting of up to three million labels. Code for CascadeXML will be made publicly available at \url{https://github.com/xmc-aalto/cascadexml}.
Revisiting RCAN: Improved Training for Image Super-Resolution
Jan 27, 2022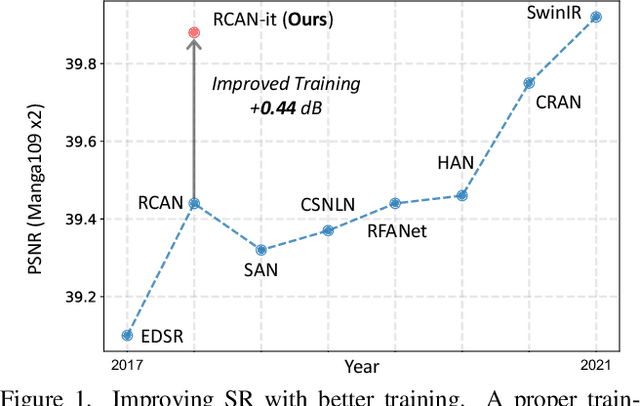
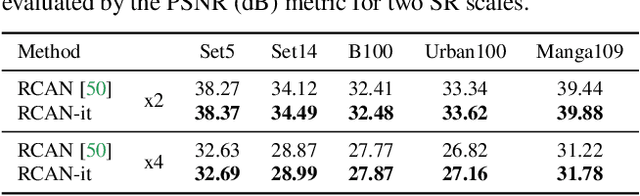
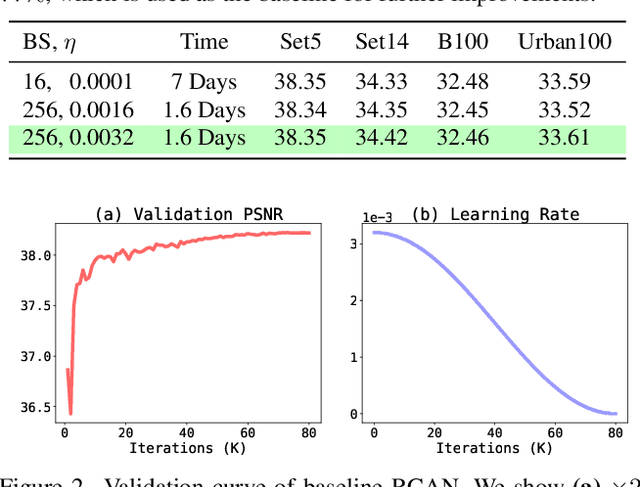
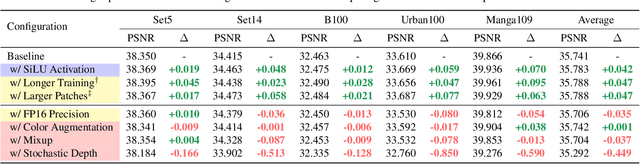
Abstract:Image super-resolution (SR) is a fast-moving field with novel architectures attracting the spotlight. However, most SR models were optimized with dated training strategies. In this work, we revisit the popular RCAN model and examine the effect of different training options in SR. Surprisingly (or perhaps as expected), we show that RCAN can outperform or match nearly all the CNN-based SR architectures published after RCAN on standard benchmarks with a proper training strategy and minimal architecture change. Besides, although RCAN is a very large SR architecture with more than four hundred convolutional layers, we draw a notable conclusion that underfitting is still the main problem restricting the model capability instead of overfitting. We observe supportive evidence that increasing training iterations clearly improves the model performance while applying regularization techniques generally degrades the predictions. We denote our simply revised RCAN as RCAN-it and recommend practitioners to use it as baselines for future research. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/zudi-lin/rcan-it.
Embedding Convolutions for Short Text Extreme Classification with Millions of Labels
Sep 13, 2021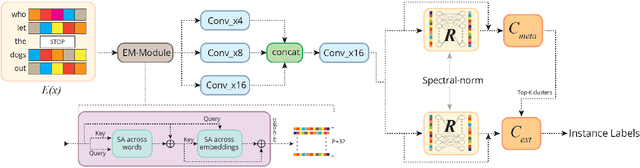
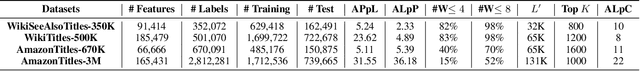
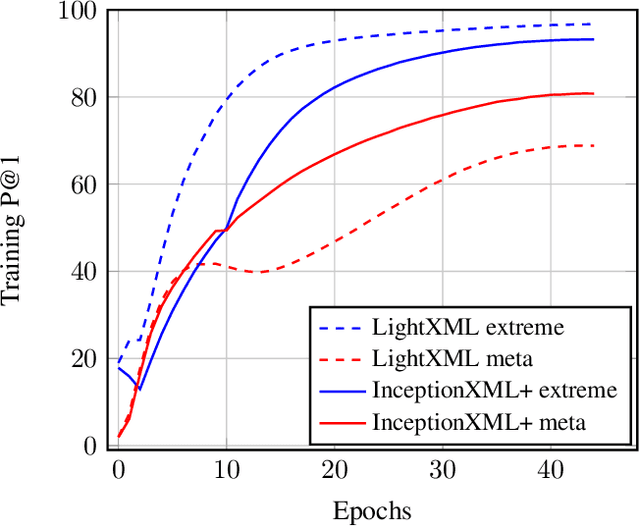
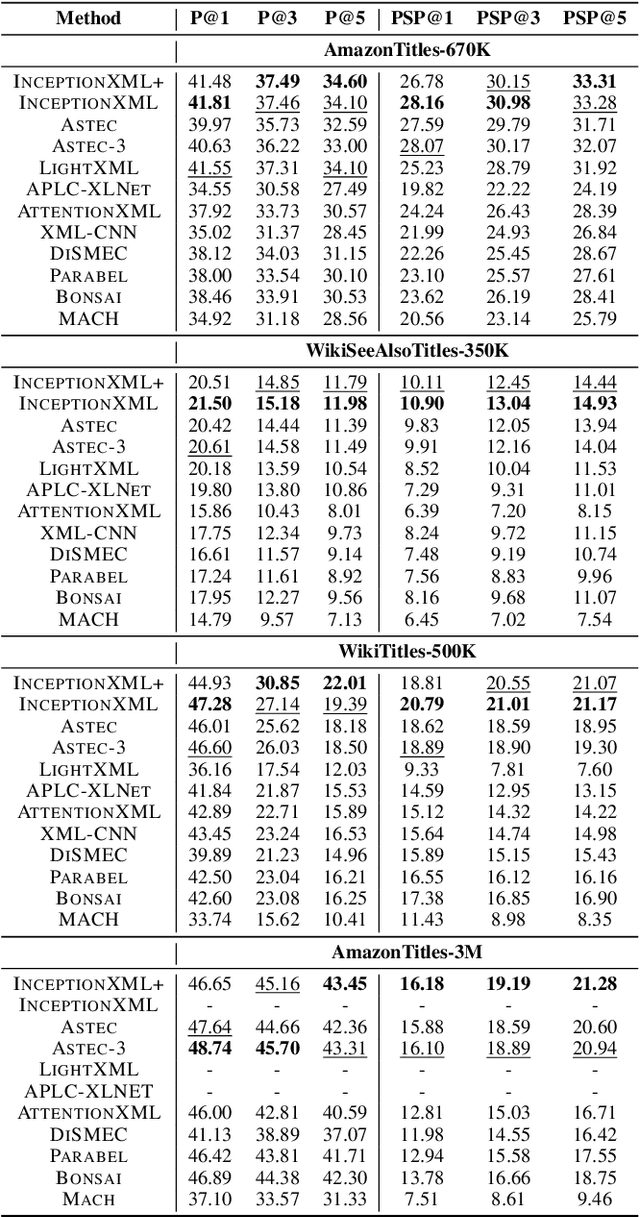
Abstract:Automatic annotation of short-text data to a large number of target labels, referred to as Short Text Extreme Classification, has recently found numerous applications in prediction of related searches and product recommendation tasks. The conventional usage of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to capture n-grams in text-classification relies heavily on uniformity in word-ordering and the presence of long input sequences to convolve over. However, this is missing in short and unstructured text sequences encountered in search and recommendation. In order to tackle this, we propose an orthogonal approach by recasting the convolution operation to capture coupled semantics along the embedding dimensions, and develop a word-order agnostic embedding enhancement module to deal with the lack of structure in such queries. Benefitting from the computational efficiency of the convolution operation, Embedding Convolutions, when applied on the enriched word embeddings, result in a light-weight and yet powerful encoder (InceptionXML) that is robust to the inherent lack of structure in short-text extreme classification. Towards scaling our model to problems with millions of labels, we also propose InceptionXML+, which addresses the shortcomings of the dynamic hard-negative mining framework in the recently proposed LightXML by improving the alignment between the label-shortlister and extreme classifier. On popular benchmark datasets, we empirically demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art deep extreme classifiers such as Astec by an average of 5% and 8% on the P@k and propensity-scored PSP@k metrics respectively.
Meta-DRN: Meta-Learning for 1-Shot Image Segmentation
Aug 01, 2020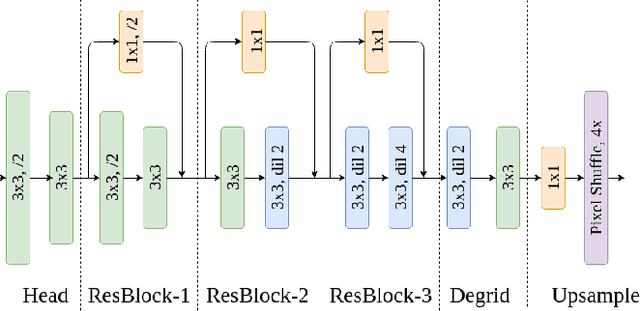
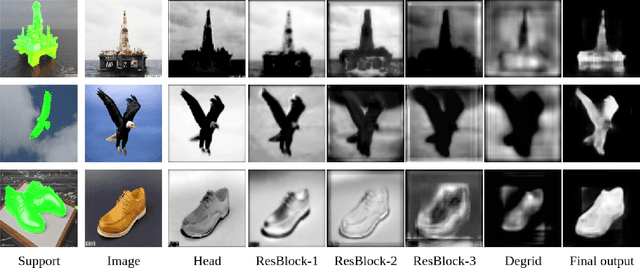
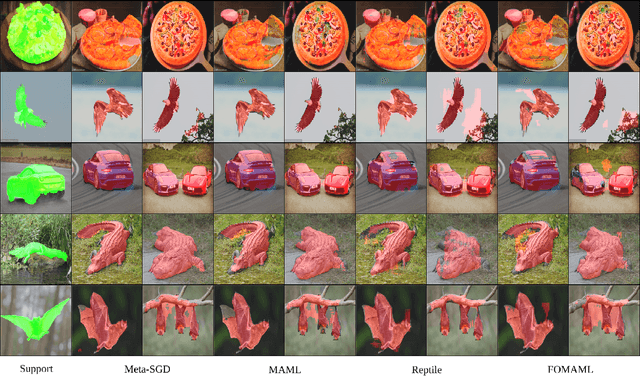
Abstract:Modern deep learning models have revolutionized the field of computer vision. But, a significant drawback of most of these models is that they require a large number of labelled examples to generalize properly. Recent developments in few-shot learning aim to alleviate this requirement. In this paper, we propose a novel lightweight CNN architecture for 1-shot image segmentation. The proposed model is created by taking inspiration from well-performing architectures for semantic segmentation and adapting it to the 1-shot domain. We train our model using 4 meta-learning algorithms that have worked well for image classification and compare the results. For the chosen dataset, our proposed model has a 70% lower parameter count than the benchmark, while having better or comparable mean IoU scores using all 4 of the meta-learning algorithms.
MXR-U-Nets for Real Time Hyperspectral Reconstruction
Apr 15, 2020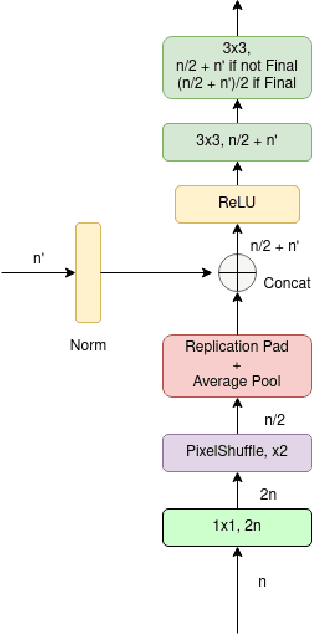
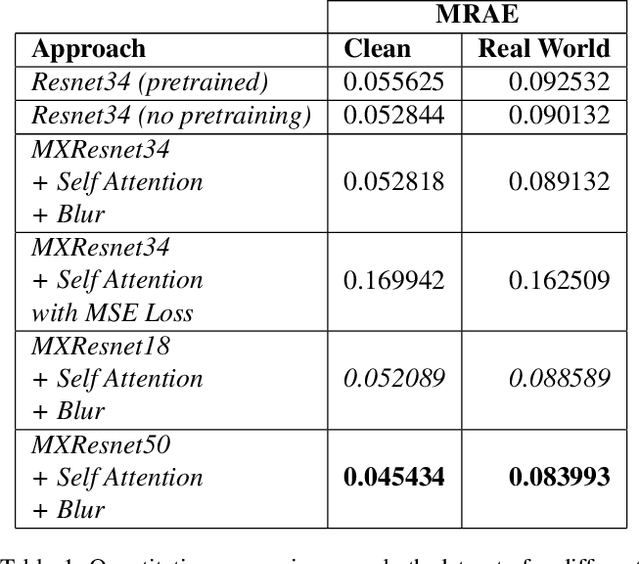
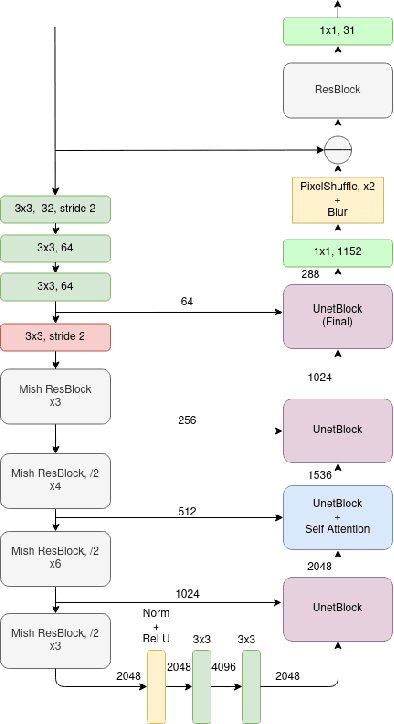
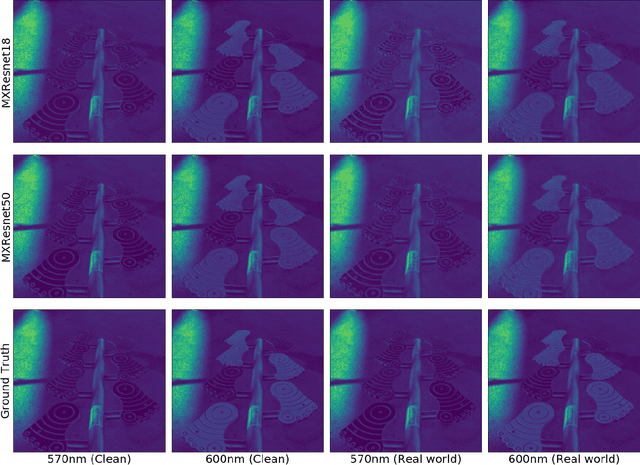
Abstract:In recent times, CNNs have made significant contributions to applications in image generation, super-resolution and style transfer. In this paper, we build upon the work of Howard and Gugger, He et al. and Misra, D. and propose a CNN architecture that accurately reconstructs hyperspectral images from their RGB counterparts. We also propose a much shallower version of our best model with a 10% relative memory footprint and 3x faster inference, thus enabling real-time video applications while still experiencing only about a 0.5% decrease in performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge