Anna Goodridge
A Small Form Factor Aerial Research Vehicle for Pick-and-Place Tasks with Onboard Real-Time Object Detection and Visual Odometry
Aug 02, 2023



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel, small form-factor, aerial vehicle research platform for agile object detection, classification, tracking, and interaction tasks. General-purpose hardware components were designed to augment a given aerial vehicle and enable it to perform safe and reliable grasping. These components include a custom collision tolerant cage and low-cost Gripper Extension Package, which we call GREP, for object grasping. Small vehicles enable applications in highly constrained environments, but are often limited by computational resources. This work evaluates the challenges of pick-and-place tasks, with entirely onboard computation of object pose and visual odometry based state estimation on a small platform, and demonstrates experiments with enough accuracy to reliably grasp objects. In a total of 70 trials across challenging cases such as cluttered environments, obstructed targets, and multiple instances of the same target, we demonstrated successfully grasping the target in 93% of trials. Both the hardware component designs and software framework are released as open-source, since our intention is to enable easy reproduction and application on a wide range of small vehicles.
A force-sensing surgical drill for real-time force feedback in robotic mastoidectomy
Apr 05, 2023Abstract:Purpose: Robotic assistance in otologic surgery can reduce the task load of operating surgeons during the removal of bone around the critical structures in the lateral skull base. However, safe deployment into the anatomical passageways necessitates the development of advanced sensing capabilities to actively limit the interaction forces between the surgical tools and critical anatomy. Methods: We introduce a surgical drill equipped with a force sensor that is capable of measuring accurate tool-tissue interaction forces to enable force control and feedback to surgeons. The design, calibration and validation of the force-sensing surgical drill mounted on a cooperatively controlled surgical robot are described in this work. Results: The force measurements on the tip of the surgical drill are validated with raw-egg drilling experiments, where a force sensor mounted below the egg serves as ground truth. The average root mean square error (RMSE) for points and path drilling experiments are 41.7 (pm 12.2) mN and 48.3 (pm 13.7) mN respectively. Conclusions: The force-sensing prototype measures forces with sub-millinewton resolution and the results demonstrate that the calibrated force-sensing drill generates accurate force measurements with minimal error compared to the measured drill forces. The development of such sensing capabilities is crucial for the safe use of robotic systems in a clinical context.
Design and Fabrication of a Fiber Bragg Grating Shape Sensor for Shape Reconstruction of a Continuum Manipulator
Mar 07, 2023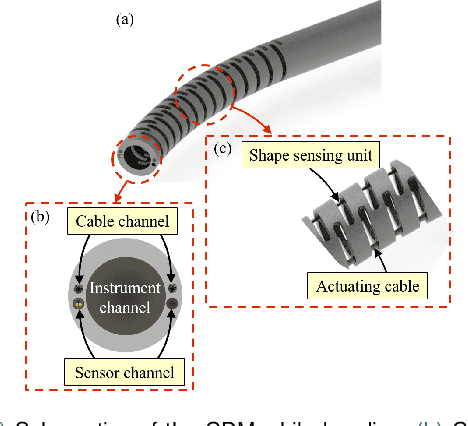
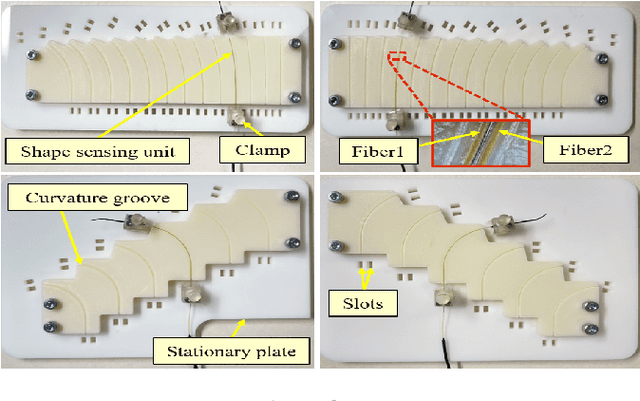
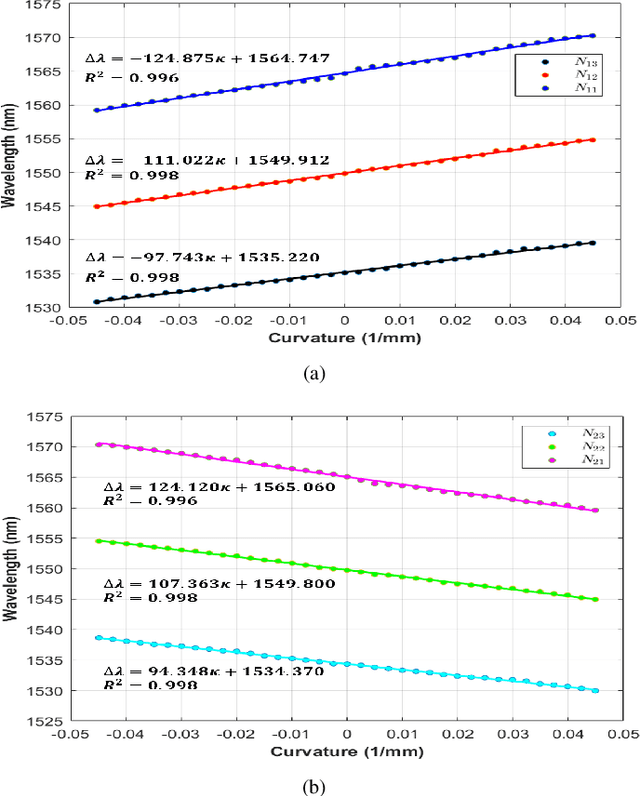
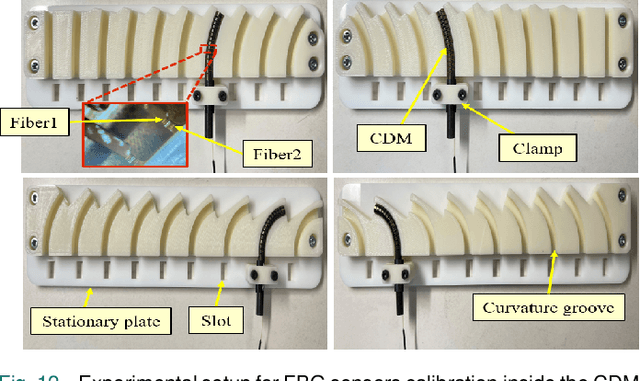
Abstract:Continuum dexterous manipulators (CDMs) are suitable for performing tasks in a constrained environment due to their high dexterity and maneuverability. Despite the inherent advantages of CDMs in minimally invasive surgery, real-time control of CDMs' shape during non-constant curvature bending is still challenging. This study presents a novel approach for the design and fabrication of a large deflection fiber Bragg grating (FBG) shape sensor embedded within the lumens inside the walls of a CDM with a large instrument channel. The shape sensor consisted of two fibers, each with three FBG nodes. A shape-sensing model was introduced to reconstruct the centerline of the CDM based on FBG wavelengths. Different experiments, including shape sensor tests and CDM shape reconstruction tests, were conducted to assess the overall accuracy of the shape sensing. The FBG sensor evaluation results revealed the linear curvature-wavelength relationship with the large curvature detection of 0.045 mm at a 90 degrees bending angle and a sensitivity of up to 5.50 nm/mm in each bending direction. The CDM's shape reconstruction experiments in a free environment demonstrated the shape tracking accuracy of 0.216+-0.126 mm for positive/negative deflections. Also, the CDM shape reconstruction error for three cases of bending with obstacles were observed to be 0.436+-0.370 mm for the proximal case, 0.485+-0.418 mm for the middle case, and 0.312+-0.261 mm for the distal case. This study indicates the adequate performance of the FBG sensor and the effectiveness of the model for tracking the shape of the large-deflection CDM with nonconstant-curvature bending for minimally-invasive orthopaedic applications.
TAToo: Vision-based Joint Tracking of Anatomy and Tool for Skull-base Surgery
Dec 29, 2022Abstract:Purpose: Tracking the 3D motion of the surgical tool and the patient anatomy is a fundamental requirement for computer-assisted skull-base surgery. The estimated motion can be used both for intra-operative guidance and for downstream skill analysis. Recovering such motion solely from surgical videos is desirable, as it is compliant with current clinical workflows and instrumentation. Methods: We present Tracker of Anatomy and Tool (TAToo). TAToo jointly tracks the rigid 3D motion of patient skull and surgical drill from stereo microscopic videos. TAToo estimates motion via an iterative optimization process in an end-to-end differentiable form. For robust tracking performance, TAToo adopts a probabilistic formulation and enforces geometric constraints on the object level. Results: We validate TAToo on both simulation data, where ground truth motion is available, as well as on anthropomorphic phantom data, where optical tracking provides a strong baseline. We report sub-millimeter and millimeter inter-frame tracking accuracy for skull and drill, respectively, with rotation errors below 1{\deg}. We further illustrate how TAToo may be used in a surgical navigation setting. Conclusion: We present TAToo, which simultaneously tracks the surgical tool and the patient anatomy in skull-base surgery. TAToo directly predicts the motion from surgical videos, without the need of any markers. Our results show that the performance of TAToo compares favorably to competing approaches. Future work will include fine-tuning of our depth network to reach a 1 mm clinical accuracy goal desired for surgical applications in the skull base.
Twin-S: A Digital Twin for Skull-base Surgery
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:Purpose: Digital twins are virtual interactive models of the real world, exhibiting identical behavior and properties. In surgical applications, computational analysis from digital twins can be used, for example, to enhance situational awareness. Methods: We present a digital twin framework for skull-base surgeries, named Twin-S, which can be integrated within various image-guided interventions seamlessly. Twin-S combines high-precision optical tracking and real-time simulation. We rely on rigorous calibration routines to ensure that the digital twin representation precisely mimics all real-world processes. Twin-S models and tracks the critical components of skull-base surgery, including the surgical tool, patient anatomy, and surgical camera. Significantly, Twin-S updates and reflects real-world drilling of the anatomical model in frame rate. Results: We extensively evaluate the accuracy of Twin-S, which achieves an average 1.39 mm error during the drilling process. We further illustrate how segmentation masks derived from the continuously updated digital twin can augment the surgical microscope view in a mixed reality setting, where bone requiring ablation is highlighted to provide surgeons additional situational awareness. Conclusion: We present Twin-S, a digital twin environment for skull-base surgery. Twin-S tracks and updates the virtual model in real-time given measurements from modern tracking technologies. Future research on complementing optical tracking with higher-precision vision-based approaches may further increase the accuracy of Twin-S.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge