Matthias Kraus
Development of a Trust-Aware User Simulator for Statistical Proactive Dialog Modeling in Human-AI Teams
Apr 24, 2023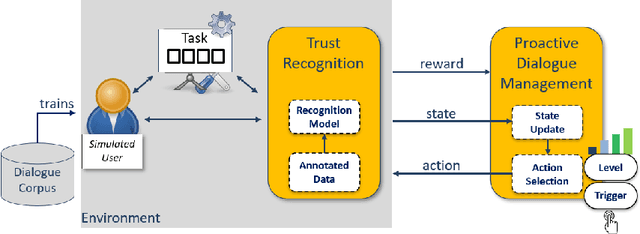
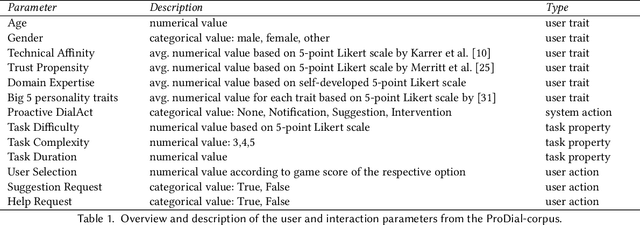
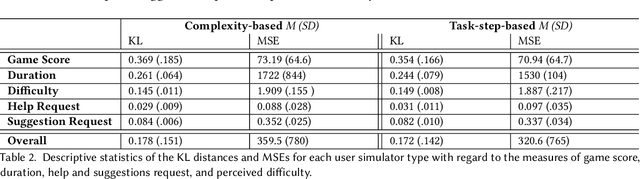
Abstract:The concept of a Human-AI team has gained increasing attention in recent years. For effective collaboration between humans and AI teammates, proactivity is crucial for close coordination and effective communication. However, the design of adequate proactivity for AI-based systems to support humans is still an open question and a challenging topic. In this paper, we present the development of a corpus-based user simulator for training and testing proactive dialog policies. The simulator incorporates informed knowledge about proactive dialog and its effect on user trust and simulates user behavior and personal information, including socio-demographic features and personality traits. Two different simulation approaches were compared, and a task-step-based approach yielded better overall results due to enhanced modeling of sequential dependencies. This research presents a promising avenue for exploring and evaluating appropriate proactive strategies in a dialog game setting for improving Human-AI teams.
ForDigitStress: A multi-modal stress dataset employing a digital job interview scenario
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:We present a multi-modal stress dataset that uses digital job interviews to induce stress. The dataset provides multi-modal data of 40 participants including audio, video (motion capturing, facial recognition, eye tracking) as well as physiological information (photoplethysmography, electrodermal activity). In addition to that, the dataset contains time-continuous annotations for stress and occurred emotions (e.g. shame, anger, anxiety, surprise). In order to establish a baseline, five different machine learning classifiers (Support Vector Machine, K-Nearest Neighbors, Random Forest, Long-Short-Term Memory Network) have been trained and evaluated on the proposed dataset for a binary stress classification task. The best-performing classifier achieved an accuracy of 88.3% and an F1-score of 87.5%.
Does It Affect You? Social and Learning Implications of Using Cognitive-Affective State Recognition for Proactive Human-Robot Tutoring
Dec 20, 2022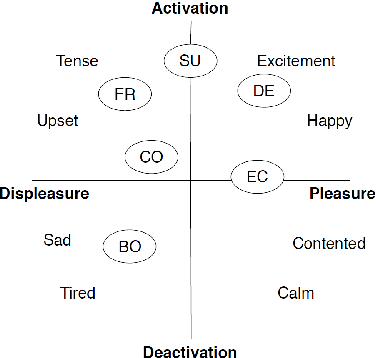
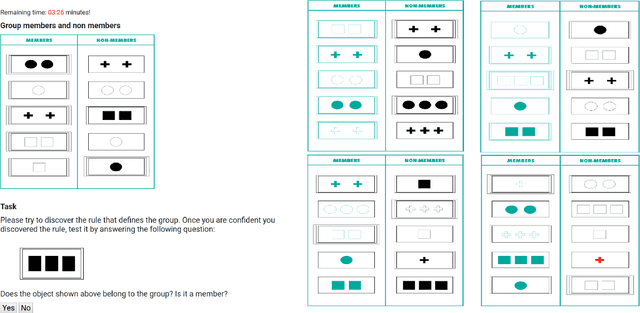
Abstract:Using robots in educational contexts has already shown to be beneficial for a student's learning and social behaviour. For levitating them to the next level of providing more effective and human-like tutoring, the ability to adapt to the user and to express proactivity is fundamental. By acting proactively, intelligent robotic tutors anticipate possible situations where problems for the student may arise and act in advance for preventing negative outcomes. Still, the decisions of when and how to behave proactively are open questions. Therefore, this paper deals with the investigation of how the student's cognitive-affective states can be used by a robotic tutor for triggering proactive tutoring dialogue. In doing so, it is aimed to improve the learning experience. For this reason, a concept learning task scenario was observed where a robotic assistant proactively helped when negative user states were detected. In a learning task, the user's states of frustration and confusion were deemed to have negative effects on the outcome of the task and were used to trigger proactive behaviour. In an empirical user study with 40 undergraduate and doctoral students, we studied whether the initiation of proactive behaviour after the detection of signs of confusion and frustration improves the student's concentration and trust in the agent. Additionally, we investigated which level of proactive dialogue is useful for promoting the student's concentration and trust. The results show that high proactive behaviour harms trust, especially when triggered during negative cognitive-affective states but contributes to keeping the student focused on the task when triggered in these states. Based on our study results, we further discuss future steps for improving the proactive assistance of robotic tutoring systems.
Towards Improving Proactive Dialog Agents Using Socially-Aware Reinforcement Learning
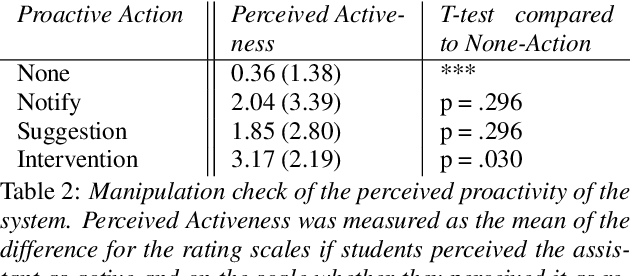
Nov 25, 2022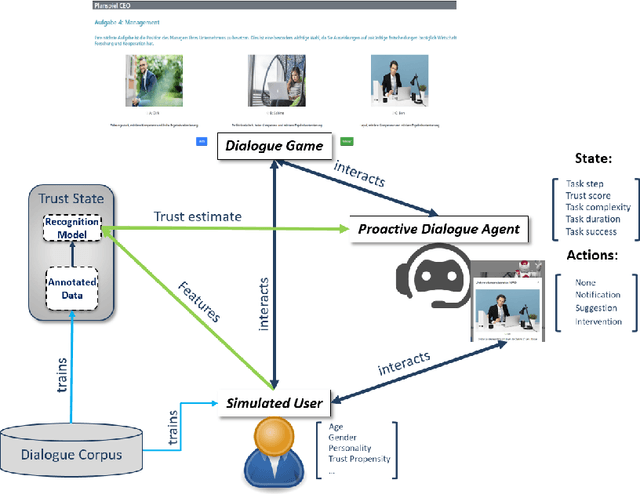
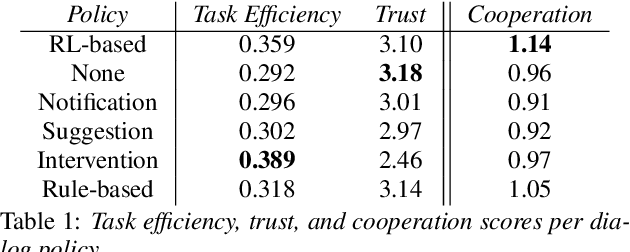
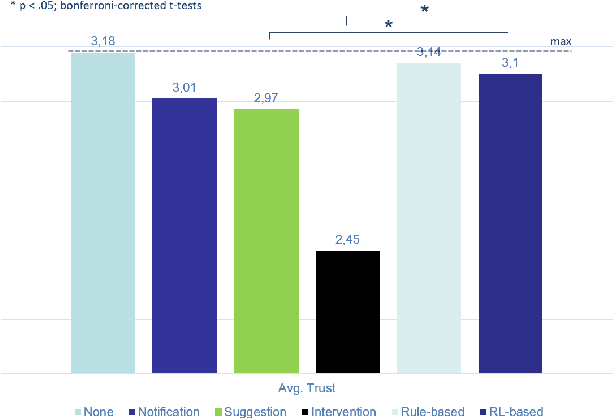
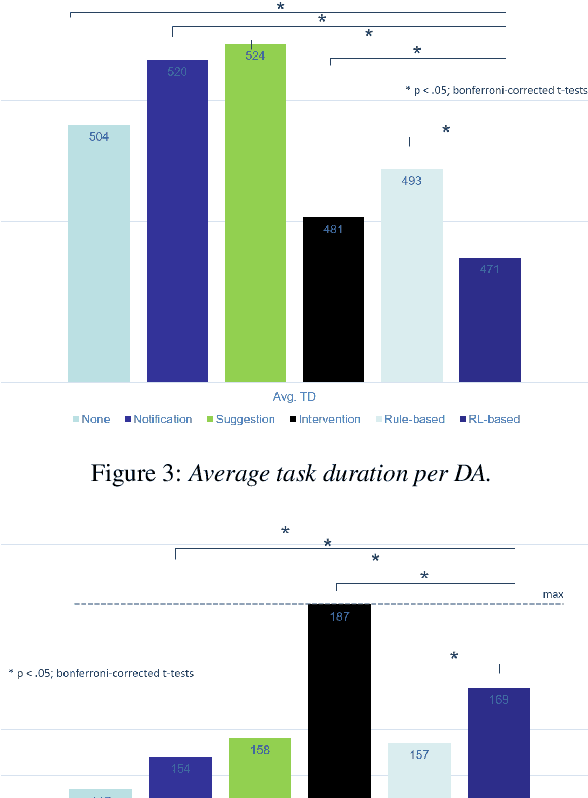
Abstract:The next step for intelligent dialog agents is to escape their role as silent bystanders and become proactive. Well-defined proactive behavior may improve human-machine cooperation, as the agent takes a more active role during interaction and takes off responsibility from the user. However, proactivity is a double-edged sword because poorly executed pre-emptive actions may have a devastating effect not only on the task outcome but also on the relationship with the user. For designing adequate proactive dialog strategies, we propose a novel approach including both social as well as task-relevant features in the dialog. Here, the primary goal is to optimize proactive behavior so that it is task-oriented - this implies high task success and efficiency - while also being socially effective by fostering user trust. Including both aspects in the reward function for training a proactive dialog agent using reinforcement learning showed the benefit of our approach for more successful human-machine cooperation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge