Alexander Heimerl
Recognizing Emotion Regulation Strategies from Human Behavior with Large Language Models
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Human emotions are often not expressed directly, but regulated according to internal processes and social display rules. For affective computing systems, an understanding of how users regulate their emotions can be highly useful, for example to provide feedback in job interview training, or in psychotherapeutic scenarios. However, at present no method to automatically classify different emotion regulation strategies in a cross-user scenario exists. At the same time, recent studies showed that instruction-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) can reach impressive performance across a variety of affect recognition tasks such as categorical emotion recognition or sentiment analysis. While these results are promising, it remains unclear to what extent the representational power of LLMs can be utilized in the more subtle task of classifying users' internal emotion regulation strategy. To close this gap, we make use of the recently introduced \textsc{Deep} corpus for modeling the social display of the emotion shame, where each point in time is annotated with one of seven different emotion regulation classes. We fine-tune Llama2-7B as well as the recently introduced Gemma model using Low-rank Optimization on prompts generated from different sources of information on the \textsc{Deep} corpus. These include verbal and nonverbal behavior, person factors, as well as the results of an in-depth interview after the interaction. Our results show, that a fine-tuned Llama2-7B LLM is able to classify the utilized emotion regulation strategy with high accuracy (0.84) without needing access to data from post-interaction interviews. This represents a significant improvement over previous approaches based on Bayesian Networks and highlights the importance of modeling verbal behavior in emotion regulation.
MultiMediate'23: Engagement Estimation and Bodily Behaviour Recognition in Social Interactions
Aug 16, 2023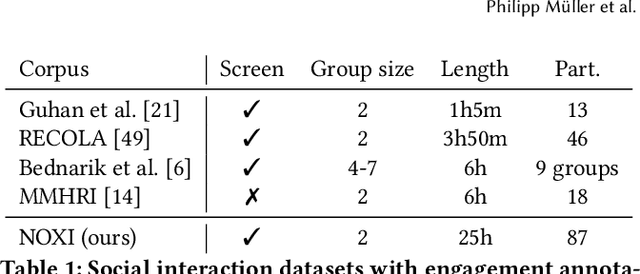
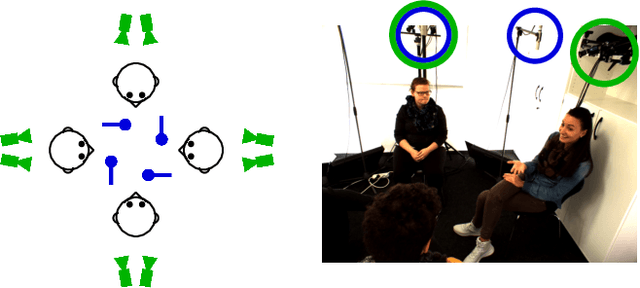
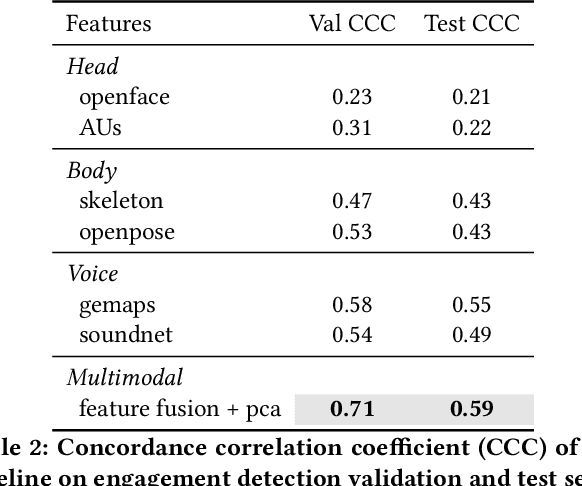
Abstract:Automatic analysis of human behaviour is a fundamental prerequisite for the creation of machines that can effectively interact with- and support humans in social interactions. In MultiMediate'23, we address two key human social behaviour analysis tasks for the first time in a controlled challenge: engagement estimation and bodily behaviour recognition in social interactions. This paper describes the MultiMediate'23 challenge and presents novel sets of annotations for both tasks. For engagement estimation we collected novel annotations on the NOvice eXpert Interaction (NOXI) database. For bodily behaviour recognition, we annotated test recordings of the MPIIGroupInteraction corpus with the BBSI annotation scheme. In addition, we present baseline results for both challenge tasks.
ForDigitStress: A multi-modal stress dataset employing a digital job interview scenario
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:We present a multi-modal stress dataset that uses digital job interviews to induce stress. The dataset provides multi-modal data of 40 participants including audio, video (motion capturing, facial recognition, eye tracking) as well as physiological information (photoplethysmography, electrodermal activity). In addition to that, the dataset contains time-continuous annotations for stress and occurred emotions (e.g. shame, anger, anxiety, surprise). In order to establish a baseline, five different machine learning classifiers (Support Vector Machine, K-Nearest Neighbors, Random Forest, Long-Short-Term Memory Network) have been trained and evaluated on the proposed dataset for a binary stress classification task. The best-performing classifier achieved an accuracy of 88.3% and an F1-score of 87.5%.
"GAN I hire you?" -- A System for Personalized Virtual Job Interview Training
Jun 08, 2022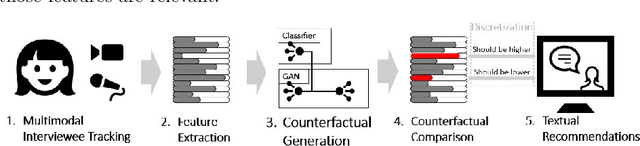
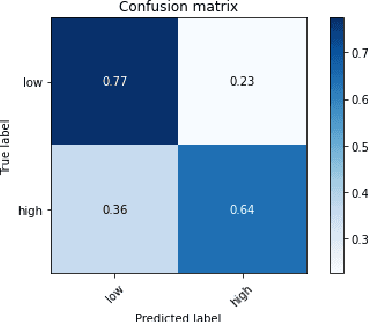

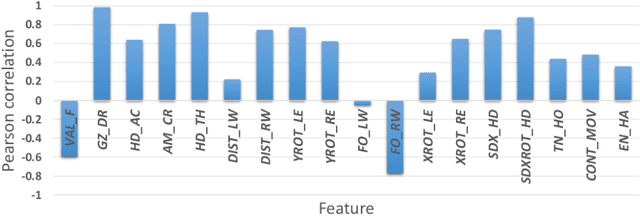
Abstract:Job interviews are usually high-stakes social situations where professional and behavioral skills are required for a satisfactory outcome. Professional job interview trainers give educative feedback about the shown behavior according to common standards. This feedback can be helpful concerning the improvement of behavioral skills needed for job interviews. A technological approach for generating such feedback might be a playful and low-key starting point for job interview training. Therefore, we extended an interactive virtual job interview training system with a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based approach that first detects behavioral weaknesses and subsequently generates personalized feedback. To evaluate the usefulness of the generated feedback, we conducted a mixed-methods pilot study using mock-ups from the job interview training system. The overall study results indicate that the GAN-based generated behavioral feedback is helpful. Moreover, participants assessed that the feedback would improve their job interview performance.
This is not the Texture you are looking for! Introducing Novel Counterfactual Explanations for Non-Experts using Generative Adversarial Learning
Dec 22, 2020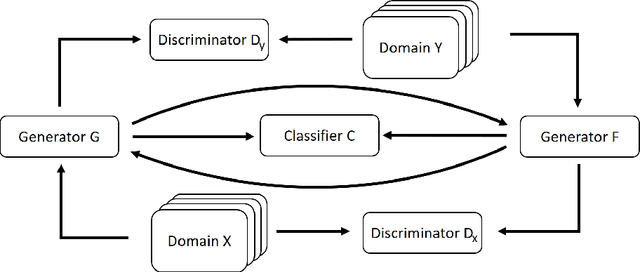
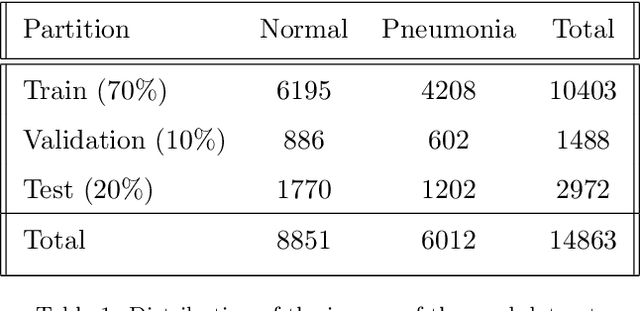
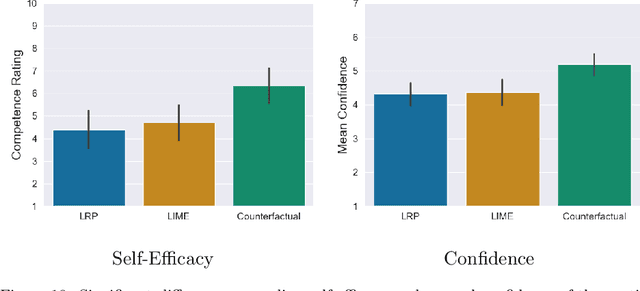
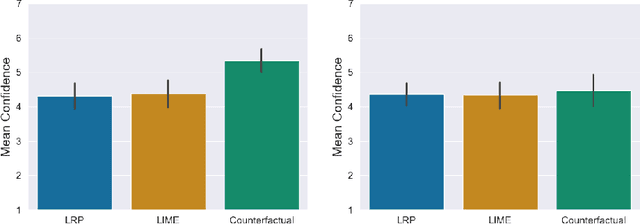
Abstract:With the ongoing rise of machine learning, the need for methods for explaining decisions made by artificial intelligence systems is becoming a more and more important topic. Especially for image classification tasks, many state-of-the-art tools to explain such classifiers rely on visual highlighting of important areas of the input data. Contrary, counterfactual explanation systems try to enable a counterfactual reasoning by modifying the input image in a way such that the classifier would have made a different prediction. By doing so, the users of counterfactual explanation systems are equipped with a completely different kind of explanatory information. However, methods for generating realistic counterfactual explanations for image classifiers are still rare. In this work, we present a novel approach to generate such counterfactual image explanations based on adversarial image-to-image translation techniques. Additionally, we conduct a user study to evaluate our approach in a use case which was inspired by a healthcare scenario. Our results show that our approach leads to significantly better results regarding mental models, explanation satisfaction, trust, emotions, and self-efficacy than two state-of-the art systems that work with saliency maps, namely LIME and LRP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge