Zicong Hong
HALO: A Unified Vision-Language-Action Model for Embodied Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown strong performance in robotic manipulation, but often struggle in long-horizon or out-of-distribution scenarios due to the lack of explicit mechanisms for multimodal reasoning and anticipating how the world will evolve under action. Recent works introduce textual chain-of-thought or visual subgoal prediction within VLA models to reason, but still fail to offer a unified human-like reasoning framework for joint textual reasoning, visual foresight, and action prediction. To this end, we propose HALO, a unified VLA model that enables embodied multimodal chain-of-thought (EM-CoT) reasoning through a sequential process of textual task reasoning, visual subgoal prediction for fine-grained guidance, and EM-CoT-augmented action prediction. We instantiate HALO with a Mixture-of-Transformers (MoT) architecture that decouples semantic reasoning, visual foresight, and action prediction into specialized experts while allowing seamless cross-expert collaboration. To enable HALO learning at scale, we introduce an automated pipeline to synthesize EM-CoT training data along with a carefully crafted training recipe. Extensive experiments demonstrate that: (1) HALO achieves superior performance in both simulated and real-world environments, surpassing baseline policy pi_0 by 34.1% on RoboTwin benchmark; (2) all proposed components of the training recipe and EM-CoT design help improve task success rate; and (3) HALO exhibits strong generalization capabilities under aggressive unseen environmental randomization with our proposed EM-CoT reasoning.
WMPO: World Model-based Policy Optimization for Vision-Language-Action Models
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown strong potential for general-purpose robotic manipulation, but their reliance on expert demonstrations limits their ability to learn from failures and perform self-corrections. Reinforcement learning (RL) addresses these through self-improving interactions with the physical environment, but suffers from high sample complexity on real robots. We introduce World-Model-based Policy Optimization (WMPO), a principled framework for on-policy VLA RL without interacting with the real environment. In contrast to widely used latent world models, WMPO focuses on pixel-based predictions that align the "imagined" trajectories with the VLA features pretrained with web-scale images. Crucially, WMPO enables the policy to perform on-policy GRPO that provides stronger performance than the often-used off-policy methods. Extensive experiments in both simulation and real-robot settings demonstrate that WMPO (i) substantially improves sample efficiency, (ii) achieves stronger overall performance, (iii) exhibits emergent behaviors such as self-correction, and (iv) demonstrates robust generalization and lifelong learning capabilities.
DiEP: Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts Compression through Differentiable Expert Pruning
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Despite the significant breakthrough of Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), the increasing scale of these MoE models presents huge memory and storage challenges. Existing MoE pruning methods, which involve reducing parameter size with a uniform sparsity across all layers, often lead to suboptimal outcomes and performance degradation due to varying expert redundancy in different MoE layers. To address this, we propose a non-uniform pruning strategy, dubbed \textbf{Di}fferentiable \textbf{E}xpert \textbf{P}runing (\textbf{DiEP}), which adaptively adjusts pruning rates at the layer level while jointly learning inter-layer importance, effectively capturing the varying redundancy across different MoE layers. By transforming the global discrete search space into a continuous one, our method handles exponentially growing non-uniform expert combinations, enabling adaptive gradient-based pruning. Extensive experiments on five advanced MoE models demonstrate the efficacy of our method across various NLP tasks. Notably, \textbf{DiEP} retains around 92\% of original performance on Mixtral 8$\times$7B with only half the experts, outperforming other pruning methods by up to 7.1\% on the challenging MMLU dataset.
D$^{2}$MoE: Dual Routing and Dynamic Scheduling for Efficient On-Device MoE-based LLM Serving
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:The mixture of experts (MoE) model is a sparse variant of large language models (LLMs), designed to hold a better balance between intelligent capability and computational overhead. Despite its benefits, MoE is still too expensive to deploy on resource-constrained edge devices, especially with the demands of on-device inference services. Recent research efforts often apply model compression techniques, such as quantization, pruning and merging, to restrict MoE complexity. Unfortunately, due to their predefined static model optimization strategies, they cannot always achieve the desired quality-overhead trade-off when handling multiple requests, finally degrading the on-device quality of service. These limitations motivate us to propose the D$^2$MoE, an algorithm-system co-design framework that matches diverse task requirements by dynamically allocating the most proper bit-width to each expert. Specifically, inspired by the nested structure of matryoshka dolls, we propose the matryoshka weight quantization (MWQ) to progressively compress expert weights in a bit-nested manner and reduce the required runtime memory. On top of it, we further optimize the I/O-computation pipeline and design a heuristic scheduling algorithm following our hottest-expert-bit-first (HEBF) principle, which maximizes the expert parallelism between I/O and computation queue under constrained memory budgets, thus significantly reducing the idle temporal bubbles waiting for the experts to load. Evaluations on real edge devices show that D$^2$MoE improves the overall inference throughput by up to 1.39$\times$ and reduces the peak memory footprint by up to 53% over the latest on-device inference frameworks, while still preserving comparable serving accuracy as its INT8 counterparts.
Accurate Expert Predictions in MoE Inference via Cross-Layer Gate
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance across various tasks, and their application in edge scenarios has attracted significant attention. However, sparse-activated Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models, which are well suited for edge scenarios, have received relatively little attention due to their high memory demands. Offload-based methods have been proposed to address this challenge, but they face difficulties with expert prediction. Inaccurate expert predictions can result in prolonged inference delays. To promote the application of MoE models in edge scenarios, we propose Fate, an offloading system designed for MoE models to enable efficient inference in resource-constrained environments. The key insight behind Fate is that gate inputs from adjacent layers can be effectively used for expert prefetching, achieving high prediction accuracy without additional GPU overhead. Furthermore, Fate employs a shallow-favoring expert caching strategy that increases the expert hit rate to 99\%. Additionally, Fate integrates tailored quantization strategies for cache optimization and IO efficiency. Experimental results show that, compared to Load on Demand and Expert Activation Path-based method, Fate achieves up to 4.5x and 1.9x speedups in prefill speed and up to 4.1x and 2.2x speedups in decoding speed, respectively, while maintaining inference quality. Moreover, Fate's performance improvements are scalable across different memory budgets.
Klotski: Efficient Mixture-of-Expert Inference via Expert-Aware Multi-Batch Pipeline
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Mixture of Experts (MoE), with its distinctive sparse structure, enables the scaling of language models up to trillions of parameters without significantly increasing computational costs. However, the substantial parameter size presents a challenge for inference, as the expansion in GPU memory cannot keep pace with the growth in parameters. Although offloading techniques utilise memory from the CPU and disk and parallelise the I/O and computation for efficiency, the computation for each expert in MoE models is often less than the I/O, resulting in numerous bubbles in the pipeline. Therefore, we propose Klotski, an efficient MoE inference engine that significantly reduces pipeline bubbles through a novel expert-aware multi-batch pipeline paradigm. The proposed paradigm uses batch processing to extend the computation time of the current layer to overlap with the loading time of the next layer. Although this idea has been effectively applied to dense models, more batches may activate more experts in the MoE, leading to longer loading times and more bubbles. Thus, unlike traditional approaches, we balance computation and I/O time and minimise bubbles by orchestrating their inference orders based on their heterogeneous computation and I/O requirements and activation patterns under different batch numbers. Moreover, to adapt to different hardware environments and models, we design a constraint-sensitive I/O-compute planner and a correlation-aware expert prefetcher for a schedule that minimises pipeline bubbles. Experimental results demonstrate that Klotski achieves a superior throughput-latency trade-off compared to state-of-the-art techniques, with throughput improvements of up to 85.12x.
Training and Serving System of Foundation Models: A Comprehensive Survey
Jan 05, 2024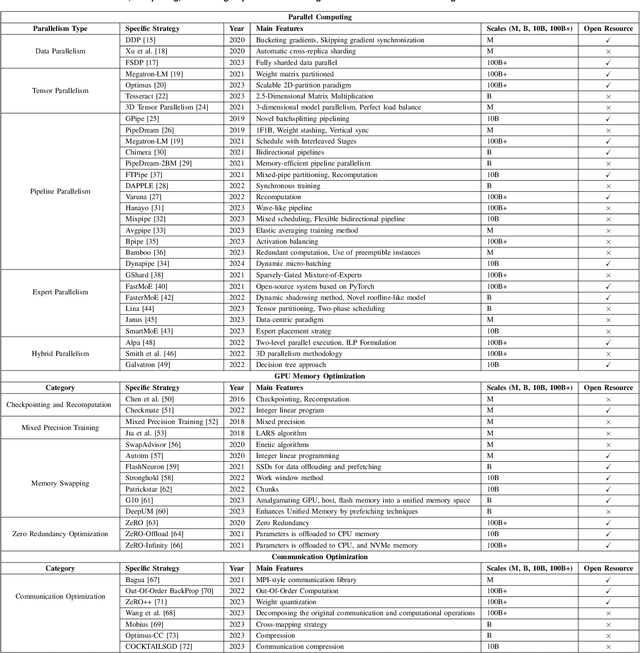
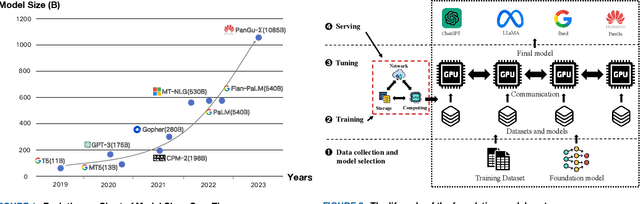
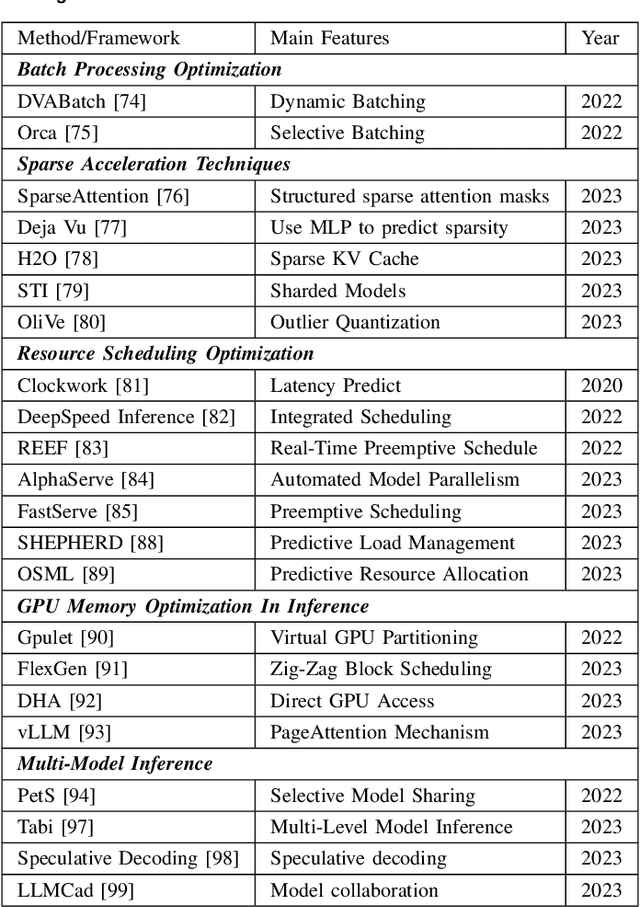
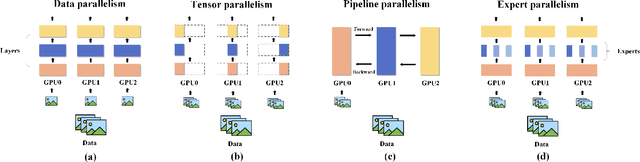
Abstract:Foundation models (e.g., ChatGPT, DALL-E, PengCheng Mind, PanGu-$\Sigma$) have demonstrated extraordinary performance in key technological areas, such as natural language processing and visual recognition, and have become the mainstream trend of artificial general intelligence. This has led more and more major technology giants to dedicate significant human and financial resources to actively develop their foundation model systems, which drives continuous growth of these models' parameters. As a result, the training and serving of these models have posed significant challenges, including substantial computing power, memory consumption, bandwidth demands, etc. Therefore, employing efficient training and serving strategies becomes particularly crucial. Many researchers have actively explored and proposed effective methods. So, a comprehensive survey of them is essential for system developers and researchers. This paper extensively explores the methods employed in training and serving foundation models from various perspectives. It provides a detailed categorization of these state-of-the-art methods, including finer aspects such as network, computing, and storage. Additionally, the paper summarizes the challenges and presents a perspective on the future development direction of foundation model systems. Through comprehensive discussion and analysis, it hopes to provide a solid theoretical basis and practical guidance for future research and applications, promoting continuous innovation and development in foundation model systems.
Intelligence-Endogenous Management Platform for Computing and Network Convergence
Aug 07, 2023



Abstract:Massive emerging applications are driving demand for the ubiquitous deployment of computing power today. This trend not only spurs the recent popularity of the \emph{Computing and Network Convergence} (CNC), but also introduces an urgent need for the intelligentization of a management platform to coordinate changing resources and tasks in the CNC. Therefore, in this article, we present the concept of an intelligence-endogenous management platform for CNCs called \emph{CNC brain} based on artificial intelligence technologies. It aims at efficiently and automatically matching the supply and demand with high heterogeneity in a CNC via four key building blocks, i.e., perception, scheduling, adaptation, and governance, throughout the CNC's life cycle. Their functionalities, goals, and challenges are presented. To examine the effectiveness of the proposed concept and framework, we also implement a prototype for the CNC brain based on a deep reinforcement learning technology. Also, it is evaluated on a CNC testbed that integrates two open-source and popular frameworks (OpenFaas and Kubernetes) and a real-world business dataset provided by Microsoft Azure. The evaluation results prove the proposed method's effectiveness in terms of resource utilization and performance. Finally, we highlight the future research directions of the CNC brain.
On Knowledge Editing in Federated Learning: Perspectives, Challenges, and Future Directions
Jun 02, 2023Abstract:As Federated Learning (FL) has gained increasing attention, it has become widely acknowledged that straightforwardly applying stochastic gradient descent (SGD) on the overall framework when learning over a sequence of tasks results in the phenomenon known as ``catastrophic forgetting''. Consequently, much FL research has centered on devising federated increasing learning methods to alleviate forgetting while augmenting knowledge. On the other hand, forgetting is not always detrimental. The selective amnesia, also known as federated unlearning, which entails the elimination of specific knowledge, can address privacy concerns and create additional ``space'' for acquiring new knowledge. However, there is a scarcity of extensive surveys that encompass recent advancements and provide a thorough examination of this issue. In this manuscript, we present an extensive survey on the topic of knowledge editing (augmentation/removal) in Federated Learning, with the goal of summarizing the state-of-the-art research and expanding the perspective for various domains. Initially, we introduce an integrated paradigm, referred to as Federated Editable Learning (FEL), by reevaluating the entire lifecycle of FL. Secondly, we provide a comprehensive overview of existing methods, evaluate their position within the proposed paradigm, and emphasize the current challenges they face. Lastly, we explore potential avenues for future research and identify unresolved issues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge