Nicolas Rohleder
ForDigitStress: A multi-modal stress dataset employing a digital job interview scenario
Mar 14, 2023



Abstract:We present a multi-modal stress dataset that uses digital job interviews to induce stress. The dataset provides multi-modal data of 40 participants including audio, video (motion capturing, facial recognition, eye tracking) as well as physiological information (photoplethysmography, electrodermal activity). In addition to that, the dataset contains time-continuous annotations for stress and occurred emotions (e.g. shame, anger, anxiety, surprise). In order to establish a baseline, five different machine learning classifiers (Support Vector Machine, K-Nearest Neighbors, Random Forest, Long-Short-Term Memory Network) have been trained and evaluated on the proposed dataset for a binary stress classification task. The best-performing classifier achieved an accuracy of 88.3% and an F1-score of 87.5%.
"GAN I hire you?" -- A System for Personalized Virtual Job Interview Training
Jun 08, 2022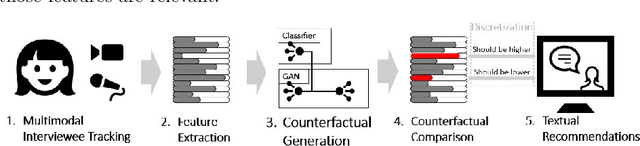

Abstract:Job interviews are usually high-stakes social situations where professional and behavioral skills are required for a satisfactory outcome. Professional job interview trainers give educative feedback about the shown behavior according to common standards. This feedback can be helpful concerning the improvement of behavioral skills needed for job interviews. A technological approach for generating such feedback might be a playful and low-key starting point for job interview training. Therefore, we extended an interactive virtual job interview training system with a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based approach that first detects behavioral weaknesses and subsequently generates personalized feedback. To evaluate the usefulness of the generated feedback, we conducted a mixed-methods pilot study using mock-ups from the job interview training system. The overall study results indicate that the GAN-based generated behavioral feedback is helpful. Moreover, participants assessed that the feedback would improve their job interview performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge