Jan Alexandersson
DFKI GmbH, Saarbruecken, Germany
Recognizing Emotion Regulation Strategies from Human Behavior with Large Language Models
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Human emotions are often not expressed directly, but regulated according to internal processes and social display rules. For affective computing systems, an understanding of how users regulate their emotions can be highly useful, for example to provide feedback in job interview training, or in psychotherapeutic scenarios. However, at present no method to automatically classify different emotion regulation strategies in a cross-user scenario exists. At the same time, recent studies showed that instruction-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) can reach impressive performance across a variety of affect recognition tasks such as categorical emotion recognition or sentiment analysis. While these results are promising, it remains unclear to what extent the representational power of LLMs can be utilized in the more subtle task of classifying users' internal emotion regulation strategy. To close this gap, we make use of the recently introduced \textsc{Deep} corpus for modeling the social display of the emotion shame, where each point in time is annotated with one of seven different emotion regulation classes. We fine-tune Llama2-7B as well as the recently introduced Gemma model using Low-rank Optimization on prompts generated from different sources of information on the \textsc{Deep} corpus. These include verbal and nonverbal behavior, person factors, as well as the results of an in-depth interview after the interaction. Our results show, that a fine-tuned Llama2-7B LLM is able to classify the utilized emotion regulation strategy with high accuracy (0.84) without needing access to data from post-interaction interviews. This represents a significant improvement over previous approaches based on Bayesian Networks and highlights the importance of modeling verbal behavior in emotion regulation.
M3TCM: Multi-modal Multi-task Context Model for Utterance Classification in Motivational Interviews
Apr 04, 2024



Abstract:Accurate utterance classification in motivational interviews is crucial to automatically understand the quality and dynamics of client-therapist interaction, and it can serve as a key input for systems mediating such interactions. Motivational interviews exhibit three important characteristics. First, there are two distinct roles, namely client and therapist. Second, they are often highly emotionally charged, which can be expressed both in text and in prosody. Finally, context is of central importance to classify any given utterance. Previous works did not adequately incorporate all of these characteristics into utterance classification approaches for mental health dialogues. In contrast, we present M3TCM, a Multi-modal, Multi-task Context Model for utterance classification. Our approach for the first time employs multi-task learning to effectively model both joint and individual components of therapist and client behaviour. Furthermore, M3TCM integrates information from the text and speech modality as well as the conversation context. With our novel approach, we outperform the state of the art for utterance classification on the recently introduced AnnoMI dataset with a relative improvement of 20% for the client- and by 15% for therapist utterance classification. In extensive ablation studies, we quantify the improvement resulting from each contribution.
MultiMediate'23: Engagement Estimation and Bodily Behaviour Recognition in Social Interactions
Aug 16, 2023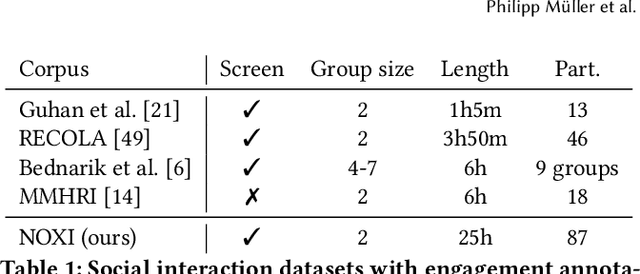
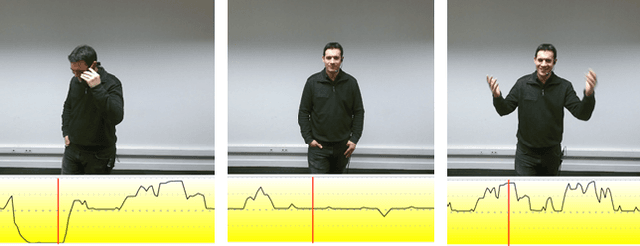
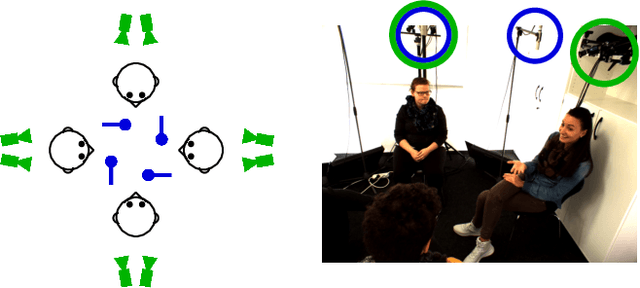
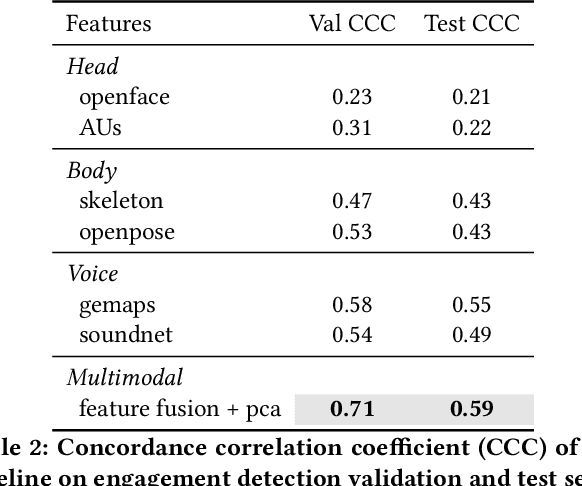
Abstract:Automatic analysis of human behaviour is a fundamental prerequisite for the creation of machines that can effectively interact with- and support humans in social interactions. In MultiMediate'23, we address two key human social behaviour analysis tasks for the first time in a controlled challenge: engagement estimation and bodily behaviour recognition in social interactions. This paper describes the MultiMediate'23 challenge and presents novel sets of annotations for both tasks. For engagement estimation we collected novel annotations on the NOvice eXpert Interaction (NOXI) database. For bodily behaviour recognition, we annotated test recordings of the MPIIGroupInteraction corpus with the BBSI annotation scheme. In addition, we present baseline results for both challenge tasks.
HUMAN: Hierarchical Universal Modular ANnotator
Oct 02, 2020



Abstract:A lot of real-world phenomena are complex and cannot be captured by single task annotations. This causes a need for subsequent annotations, with interdependent questions and answers describing the nature of the subject at hand. Even in the case a phenomenon is easily captured by a single task, the high specialisation of most annotation tools can result in having to switch to another tool if the task only slightly changes. We introduce HUMAN, a novel web-based annotation tool that addresses the above problems by a) covering a variety of annotation tasks on both textual and image data, and b) the usage of an internal deterministic state machine, allowing the researcher to chain different annotation tasks in an interdependent manner. Further, the modular nature of the tool makes it easy to define new annotation tasks and integrate machine learning algorithms e.g., for active learning. HUMAN comes with an easy-to-use graphical user interface that simplifies the annotation task and management.
Insights into the Dialogue Processing of VERBMOBIL
Mar 18, 1997

Abstract:We present the dialogue module of the speech-to-speech translation system VERBMOBIL. We follow the approach that the solution to dialogue processing in a mediating scenario can not depend on a single constrained processing tool, but on a combination of several simple, efficient, and robust components. We show how our solution to dialogue processing works when applied to real data, and give some examples where our module contributes to the correct translation from German to English.
A Robust and Efficient Three-Layered Dialogue Component for a Speech-to-Speech Translation System
Feb 10, 1995Abstract:We present the dialogue component of the speech-to-speech translation system VERBMOBIL. In contrast to conventional dialogue systems it mediates the dialogue while processing maximally 50% of the dialogue in depth. Special requirements like robustness and efficiency lead to a 3-layered hybrid architecture for the dialogue module, using statistics, an automaton and a planner. A dialogue memory is constructed incrementally.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge