Anthony Colas
M3: A Multi-Task Mixed-Objective Learning Framework for Open-Domain Multi-Hop Dense Sentence Retrieval
Mar 21, 2024Abstract:In recent research, contrastive learning has proven to be a highly effective method for representation learning and is widely used for dense retrieval. However, we identify that relying solely on contrastive learning can lead to suboptimal retrieval performance. On the other hand, despite many retrieval datasets supporting various learning objectives beyond contrastive learning, combining them efficiently in multi-task learning scenarios can be challenging. In this paper, we introduce M3, an advanced recursive Multi-hop dense sentence retrieval system built upon a novel Multi-task Mixed-objective approach for dense text representation learning, addressing the aforementioned challenges. Our approach yields state-of-the-art performance on a large-scale open-domain fact verification benchmark dataset, FEVER. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/TonyBY/M3
Knowledge-grounded Natural Language Recommendation Explanation
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:Explanations accompanied by a recommendation can assist users in understanding the decision made by recommendation systems, which in turn increases a user's confidence and trust in the system. Recently, research has focused on generating natural language explanations in a human-readable format. Thus far, the proposed approaches leverage item reviews written by users, which are often subjective, sparse in language, and unable to account for new items that have not been purchased or reviewed before. Instead, we aim to generate fact-grounded recommendation explanations that are objectively described with item features while implicitly considering a user's preferences, based on the user's purchase history. To achieve this, we propose a knowledge graph (KG) approach to natural language explainable recommendation. Our approach draws on user-item features through a novel collaborative filtering-based KG representation to produce fact-grounded, personalized explanations, while jointly learning user-item representations for recommendation scoring. Experimental results show that our approach consistently outperforms previous state-of-the-art models on natural language explainable recommendation.
Can Knowledge Graphs Simplify Text?
Aug 17, 2023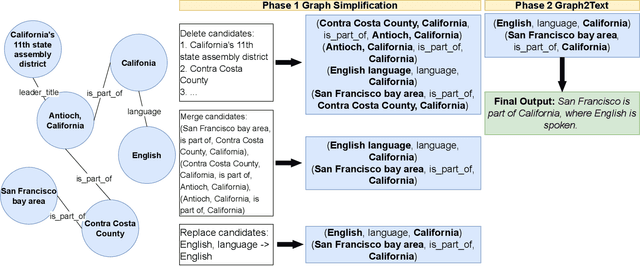
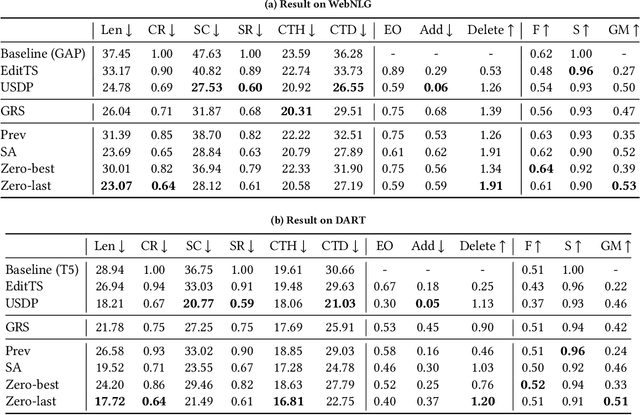
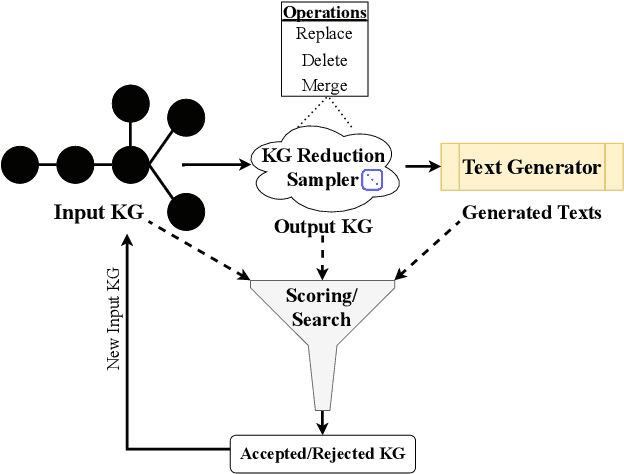
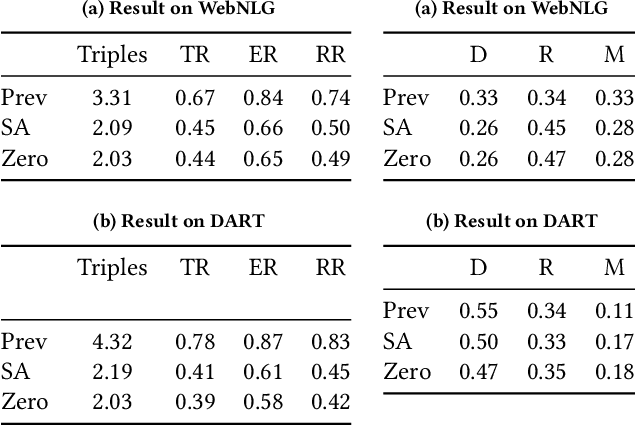
Abstract:Knowledge Graph (KG)-to-Text Generation has seen recent improvements in generating fluent and informative sentences which describe a given KG. As KGs are widespread across multiple domains and contain important entity-relation information, and as text simplification aims to reduce the complexity of a text while preserving the meaning of the original text, we propose KGSimple, a novel approach to unsupervised text simplification which infuses KG-established techniques in order to construct a simplified KG path and generate a concise text which preserves the original input's meaning. Through an iterative and sampling KG-first approach, our model is capable of simplifying text when starting from a KG by learning to keep important information while harnessing KG-to-text generation to output fluent and descriptive sentences. We evaluate various settings of the KGSimple model on currently-available KG-to-text datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness compared to unsupervised text simplification models which start with a given complex text. Our code is available on GitHub.
Simple Rule Injection for ComplEx Embeddings
Aug 07, 2023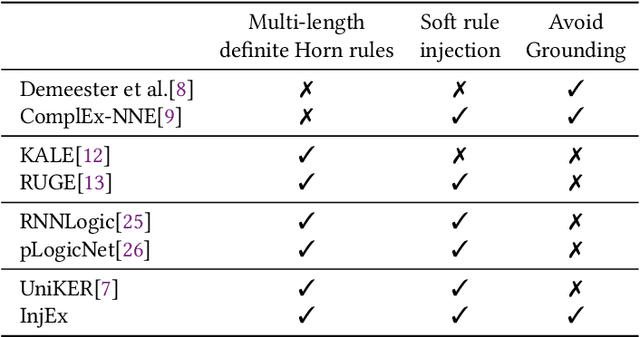
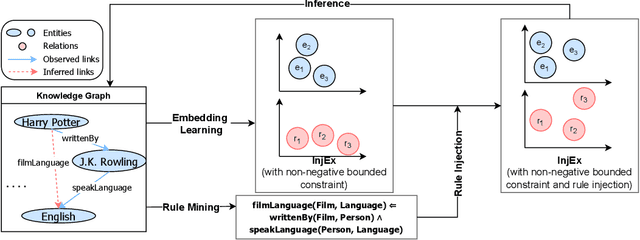
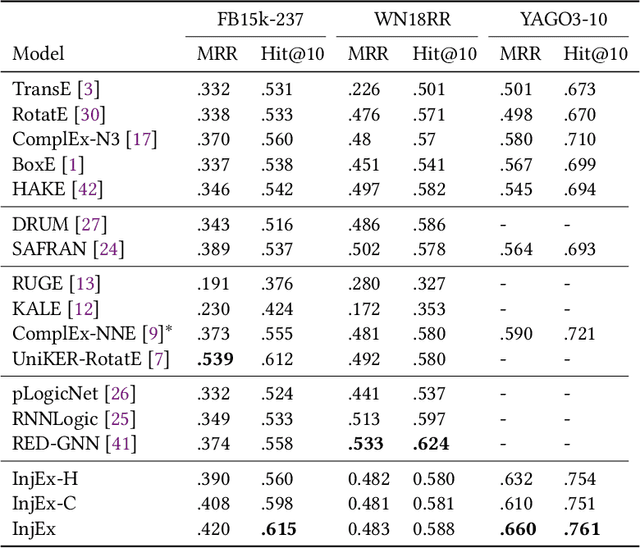
Abstract:Recent works in neural knowledge graph inference attempt to combine logic rules with knowledge graph embeddings to benefit from prior knowledge. However, they usually cannot avoid rule grounding, and injecting a diverse set of rules has still not been thoroughly explored. In this work, we propose InjEx, a mechanism to inject multiple types of rules through simple constraints, which capture definite Horn rules. To start, we theoretically prove that InjEx can inject such rules. Next, to demonstrate that InjEx infuses interpretable prior knowledge into the embedding space, we evaluate InjEx on both the knowledge graph completion (KGC) and few-shot knowledge graph completion (FKGC) settings. Our experimental results reveal that InjEx outperforms both baseline KGC models as well as specialized few-shot models while maintaining its scalability and efficiency.
MythQA: Query-Based Large-Scale Check-Worthy Claim Detection through Multi-Answer Open-Domain Question Answering
Jul 21, 2023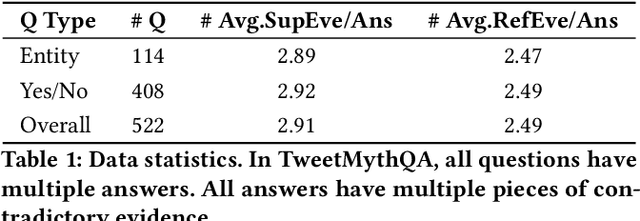
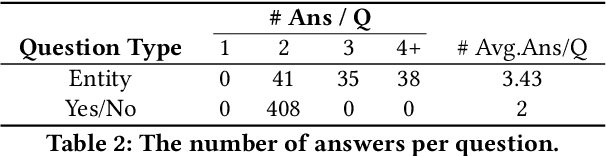
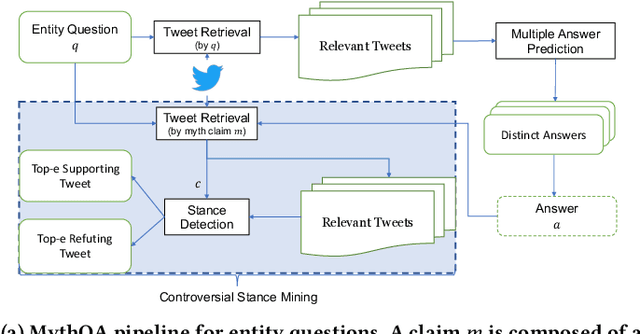
Abstract:Check-worthy claim detection aims at providing plausible misinformation to downstream fact-checking systems or human experts to check. This is a crucial step toward accelerating the fact-checking process. Many efforts have been put into how to identify check-worthy claims from a small scale of pre-collected claims, but how to efficiently detect check-worthy claims directly from a large-scale information source, such as Twitter, remains underexplored. To fill this gap, we introduce MythQA, a new multi-answer open-domain question answering(QA) task that involves contradictory stance mining for query-based large-scale check-worthy claim detection. The idea behind this is that contradictory claims are a strong indicator of misinformation that merits scrutiny by the appropriate authorities. To study this task, we construct TweetMythQA, an evaluation dataset containing 522 factoid multi-answer questions based on controversial topics. Each question is annotated with multiple answers. Moreover, we collect relevant tweets for each distinct answer, then classify them into three categories: "Supporting", "Refuting", and "Neutral". In total, we annotated 5.3K tweets. Contradictory evidence is collected for all answers in the dataset. Finally, we present a baseline system for MythQA and evaluate existing NLP models for each system component using the TweetMythQA dataset. We provide initial benchmarks and identify key challenges for future models to improve upon. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/TonyBY/Myth-QA
DrugEHRQA: A Question Answering Dataset on Structured and Unstructured Electronic Health Records For Medicine Related Queries
May 03, 2022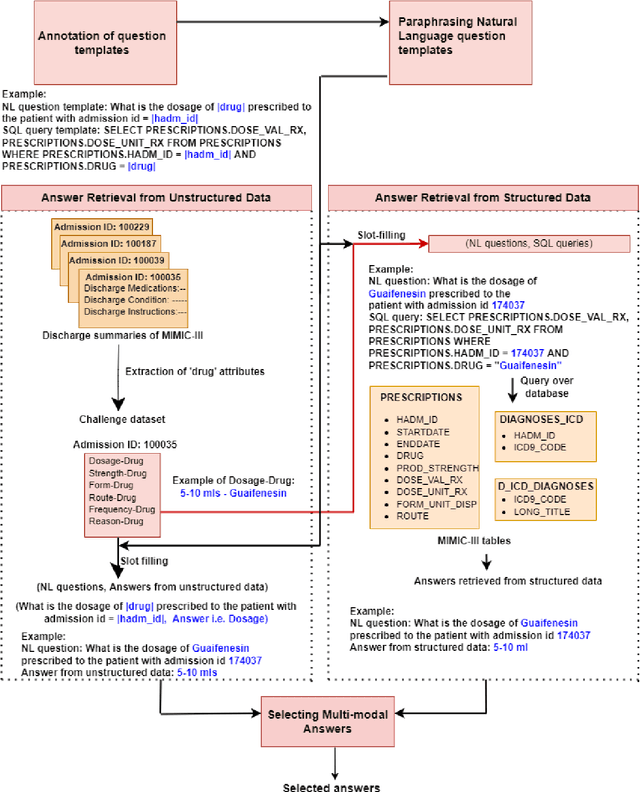
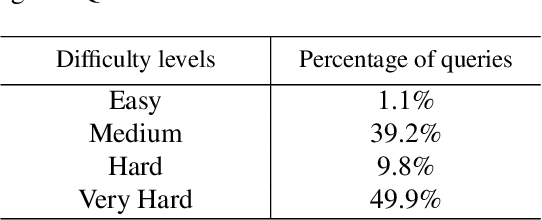

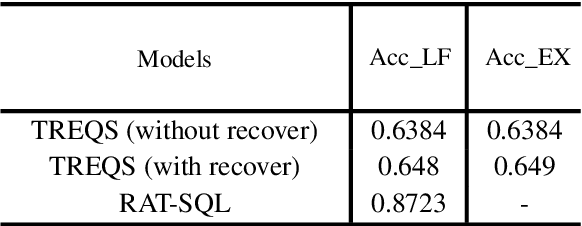
Abstract:This paper develops the first question answering dataset (DrugEHRQA) containing question-answer pairs from both structured tables and unstructured notes from a publicly available Electronic Health Record (EHR). EHRs contain patient records, stored in structured tables and unstructured clinical notes. The information in structured and unstructured EHRs is not strictly disjoint: information may be duplicated, contradictory, or provide additional context between these sources. Our dataset has medication-related queries, containing over 70,000 question-answer pairs. To provide a baseline model and help analyze the dataset, we have used a simple model (MultimodalEHRQA) which uses the predictions of a modality selection network to choose between EHR tables and clinical notes to answer the questions. This is used to direct the questions to the table-based or text-based state-of-the-art QA model. In order to address the problem arising from complex, nested queries, this is the first time Relation-Aware Schema Encoding and Linking for Text-to-SQL Parsers (RAT-SQL) has been used to test the structure of query templates in EHR data. Our goal is to provide a benchmark dataset for multi-modal QA systems, and to open up new avenues of research in improving question answering over EHR structured data by using context from unstructured clinical data.
GAP: A Graph-aware Language Model Framework for Knowledge Graph-to-Text Generation
Apr 13, 2022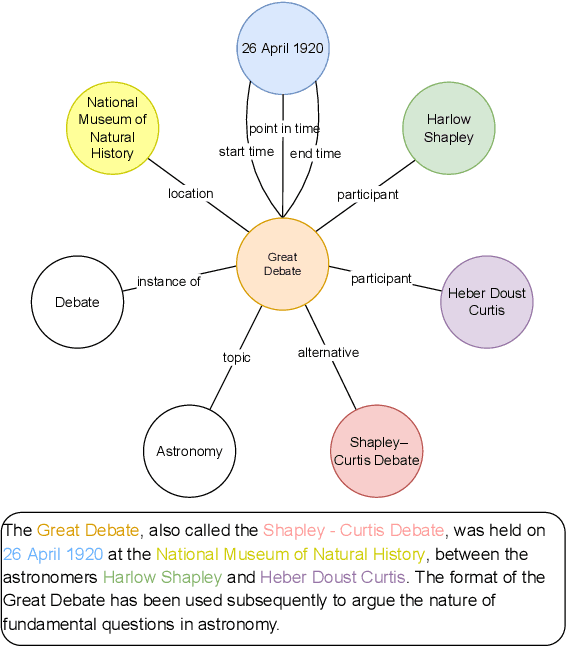
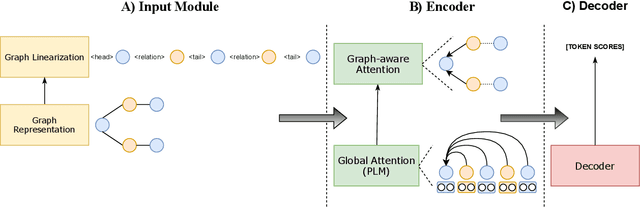
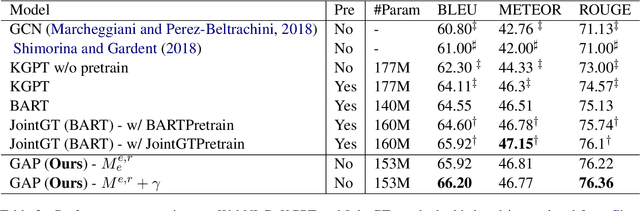
Abstract:Recent improvements in KG-to-text generation are due to additional auxiliary pre-trained tasks designed to give the fine-tune task a boost in performance. These tasks require extensive computational resources while only suggesting marginal improvements. Here, we demonstrate that by fusing graph-aware elements into existing pre-trained language models, we are able to outperform state-of-the-art models and close the gap imposed by additional pre-train tasks. We do so by proposing a mask structure to capture neighborhood information and a novel type encoder that adds a bias to the graph-attention weights depending on the connection type. Experiments on two KG-to-text benchmark datasets show these models to be superior in quality while involving fewer parameters and no additional pre-trained tasks. By formulating the problem as a framework, we can interchange the various proposed components and begin interpreting KG-to-text generative models based on the topological and type information found in a graph.
EventNarrative: A large-scale Event-centric Dataset for Knowledge Graph-to-Text Generation
Oct 30, 2021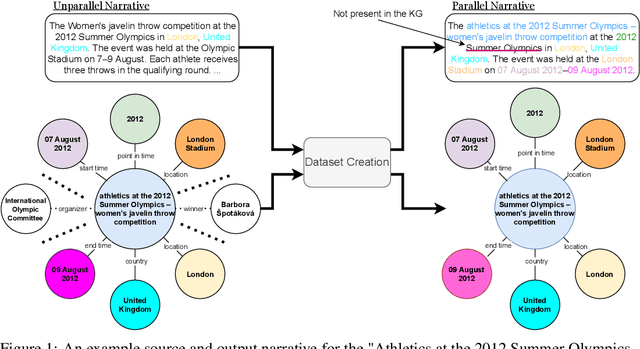
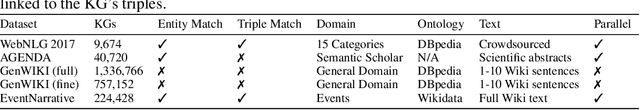
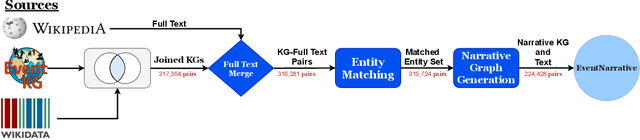
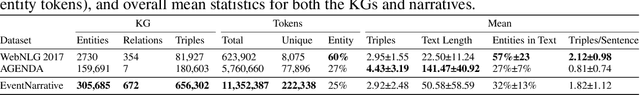
Abstract:We introduce EventNarrative, a knowledge graph-to-text dataset from publicly available open-world knowledge graphs. Given the recent advances in event-driven Information Extraction (IE), and that prior research on graph-to-text only focused on entity-driven KGs, this paper focuses on event-centric data. However, our data generation system can still be adapted to other other types of KG data. Existing large-scale datasets in the graph-to-text area are non-parallel, meaning there is a large disconnect between the KGs and text. The datasets that have a paired KG and text, are small scale and manually generated or generated without a rich ontology, making the corresponding graphs sparse. Furthermore, these datasets contain many unlinked entities between their KG and text pairs. EventNarrative consists of approximately 230,000 graphs and their corresponding natural language text, 6 times larger than the current largest parallel dataset. It makes use of a rich ontology, all of the KGs entities are linked to the text, and our manual annotations confirm a high data quality. Our aim is two-fold: help break new ground in event-centric research where data is lacking, and to give researchers a well-defined, large-scale dataset in order to better evaluate existing and future knowledge graph-to-text models. We also evaluate two types of baseline on EventNarrative: a graph-to-text specific model and two state-of-the-art language models, which previous work has shown to be adaptable to the knowledge graph-to-text domain.
ChronoR: Rotation Based Temporal Knowledge Graph Embedding
Mar 18, 2021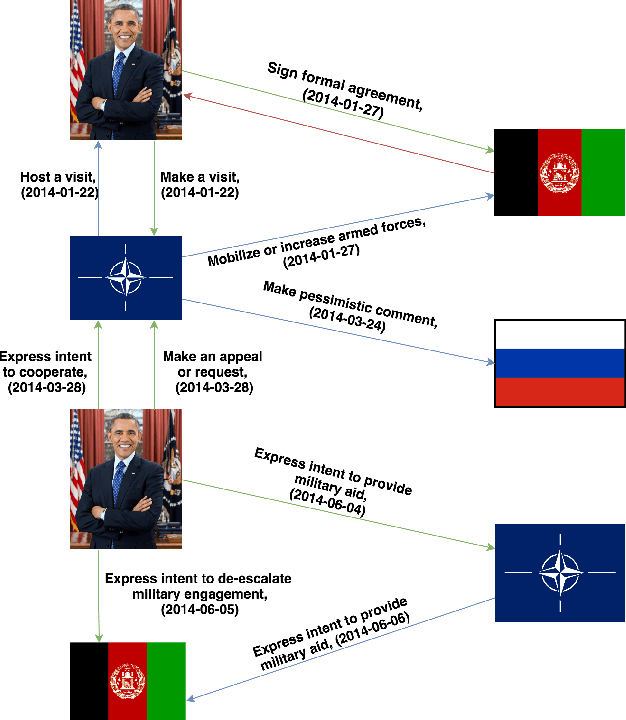
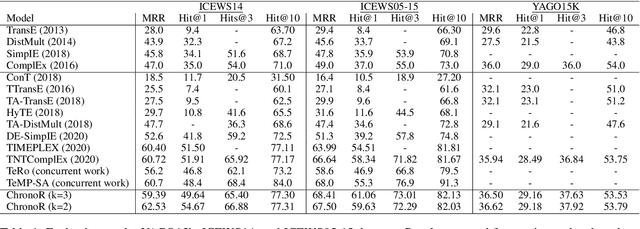
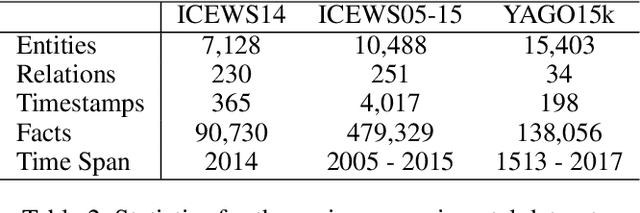
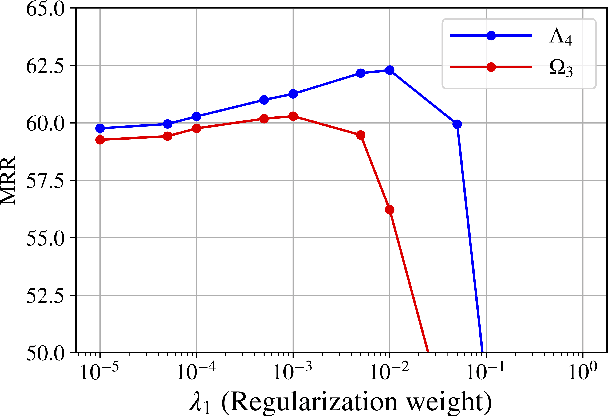
Abstract:Despite the importance and abundance of temporal knowledge graphs, most of the current research has been focused on reasoning on static graphs. In this paper, we study the challenging problem of inference over temporal knowledge graphs. In particular, the task of temporal link prediction. In general, this is a difficult task due to data non-stationarity, data heterogeneity, and its complex temporal dependencies. We propose Chronological Rotation embedding (ChronoR), a novel model for learning representations for entities, relations, and time. Learning dense representations is frequently used as an efficient and versatile method to perform reasoning on knowledge graphs. The proposed model learns a k-dimensional rotation transformation parametrized by relation and time, such that after each fact's head entity is transformed using the rotation, it falls near its corresponding tail entity. By using high dimensional rotation as its transformation operator, ChronoR captures rich interaction between the temporal and multi-relational characteristics of a Temporal Knowledge Graph. Experimentally, we show that ChronoR is able to outperform many of the state-of-the-art methods on the benchmark datasets for temporal knowledge graph link prediction.
Efficient Deployment of Conversational Natural Language Interfaces over Databases
Jun 04, 2020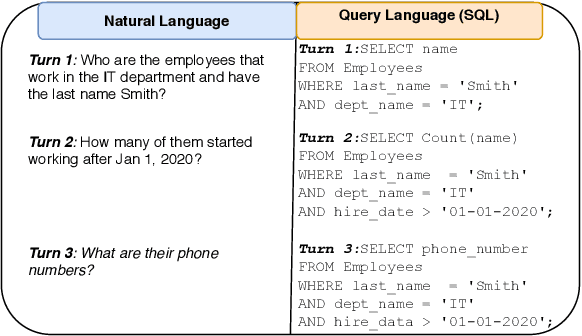

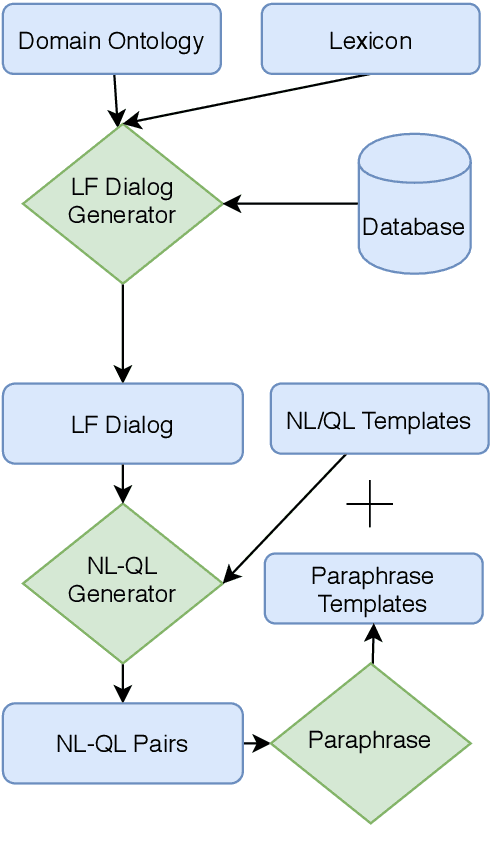
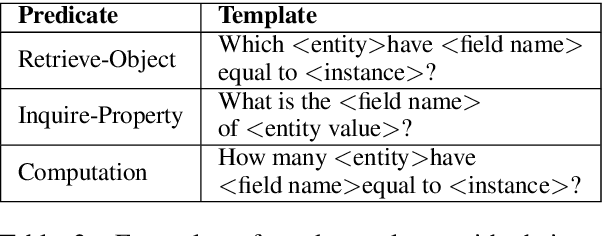
Abstract:Many users communicate with chatbots and AI assistants in order to help them with various tasks. A key component of the assistant is the ability to understand and answer a user's natural language questions for question-answering (QA). Because data can be usually stored in a structured manner, an essential step involves turning a natural language question into its corresponding query language. However, in order to train most natural language-to-query-language state-of-the-art models, a large amount of training data is needed first. In most domains, this data is not available and collecting such datasets for various domains can be tedious and time-consuming. In this work, we propose a novel method for accelerating the training dataset collection for developing the natural language-to-query-language machine learning models. Our system allows one to generate conversational multi-term data, where multiple turns define a dialogue session, enabling one to better utilize chatbot interfaces. We train two current state-of-the-art NL-to-QL models, on both an SQL and SPARQL-based datasets in order to showcase the adaptability and efficacy of our created data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge