Vehicle Dataset Indian Vehicle Dataset
Papers and Code
SR4-Fit: An Interpretable and Informative Classification Algorithm Applied to Prediction of U.S. House of Representatives Elections
Feb 05, 2026The growth of machine learning demands interpretable models for critical applications, yet most high-performing models are ``black-box'' systems that obscure input-output relationships, while traditional rule-based algorithms like RuleFit suffer from a lack of predictive power and instability despite their simplicity. This motivated our development of Sparse Relaxed Regularized Regression Rule-Fit (SR4-Fit), a novel interpretable classification algorithm that addresses these limitations while maintaining superior classification performance. Using demographic characteristics of U.S. congressional districts from the Census Bureau's American Community Survey, we demonstrate that SR4-Fit can predict House election party outcomes with unprecedented accuracy and interpretability. Our results show that while the majority party remains the strongest predictor, SR4-Fit has revealed intrinsic combinations of demographic factors that affect prediction outcomes that were unable to be interpreted in black-box algorithms such as random forests. The SR4-Fit algorithm surpasses both black-box models and existing interpretable rule-based algorithms such as RuleFit with respect to accuracy, simplicity, and robustness, generating stable and interpretable rule sets while maintaining superior predictive performance, thus addressing the traditional trade-off between model interpretability and predictive capability in electoral forecasting. To further validate SR4-Fit's performance, we also apply it to six additional publicly available classification datasets, like the breast cancer, Ecoli, page blocks, Pima Indians, vehicle, and yeast datasets, and find similar results.
A UAV-Based Multispectral and RGB Dataset for Multi-Stage Paddy Crop Monitoring in Indian Agricultural Fields
Jan 03, 2026We present a large-scale unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based RGB and multispectral image dataset collected over paddy fields in the Vijayawada region, Andhra Pradesh, India, covering nursery to harvesting stages. We used a 20-megapixel RGB camera and a 5-megapixel four-band multispectral camera capturing red, green, red-edge, and near-infrared bands. Standardised operating procedure (SOP) and checklists were developed to ensure repeatable data acquisition. Our dataset comprises of 42,430 raw images (415 GB) captured over 5 acres with 1 cm/pixel ground sampling distance (GSD) with associated metadata such as GPS coordinates, flight altitude, and environmental conditions. Captured images were validated using Pix4D Fields to generate orthomosaic maps and vegetation index maps, such as normalised difference vegetation index (NDVI) and normalised difference red-edge (NDRE) index. Our dataset is one of the few datasets that provide high-resolution images with rich metadata that cover all growth stages of Indian paddy crops. The dataset is available on IEEE DataPort with DOI, . It can support studies on targeted spraying, disease analysis, and yield estimation.
Solving Scene Understanding for Autonomous Navigation in Unstructured Environments
Jul 27, 2025Autonomous vehicles are the next revolution in the automobile industry and they are expected to revolutionize the future of transportation. Understanding the scenario in which the autonomous vehicle will operate is critical for its competent functioning. Deep Learning has played a massive role in the progress that has been made till date. Semantic Segmentation, the process of annotating every pixel of an image with an object class, is one crucial part of this scene comprehension using Deep Learning. It is especially useful in Autonomous Driving Research as it requires comprehension of drivable and non-drivable areas, roadside objects and the like. In this paper semantic segmentation has been performed on the Indian Driving Dataset which has been recently compiled on the urban and rural roads of Bengaluru and Hyderabad. This dataset is more challenging compared to other datasets like Cityscapes, since it is based on unstructured driving environments. It has a four level hierarchy and in this paper segmentation has been performed on the first level. Five different models have been trained and their performance has been compared using the Mean Intersection over Union. These are UNET, UNET+RESNET50, DeepLabsV3, PSPNet and SegNet. The highest MIOU of 0.6496 has been achieved. The paper discusses the dataset, exploratory data analysis, preparation, implementation of the five models and studies the performance and compares the results achieved in the process.
Exploration of an End-to-End Automatic Number-plate Recognition neural network for Indian datasets
Jul 14, 2022



Indian vehicle number plates have wide variety in terms of size, font, script and shape. Development of Automatic Number Plate Recognition (ANPR) solutions is therefore challenging, necessitating a diverse dataset to serve as a collection of examples. However, a comprehensive dataset of Indian scenario is missing, thereby, hampering the progress towards publicly available and reproducible ANPR solutions. Many countries have invested efforts to develop comprehensive ANPR datasets like Chinese City Parking Dataset (CCPD) for China and Application-oriented License Plate (AOLP) dataset for US. In this work, we release an expanding dataset presently consisting of 1.5k images and a scalable and reproducible procedure of enhancing this dataset towards development of ANPR solution for Indian conditions. We have leveraged this dataset to explore an End-to-End (E2E) ANPR architecture for Indian scenario which was originally proposed for Chinese Vehicle number-plate recognition based on the CCPD dataset. As we customized the architecture for our dataset, we came across insights, which we have discussed in this paper. We report the hindrances in direct reusability of the model provided by the authors of CCPD because of the extreme diversity in Indian number plates and differences in distribution with respect to the CCPD dataset. An improvement of 42.86% was observed in LP detection after aligning the characteristics of Indian dataset with Chinese dataset. In this work, we have also compared the performance of the E2E number-plate detection model with YOLOv5 model, pre-trained on COCO dataset and fine-tuned on Indian vehicle images. Given that the number Indian vehicle images used for fine-tuning the detection module and yolov5 were same, we concluded that it is more sample efficient to develop an ANPR solution for Indian conditions based on COCO dataset rather than CCPD dataset.
An Indian Roads Dataset for Supported and Suspended Traffic Lights Detection
Sep 09, 2022



Autonomous vehicles are growing rapidly, in well-developed nations like America, Europe, and China. Tech giants like Google, Tesla, Audi, BMW, and Mercedes are building highly efficient self-driving vehicles. However, the technology is still not mainstream for developing nations like India, Thailand, Africa, etc., In this paper, we present a thorough comparison of the existing datasets based on well-developed nations as well as Indian roads. We then developed a new dataset "Indian Roads Dataset" (IRD) having more than 8000 annotations extracted from 3000+ images shot using a 64 (megapixel) camera. All the annotations are manually labelled adhering to the strict rules of annotations. Real-time video sequences have been captured from two different cities in India namely New Delhi and Chandigarh during the day and night-light conditions. Our dataset exceeds previous Indian traffic light datasets in size, annotations, and variance. We prove the amelioration of our dataset by providing an extensive comparison with existing Indian datasets. Various dataset criteria like size, capturing device, a number of cities, and variations of traffic light orientations are considered. The dataset can be downloaded from here https://sites.google.com/view/ird-dataset/home
TrafficCAM: A Versatile Dataset for Traffic Flow Segmentation
Nov 17, 2022



Traffic flow analysis is revolutionising traffic management. Qualifying traffic flow data, traffic control bureaus could provide drivers with real-time alerts, advising the fastest routes and therefore optimising transportation logistics and reducing congestion. The existing traffic flow datasets have two major limitations. They feature a limited number of classes, usually limited to one type of vehicle, and the scarcity of unlabelled data. In this paper, we introduce a new benchmark traffic flow image dataset called TrafficCAM. Our dataset distinguishes itself by two major highlights. Firstly, TrafficCAM provides both pixel-level and instance-level semantic labelling along with a large range of types of vehicles and pedestrians. It is composed of a large and diverse set of video sequences recorded in streets from eight Indian cities with stationary cameras. Secondly, TrafficCAM aims to establish a new benchmark for developing fully-supervised tasks, and importantly, semi-supervised learning techniques. It is the first dataset that provides a vast amount of unlabelled data, helping to better capture traffic flow qualification under a low cost annotation requirement. More precisely, our dataset has 4,402 image frames with semantic and instance annotations along with 59,944 unlabelled image frames. We validate our new dataset through a large and comprehensive range of experiments on several state-of-the-art approaches under four different settings: fully-supervised semantic and instance segmentation, and semi-supervised semantic and instance segmentation tasks. Our benchmark dataset will be released.
A Dataset and Model for Crossing Indian Roads
Nov 15, 2022



Roads in medium-sized Indian towns often have lots of traffic but no (or disregarded) traffic stops. This makes it hard for the blind to cross roads safely, because vision is crucial to determine when crossing is safe. Automatic and reliable image-based safety classifiers thus have the potential to help the blind to cross Indian roads. Yet, we currently lack datasets collected on Indian roads from the pedestrian point-of-view, labelled with road crossing safety information. Existing classifiers from other countries are often intended for crossroads, and hence rely on the detection and presence of traffic lights, which is not applicable in Indian conditions. We introduce INDRA (INdian Dataset for RoAd crossing), the first dataset capturing videos of Indian roads from the pedestrian point-of-view. INDRA contains 104 videos comprising of 26k 1080p frames, each annotated with a binary road crossing safety label and vehicle bounding boxes. We train various classifiers to predict road crossing safety on this data, ranging from SVMs to convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The best performing model DilatedRoadCrossNet is a novel single-image architecture tailored for deployment on the Nvidia Jetson Nano. It achieves 79% recall at 90% precision on unseen images. Lastly, we present a wearable road crossing assistant running DilatedRoadCrossNet, which can help the blind cross Indian roads in real-time. The project webpage is http://roadcross-assistant.github.io/Website/.
Indian Commercial Truck License Plate Detection and Recognition for Weighbridge Automation
Nov 23, 2022



Detection and recognition of a licence plate is important when automating weighbridge services. While many large databases are available for Latin and Chinese alphanumeric license plates, data for Indian License Plates is inadequate. In particular, databases of Indian commercial truck license plates are inadequate, despite the fact that commercial vehicle license plate recognition plays a profound role in terms of logistics management and weighbridge automation. Moreover, models to recognise license plates are not effectively able to generalise to such data due to its challenging nature, and due to the abundant frequency of handwritten license plates, leading to the usage of diverse font styles. Thus, a database and effective models to recognise and detect such license plates are crucial. This paper provides a database on commercial truck license plates, and using state-of-the-art models in real-time object Detection: You Only Look Once Version 7, and SceneText Recognition: Permuted Autoregressive Sequence Models, our method outperforms the other cited references where the maximum accuracy obtained was less than 90%, while we have achieved 95.82% accuracy in our algorithm implementation on the presented challenging license plate dataset. Index Terms- Automatic License Plate Recognition, character recognition, license plate detection, vision transformer.
Towards Accurate Vehicle Behaviour Classification With Multi-Relational Graph Convolutional Networks
Feb 03, 2020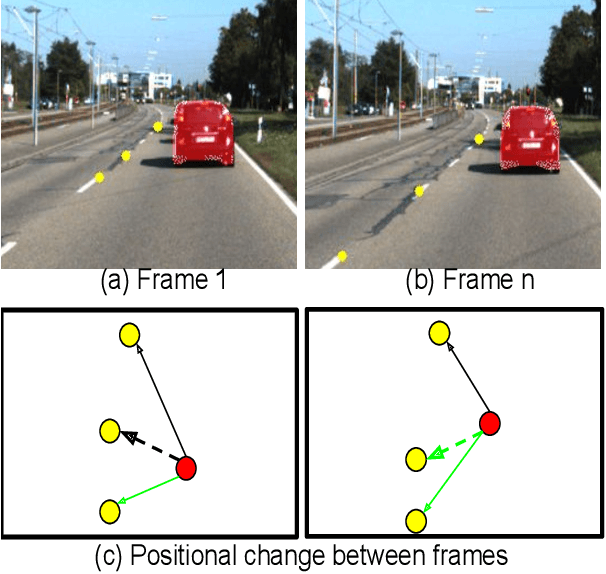
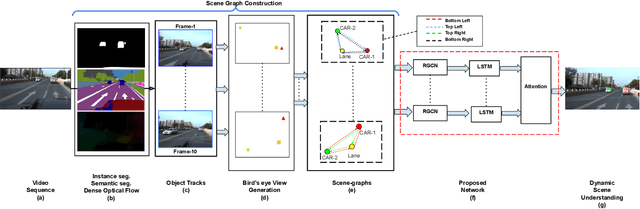


Understanding on-road vehicle behaviour from a temporal sequence of sensor data is gaining in popularity. In this paper, we propose a pipeline for understanding vehicle behaviour from a monocular image sequence or video. A monocular sequence along with scene semantics, optical flow and object labels are used to get spatial information about the object (vehicle) of interest and other objects (semantically contiguous set of locations) in the scene. This spatial information is encoded by a Multi-Relational Graph Convolutional Network (MR-GCN), and a temporal sequence of such encodings is fed to a recurrent network to label vehicle behaviours. The proposed framework can classify a variety of vehicle behaviours to high fidelity on datasets that are diverse and include European, Chinese and Indian on-road scenes. The framework also provides for seamless transfer of models across datasets without entailing re-annotation, retraining and even fine-tuning. We show comparative performance gain over baseline Spatio-temporal classifiers and detail a variety of ablations to showcase the efficacy of the framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge